Difference between revisions of "Toolbox on SPIS"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| (138 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{SPIS Banner}}{{ | + | {{SPIS French}} {{SPIS Spanish}} |
| + | {{SPIS Banner}}<br/> | ||
| + | {{#widget:YouTube|id=x-nTUgkiv7o|height=300|width=800}} | ||
| + | === '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Background</span>''' === | ||
| + | Most water pumps utilized for irrigation purposes worldwide are powered by engines run on fossil fuels (diesel, petrol, gas) or on electricity supplied from the grid. However, fossil energy sources are limited and emissions from their utilization have negative climate impacts. At the same time, the electricity supply in many developing countries is often insufficient, unreliable or wholly absent in rural areas. As prices for solar panels have reduced, solar pumps for irrigation have become an economical, technical and environmentally viable alternative. <span class="mw-customtoggle-SPISB" style="font-size:small; font-weight: bold; display:inline-block; float:right; color: blue"><span class="mw-customtoggletext">read more</span></span> | ||
| + | <div id="mw-customcollapsible-SPISB" class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| + | === '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Objective</span>''' === | ||
| − | + | Major hindrance for the uptake of the technology is still a lack of information on solar pumps for irrigation and its relatively high investment costs. The knowledge on the potential, limitations and risks of Solar Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) is incomplete among extension officers, suppliers, policy makers, financing institutions and other stakeholders. As a result, farmers as a major end-user group struggle to get sound information in order to make informed decisions and maintain a SPIS well. Often SPIS are designed in a way that farmers needs and site specific conditions (environmental, agronomic and technical aspects) are not comprehensively addressed. Consequently, the potential of the technology is not optimized, or worse, has negative ecological and economic impacts. The Toolbox addresses this issue by providing a holistic set of practical knowledge materials through which SPIS advisors can guide their clients towards a financially and environmentally sound choice. | |
| − | The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | === '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Target Group</span>''' === |
| − | The | + | |
| − | + | The Toolbox serves all stakeholders who advise SPIS end-users, finance investments in SPIS or conceptualize policies for SPIS: | |
| − | The | + | |
| + | *agricultural (irrigation) extension officers | ||
| + | *technology suppliers | ||
| + | *credit officers / risk managers in financing institutions | ||
| + | *policy advisors | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | === '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Contents of the Toolbox</span>'''<br/> === | ||
| + | |||
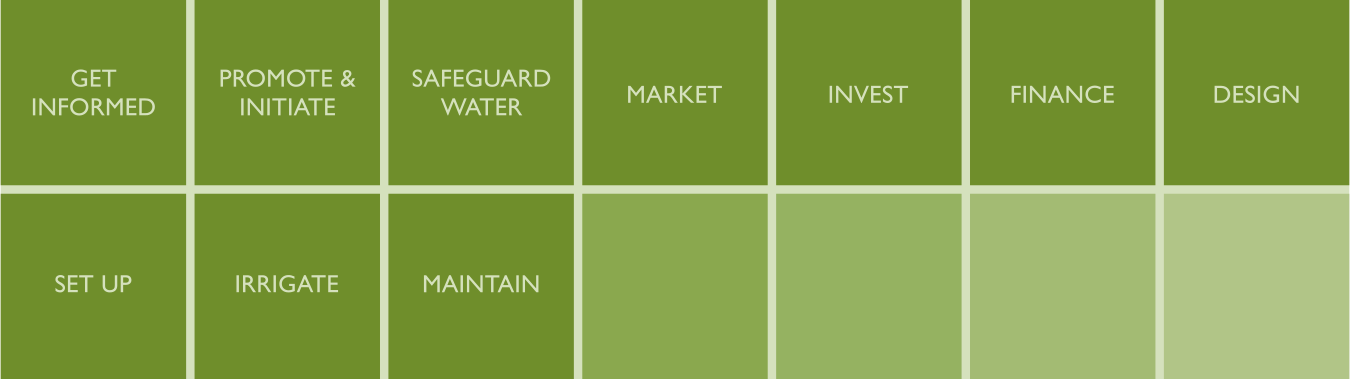
| + | <span lang="en-us">Click on box to get more information about each module or tools.</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{SPIS Bars}}<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === '''<font color="#879637">The SPIS Toolbox in a nutshell</font>'''<br/> === | ||
| + | |||
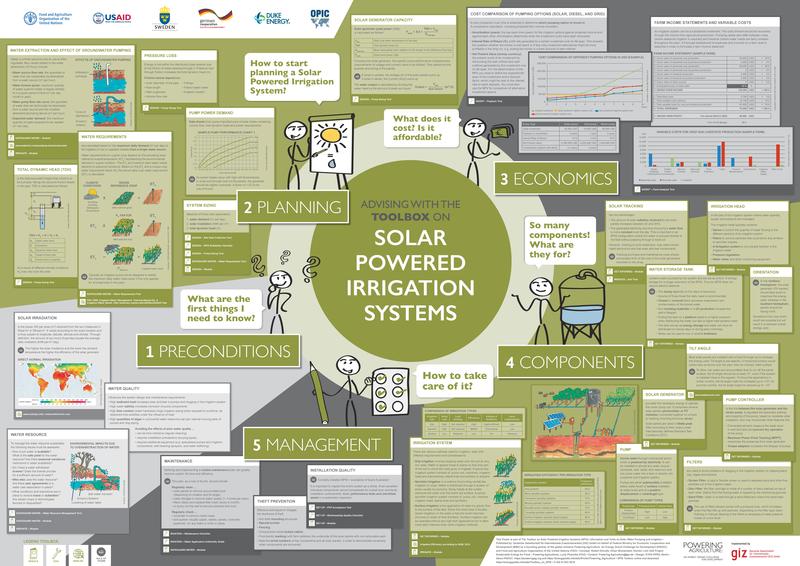
| + | Discover the SPIS Toolbox poster and get an insight into the world of SPIS. [[File:Download.JPG|8px|alt=Download.JPG|link=File:PA PosterA0.pdf]] [[File:PA PosterA0.pdf|border|center|800px|alt=PA PosterA0.pdf|link=https://energypedia.info/images/a/ae/PA_PosterA0.pdf]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === '''<font color="#879637">SPIS Toolbox for decision-making</font>'''<br/> === | ||
