Pico Hydro Power
Definition of Pico hydropower
Usually turbines smaller than 10 kW are called "pico". Pico hydro rarely is fed into a power grid, but mostly serves a village or a workshop with electricity. As the terminology of micro/pico/... is not clear please specify power output by numbers where relevant.
Concept of Pico hydropower
Pico hydropower is the only form of small renewable energy production which works continuously without battery storage. Where applicable it is the most cost efficient solution to supply electrical energy. Pico turbines can provide power for small clusters or even single households
Individual hydropower supply cuts out the efforts of organising a community. Identifying, planning and managing takes a higher proportion of the whole installation efforts as smaller a sites becomes. For less consumers served, specialists have similar efforts in accessing sites. On the other hand small installation are more likely to be "do it your self".
With guidance by info materials and advise from a local shop consumers could be enabled to install their own pico turbine. If pico hydropower can become an "over the counter" product it meets a immense demand.
One example may be the north of Laos where cheap Chinese pico-turbines flooded the country in ten-thousands or more.
Requirements:
- suitable locations
- accessibility of affordable equipment (turbines) and installation know how
Electricity has a high value so working systems will spread quickly.
In many countries self-made solutions can be found, whereby a wooden water wheel is coupled with a car-alternator to produce electricity. Professional solutions increase efficiency reliability and safety.
Pico Hydro Turbines
2008 PT.Entec Indonesia developed the TP100, a crossflow turbine to be produced in small workshops.
Chances and challenges
Advantages
- Cheapest technical solution for independent power supply.
- Clean, sustain-/ renewable energy resource.
- Reliable => long lifetime as it is based upon robust mechanical techniques.
- Minimal running and follow up costs (unlike batteries at PV systems).
- Small maintenance efforts, which are easy to follow.
Disadvantages
- Site specific power output => pre-feasibility check required.
- Site specific installation => basic hydro know-how required.
- All cost are investment cost => upfront.
- Mostly shared connections => require community organised operation, management and use of water resources.
- Difficult access of clients => requires hubs and/or supply structure.
Capacity
Power output is limited by local conditions of height and amount of water available. Turbines are chosen by site conditions.
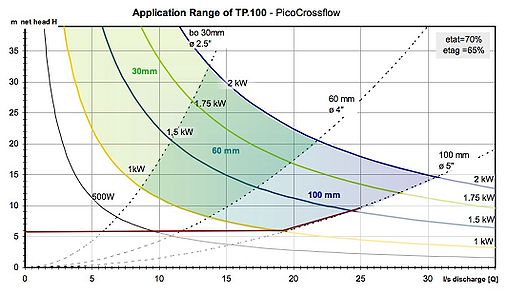
The following is an example for one specific turbine designed in Indonesia.
Explanation:
The colored lines indicate the power output at certain height/flow situations. The red horizontal line such turbine is technically not feasible, the blue "2 kW" line indicates a tech. maximum (for this specific turbine). The dotted lines separate three areas wherein turbines have certain sizes (30, 60 and 100 mm wide).
Example: at a site with 15 m height difference and a flow of 15 l/s the turbine can produce 1.5 kW (it will have a width of 60 mm). If on the same site (15 m) 25 l/s flow, power output will be 1.8 kW.
Remark:
to produce the same electric power by photovoltaic you require about 50 m2 PV-panels (and min. 20 batteries).