Difference between revisions of "Zimbabwe Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
= Overview<br/> = | = Overview<br/> = | ||
| − | Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in southern Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It shares its borders with Zambia to the northwest, Mozambique to the east, South Africa in the south and Botswana in the southwest. The capital city is Harare. Much of Zimbabwe is elevated in the high veld/central plateau that stretches from the southwest to the northwest at altitudes between 1,200 and 1,600 meters. The world’s largest curtain of falling water the Victoria Falls is located in the northwest of Zimbabwe<ref name="CIA. The World Factbook Zimbabwe: | + | Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in southern Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It shares its borders with Zambia to the northwest, Mozambique to the east, South Africa in the south and Botswana in the southwest. The capital city is Harare. Much of Zimbabwe is elevated in the high veld/central plateau that stretches from the southwest to the northwest at altitudes between 1,200 and 1,600 meters. The world’s largest curtain of falling water the Victoria Falls is located in the northwest of Zimbabwe<ref name="CIA. The World Factbook Zimbabwe: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/zi.html">CIA. The World Factbook Zimbabwe: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/zi.html</ref>. |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
Zimbabwe relies on hydroelectric power. In rural parts of the country, 80-90% of the people depend on wood fuel and kerosene for cooking lighting. Food processing tasks like milling grain are usually carried out with diesel-powered system<ref name="Reegle. Zimbabwe Energy Profile. http://www.reegle.info/countries/zimbabwe-energy-profile/ZW">Reegle. Zimbabwe Energy Profile. http://www.reegle.info/countries/zimbabwe-energy-profile/ZW</ref>. | Zimbabwe relies on hydroelectric power. In rural parts of the country, 80-90% of the people depend on wood fuel and kerosene for cooking lighting. Food processing tasks like milling grain are usually carried out with diesel-powered system<ref name="Reegle. Zimbabwe Energy Profile. http://www.reegle.info/countries/zimbabwe-energy-profile/ZW">Reegle. Zimbabwe Energy Profile. http://www.reegle.info/countries/zimbabwe-energy-profile/ZW</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Zimbabwe Primary Energy Supply 2009.png|thumb|center|550px|Source: Adapted from Reegle. Energy Profile of Zimbabwe. Available at: http://www.reegle.info/countries/zimbabwe-energy-profile/ZW]] | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 137: | Line 139: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
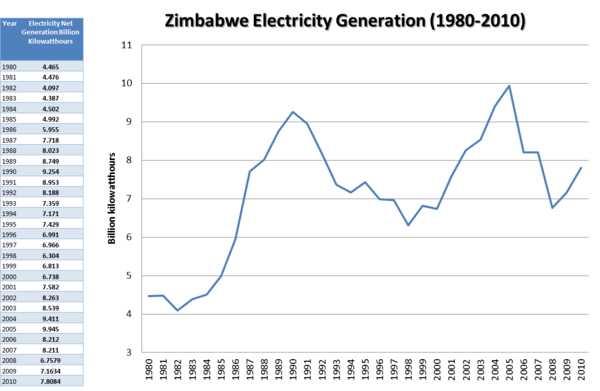
| − | [[File:Zimbabwe Electricity Generation.png|thumb|center| | + | [[File:Zimbabwe Electricity Generation.png|thumb|center|600px|Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration. Available at: http://www.eia.gov/countries/country-data.cfm?fips=ZI#elec]] |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 143: | Line 145: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
<div><div class="page" title="Page 36"><div class="layoutArea"><div class="column"> | <div><div class="page" title="Page 36"><div class="layoutArea"><div class="column"> | ||
| − | {| border="0" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="5" style="font-size: 14px; width: | + | {| border="0" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="5" style="font-size: 14px; width: 800px;" align="center" |
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="5" style="text-align: center; background-color: rgb(79, 129, 189);" | <font color="#ffffff"><span style="line-height: 20.390625px;">'''Energy Production'''</span></font> | | colspan="5" style="text-align: center; background-color: rgb(79, 129, 189);" | <font color="#ffffff"><span style="line-height: 20.390625px;">'''Energy Production'''</span></font> | ||
| Line 167: | Line 169: | ||
| <div class="page" title="Page 36"><div class="layoutArea"><div class="column"> | | <div class="page" title="Page 36"><div class="layoutArea"><div class="column"> | ||