| + | |||
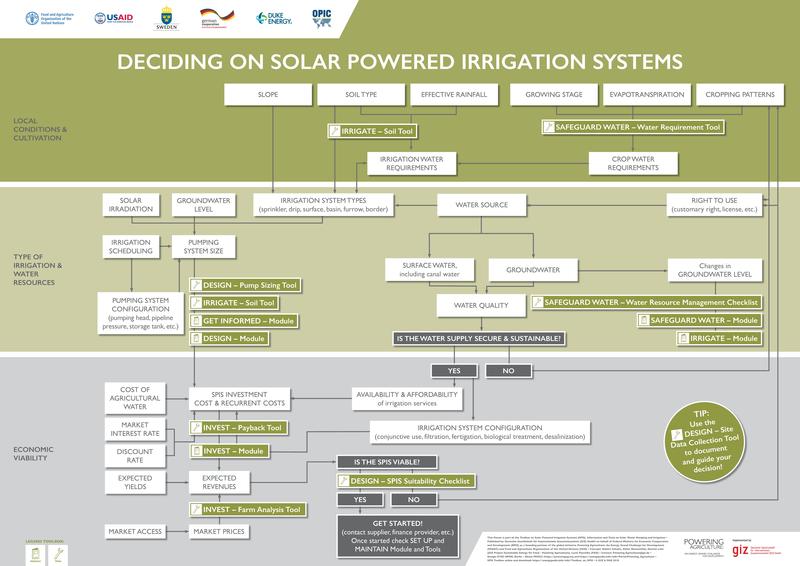
| + | Discover the SPIS Toolbox poster for decision-making processes. [[File:Download.JPG|8px|alt=Download.JPG|link=File:PA PosterA1.pdf]] [[File:PA PosterA1.pdf|border|center|800px|alt=PA PosterA1.pdf|link=https://energypedia.info/images/f/fd/PA_PosterA1.pdf]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Contact</span>''' === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Email your feedback, experiences and recommendations to [mailto:Powering.Agriculture@giz.de powering.agriculture@giz.de]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Imprint</span>''' === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Toolbox on Solar Powered Irrigation Systems is made possible through the global initiative Powering Agriculture: An Energy Grand Challenge for Development (PAEGC). In 2012, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida), the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), Duke Energy, and the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) combined resources to create the PAEGC initiative. The objective of PAEGC is to support new and sustainable approaches to accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy solutions for increasing agriculture productivity and/or value for farmers and agribusinesses in developing countries and emerging regions that lack access to reliable, affordable clean energy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span class="mw-customtoggle-SPIS4" style="font-size:small; font-weight: bold; display:inline-block; float:right; color: blue"><span class="mw-customtoggletext">read more</span></span> | ||
| + | <div id="mw-customcollapsible-SPIS4" class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| + | <span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">'''Published by'''</span><br/>Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH on behalf of BMZ as a founding partner of the global initiative Powering Agriculture: An Energy Grand Challenge for Development (PAEGC) and<br/>The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">'''Responsible'''</span> | ||
| + | [[File:Logo GIZ.gif|250px|alt=Logo GIZ.gif]]<div style="clear: both;"></div><div style="clear: both;"></div> | ||
| + | GIZ Project Sustainable Energy for Food – Powering Agriculture<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">'''Contact'''</span><br/>[mailto:Powering.Agriculture@giz.de Powering.Agriculture@giz.de]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">'''About'''</span><br/>Powering Agriculture: An Energy Grand Challenge for Development: [https://poweringag.org https://poweringag.org]<br/>energypedia Portal: [[Portal:Powering Agriculture|https://energypedia.info/wiki/Portal:Powering_Agriculture]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">'''Version'''</span><br/>1.0 (March 2018)<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">'''Disclaimer'''</span><br/>The designations employed and the presentation of material in this information product do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) or any of the PAEGC Founding Partners concerning the legal or development status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. The mention of specific companies or products of manufacturers, whether or not these have been patented, does not imply that these have been endorsed or recommended by GIZ, FAO, or any of the PAEGC Founding Partners in preference to others of a similar nature that are not mentioned. The views expressed in this information product are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of GIZ, FAO, or any of the PAEGC Founding Partners.