Toolbox on SPIS

Introduction
The Toolbox on Solar Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) is designed to enable advisors, service providers and practitioners in the field of solar irrigation to provide broad hands-on guidance to end-users, policy-makers and financiers. Risks related to system efficiency, financial viability and the unsustainable use of water resources can thus be minimized. The Toolbox comprises informative modules supplemented with user-friendly software tools (calculations sheets, checklists, guidelines). read more
Modules and tools touch upon:
- assessing the water requirements,
- comparing the financial viability,
- determining farm profitability and payback of investment in SPIS,
- sustainably design and maintain a SPIS,
- highlight critical workmanship quality aspects,
- and many more.
Introduction
Most water pumps utilized for irrigation purposes worldwide are powered by engines run on fossil fuels (diesel, petrol, gas) or on electricity supplied from the grid. Fossil energy sources are limited and emissions from their utilization have negative climate impacts. At the same time, the electricity supply in many developing countries is often insufficient and unreliable or wholly absent in rural areas. Moreover, prices of solar panels have reduced while the quality has improved. Today, solar pumps for irrigation have become an economical, technical and environmentally viable alternative to conventional pumping systems. read more
However, major hindrance for the uptake of the technology is still a lack of information on solar pumps for irrigation and its relatively high investment costs. The knowledge on the potentials, limitations and risks of Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) is incomplete among policy makers, producers and other stakeholders. For example, SPIS are seldom designed in a way that producer needs and site specific conditions (environmental, agronomic and technical aspects) are comprehensively addressed. Consequently, the potential of the technology is not optimized, or worse, has negative ecological and economic impacts.
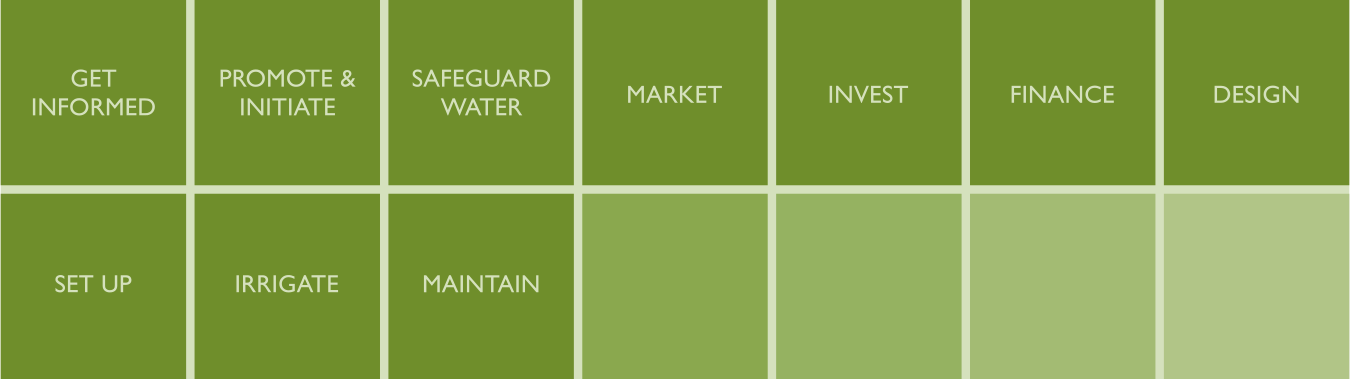
This manual provides up-to-date information on the technology and methods of promotion, as well as how to finance SPIS. Furthermore it gives insight into how SPIS are designed, set up and maintained. It is accompanied by a set of tools, such as maintenance checklists, data collection guidelines and design calculations. It strives to help find the optimal design of a system, thereby avoiding risks related to system efficiency, financial viability and the unsustainable use of water resources. The manual and tools target stakeholders who advise or finance medium-sized agricultural enterprises. These are agricultural (irrigation) extension advisors and credit officers / risk managers in financing institutions. Furthermore the manual support the advisory function of SPIS suppliers, by providing them with a holistic set of knowledge through which they can guide their clients towards a financially and environmentally sound decision.The manual follows the course of action involved when giving advice on SPIS for an agricultural enterprise. It consists of this introduction and seven further modules. The modular approach enables the user to pick out specific information relevant to his/her situation. Each module however relates to and supplements the other modules.
- GET INFORMED specifies the components and common configurations of a SPIS. Each component is described in detail.
- PROMOTE & INITIATE provides important information and tips for someone who wants to promote the SPIS technology in a particular area. It focuses on the analysis of opportunities and risks, the stakeholders involved, as well as promotion strategies and activities.
- SAFEGUARD WATER focuses on water governance issues and potential negative impacts of (ground-)water depletion through solar pumping.
- FINANCE provides information to financial service providers financing or planning to finance SPIS. The module targets stakeholders at management level who decide on credit policies and loan officers who assess single loan applications for financing SPIS.
