Difference between revisions of "Wind, Hydro and other Energy Sources in Agrifood Systems"
***** (***** | *****) m (→Geothermal) |
***** (***** | *****) m (→Geothermal) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
= Geothermal = | = Geothermal = | ||
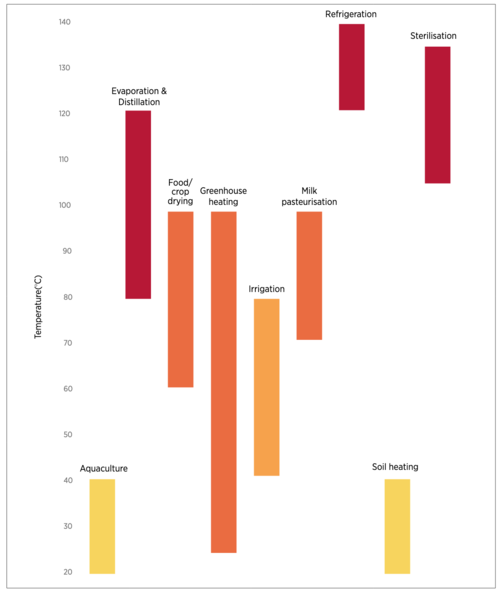
| − | [[Geothermal_Energy|Geothermal energy]] refers to the thermal energy beneath the earth's crust | + | [[Geothermal_Energy|Geothermal energy]] refers to the thermal energy beneath the earth's crust and in 2017, there were geothermal plants operating in 25 countries. Geothermal energy can be used in its primary form (i.e. heat) for food processing and drying as well as heating green houses and aquaculture ponds. The use of the geothermal energy in the agrifood systems depends on the fluid temperature and is shown in figure below. |
[[File:Geothermal energy for agriculture.png|border|left|500px]]<div style="clear: both;"></div> | [[File:Geothermal energy for agriculture.png|border|left|500px]]<div style="clear: both;"></div> | ||
| + | [[Category:Micro_Hydro]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Powering_Agriculture]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Climate_Change]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Climate_Change_Mitigation]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Wind]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Hydro]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Water-Energy-Food_Nexus]] | ||
[[Category:Pumping]] | [[Category:Pumping]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 08:47, 13 July 2020
| ►Back to the WE4F Portal |
Hydropower
Hydropower is one of the most reliable energy sources among the renewables. Available in different sizes, hydropower plants can be low cost and still generate enough energy for agricultural purposes. Power is generated from water streams or rivers that run through a turbine which rotates and turns tools or a generator for electricity production. The possibility of using a “zero-head” or “in-stream” turbine allows using kinetic and not potential energy, producing a maximum amount of electrical power without building dams or height differences, lowering investment costs for infrastructure and making it a low-cost accessible solution for powering agriculture. Read more…
Actors & Innovations
Water powered Water Pumps
In some regions, the use of solar pumps is not suitable due to the geographical situation, which may hinder the access of skilled personal to maintain the technology, or where there is not enough radiation that reaches the site. This is often the case in mountainous areas, where water is abundantly available though. Here, hydro-power, or so-called water powered water pumps can be used. These are low-cost, zero-emission pumps that require low maintenance. Read more…
Publications & Tools
Micro Hydro Power Scout Guide
The GIZ Hydro Guide has been developed as a tool to design and inform small-scale hydro power projects and gives a thematic introduction into hydro power. Mainly designed for actors in the field, this guide has been designed as a tool to shape and prepare small-scale hydro power projects in a professional manner regarding the implementation. Read more…
Wind Power
The same principle as for hydropower systems can be found among wind power generation. Wind is the result of global and local temperature difference and represents another source of renewable energy. It has been used since ancient times for several purposes, like sailing, water pumping, and grinding. Modern technologies such as a wind turbine can use wind for electricity production. Since wind turbines produce different power outputs at different wind speeds, calculating the energy yield of wind power is complex.
Wind pumps are one of the main uses in agricultural processes. The design of a wind pump always depends on the application it is meant for. One can distinguish between mechanical and electrical wind pumps. Electrical pumps have a lower efficiency, but they can be placed away from the location of the wind turbine. To choose the right wind turbine, considerations about the desired pumping technology and extraction depth have to be made upfront. In off-grid areas, where there is sufficient wind (> 5 m/s) and ground water supply, wind pumps often offer a cost-effective method for domestic and community water supply and small-scale farming. Read more…
Geothermal
Geothermal energy refers to the thermal energy beneath the earth's crust and in 2017, there were geothermal plants operating in 25 countries. Geothermal energy can be used in its primary form (i.e. heat) for food processing and drying as well as heating green houses and aquaculture ponds. The use of the geothermal energy in the agrifood systems depends on the fluid temperature and is shown in figure below.