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | GIZ, FAO and the PAEGC Founding Partners encourage the use, reproduction and dissemination of material in this information product. Except where otherwise indicated, material may be copied, downloaded and printed for private study, research and teaching purposes, or for use in non-commercial products or services, provided that appropriate acknowledgement of GIZ and FAO as the source and copyright holder is given.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | © GIZ and FAO, 2018<br/> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | [[File:PAEGC Logos.jpg|left|800px|alt=PAEGC Logos.jpg]]<br/> | ||
| − | + | {{SPIS_Magic_Words}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{#Widget:Heatmap}} | |
Revision as of 09:18, 29 January 2020
Template:SPIS French Template:SPIS Spanish

Introduction
The Toolbox on Solar Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) is designed to enable advisors, service providers and practitioners in the field of solar irrigation to provide broad hands-on guidance to end-users, policy-makers and financiers. Risks related to system efficiency, financial viability and the unsustainable use of water resources can thus be minimized. The Toolbox comprises informative modules supplemented with user-friendly software tools (calculations sheets, checklists, guidelines). read more
Modules and tools touch upon:
- assessing the water requirements,
- comparing the financial viability,
- determining farm profitability and payback of investment in SPIS,
- sustainably design and maintain a SPIS,
- highlight critical workmanship quality aspects,
- and many more.
Background
Most water pumps utilized for irrigation purposes worldwide are powered by engines run on fossil fuels (diesel, petrol, gas) or on electricity supplied from the grid. However, fossil energy sources are limited and emissions from their utilization have negative climate impacts. At the same time, the electricity supply in many developing countries is often insufficient, unreliable or wholly absent in rural areas. As prices for solar panels have reduced, solar pumps for irrigation have become an economical, technical and environmentally viable alternative. read more
Objective
Major hindrance for the uptake of the technology is still a lack of information on solar pumps for irrigation and its relatively high investment costs. The knowledge on the potential, limitations and risks of Solar Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) is incomplete among extension officers, suppliers, policy makers, financing institutions and other stakeholders. As a result, farmers as a major end-user group struggle to get sound information in order to make informed decisions and maintain a SPIS well. Often SPIS are designed in a way that farmers needs and site specific conditions (environmental, agronomic and technical aspects) are not comprehensively addressed. Consequently, the potential of the technology is not optimized, or worse, has negative ecological and economic impacts. The Toolbox addresses this issue by providing a holistic set of practical knowledge materials through which SPIS advisors can guide their clients towards a financially and environmentally sound choice.
Target Group
The Toolbox serves all stakeholders who advise SPIS end-users, finance investments in SPIS or conceptualize policies for SPIS:
- agricultural (irrigation) extension officers
- technology suppliers
- credit officers / risk managers in financing institutions
- policy advisors
Contents of the Toolbox
Click on box to get more information about each module or tools.