- DESIGN helps to select the suitable system configuration for a specific situation. A substantial set of tools helps to assess site conditions, select and design the appropriate type of SPIS and conduct a simplified financial viability assessment and calculates the detailed financial viability of the producer.
- SET UP provides information and tools to enable the installation of a SPIS. It focuses on the selection of installers, acceptance and system tests as well as documentation and hand over of the system.
- MAINTAIN elaborates on maintenance plans, the selection of service providers, regular routines and documentation and monitoring.
Module Structure
The modules are all structured uniformly. It starts with the module aim and orientation and a brief description of the relevant process steps. These are processes that are recommended to be considered in a particular order. They are numbered and summarized in a flow diagram at the beginning of each module for easy reference read more
Structure of Each Process Step
Each step in the process of each module is described on one or two pages. The process step is concluded with an overview of the most relevant aspects:
- Outcome / products
- Data requirements;
- People and stakeholders involved;
- Important issues to be considered.
At the end of each module links for further readings and multimedia files are provided. This last page is also used to describe what tools supplement to the module. The tools are available online and users can adapt them to their specific needs.
Content of Modules
Overview of Tools
| Name | Type | Description |
| PROMOTE 01 - SPIS Rapid Assessment | .doc | Table of Content for rapid assessment report on status SPIS in target area |
| SAFEGUARD WATER 01 - Water Requirement Tool |
.xls | Basic water requirement calculation tools for crops and livestock |
| SAFEGUARD WATER 02 - Water Management Tool |
.doc | List of questions to check if the water is managed sustainably |
| DESIGN 01 - Site Data Collection Tool |
.xls | Questionnaire of 29 pages to collect technical, organizational
and financial information on site |
| DESIGN 02 - SPIS Suitability Check Tool | .xls | Qualitative checklist on suitability of a site for SPIS |
| DESIGN 03 - Pump Sizing Tool | .xlsm | Excel calculation sheet to calculate pumping head and select pump type |
| DESIGN 04 - Case Study Mr. Paolo | .doc | Case study exercise to calculate design parameters and financial viability of a SPIS (Q & A) |
| DESIGN 05 - Pressure Loss Tool | .doc | Checklist on pressure losses in the conveyance and irrigation system |
| DESIGN 06- Farm Analysis Tool | .xlsm | Excel-based financial analysis tool for an agricultural enterprise |
| DESIGN 07- Simplified Financial Viability Calculation | .xlsm | Simplified Excel-based financial analysis tool for comparing different technologies against agricultural income |
| SET UP 01 - PVP Acceptance Test | .doc | Guideline to compare the installed with the actual capacity of the pump |
| SET UP 02- Workmanship Quality Checklist | .xls | Checklist on workmanship quality after installation of a SPIS |
| MAINTAIN 01 – Maintenance Checklist | .xls | List of questions to check if SPIS is properly maintained |
| MAINTAIN 02 - Water Application Uniformity Guide | .xls | Background to importance of uniform application of water and instructions to determine the water application uniformity for drip and sprinkler irrigation systems, with accompanying calculation sheet |
Technical Glossary
Abbreviations
Imprint
The Toolbox for SPIS Advisors is made possible through the global initiative Powering Agriculture: An Energy Grand Challenge for Development (PAEGC). In 2012, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida), the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), Duke Energy, and the Overseas Private Investment Cooperation (OPIC) combined resources to create the PAEGC initiative. The objective of PAEGC is to support new and sustainable approaches to accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy solutions for increasing agriculture productivity and/or value for farmers and agribusinesses in developing countries and emerging regions that lack access to reliable, affordable clean energy.
read more
Disclaimer The designations employed and the presentation of material in this information product do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH or any of the PAEGC Founding Partners concerning the legal or development status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. The mention of specific companies or products of manufacturers, whether or not these have been patented, does not imply that these have been endorsed or recommended by GIZ, or any of the PAEGC Founding Partners in preference to others of a similar nature that are not mentioned. The views expressed in this information product are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of GIZ, or any of the PAEGC Founding Partners.
GIZ and the PAEGC Founding Partners encourage the use, reproduction and dissemination of material in this information product. Except where otherwise indicated, material may be copied, downloaded and printed for private study, research and teaching purposes, or for use in non-commercial products or services, provided that appropriate acknowledgement of GIZ as the source and copyright holder is given.
Published by
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) on behalf of BMZ
Author
GIZ Project “Sustainable Energy for Food – Powering Agriculture”
More information and contact
https://poweringag.org
[1]
SPIS Toolbox online and download
[ https://energypedia.info/wiki/Toolbox_for_SPIS_Advisors https://energypedia.info/wiki/Toolbox_for_SPIS_Advisors]
© GIZ, 2017




