*'''4,202.0''' GWh Total hydropower electricity generation<ref name="African Union/African Energy Commission.">African Union/African Energy Commission. "African Energy Statistics 2012". Available at: http://www.afrec-energy.org/Docs/FR/PDF/2012/AEIS_FR_EN.pdf</ref> | *'''4,202.0''' GWh Total hydropower electricity generation<ref name="African Union/African Energy Commission.">African Union/African Energy Commission. "African Energy Statistics 2012". Available at: http://www.afrec-energy.org/Docs/FR/PDF/2012/AEIS_FR_EN.pdf</ref> | ||
| − | |||
</div></div></div> | </div></div></div> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:22, 8 September 2013
| Zimbabwe | |||
|
Capital |
Harare | ||
|
Official language(s) |
Chewa, Chibarwe, English | ||
|
Government |
Presidential System | ||
|
President |
Robert Gabriel Mugabe | ||
|
Total area |
390,757 km2 | ||
|
Population |
12 973 808 (2012 Estimate)[2] | ||
|
Rural population |
7756587.12 (2010)[3] | ||
|
GDP (nominal) |
US$ 10.978 billion (2013 Estimate)[4] | ||
|
GDP Per capita |
US$ 589 (2013 Estimate)[4] | ||
|
Currency |
Various[5] | ||
|
Time zone |
Central Africa Time (UTC+2) | ||
|
Electricity generation |
7.8084 billion kilowatthours (2010)[6] | ||
|
Access to Electricity |
National: 41.5%[7] Urban: 80% Rural: 19% | ||
|
Wind energy (installed capacity) |
MW(Year) | ||
|
Solar Energy (installed capacity) |
MW (Year) | ||
Overview
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in southern Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It shares its borders with Zambia to the northwest, Mozambique to the east, South Africa in the south and Botswana in the southwest. The capital city is Harare. Much of Zimbabwe is elevated in the high veld/central plateau that stretches from the southwest to the northwest at altitudes between 1,200 and 1,600 meters. The world’s largest curtain of falling water the Victoria Falls is located in the northwest of Zimbabwe[8].
Zimbabwe relies on hydroelectric power. In rural parts of the country, 80-90% of the people depend on wood fuel and kerosene for cooking lighting. Food processing tasks like milling grain are usually carried out with diesel-powered system[9].

Total electricity generation in 2009 was 7,900 gigawatt hours (Gwh). 53% of this was produced from renewable sources. Electricity consumption per capita in 2009 stood at 1,022-kilowatt hours (kWh). 33.9% of this total installed capacity was from hydroelectric plants.
| Energy Production | ||||
| 2005 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
|
|
|
|
|
Energy Sources
Hydropower
Solar Energy
Biomass
Biogas
Wind Energy
Geothermal Energy
Fossil Fuels
Key Problems of the Energy Sector
Policy Framework, Laws and Regulations
General Energy Policy, Energy Strategy
Important Laws and Regulations
Specific Strategies
(Biomass, Renewable Energies, Rural Electrification, Energy Access Strategy, Poverty Reduction Strategy etc.)
Institutional Set-up in the Energy Sector
Activities of Donors and Implementing Agencies
Further Information
References
- ↑ The following languages, namely Chewa, Chibarwe, English, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Ndebele, Shangani, Shona, sign language, Sotho, Tonga, Tswana, Venda and Xhosa, are the officially recognised languages of Zimbabwe. Available at: http://www.kubatana.net/docs/legisl/constitution_zim_draft_copac_130125.pdf
- ↑ "Census Results in Brief". Zimbabwe National Statistical AgencyfckLRAvailable at: http://www.zimstat.co.zw/dmdocuments/CensusPreliminary2012.pdf
- ↑ Rural Population in Zimbabwe. Available at: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/zimbabwe/rural-population-wb-data.html
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 International Monetary Fund. Available at: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=46&pr.y=0&sy=2009&ey=2012&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=698&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=
- ↑ The Zimbabwean dollar is no longer in active use after it was officially suspended by the government due to hyperinflation. The United States dollar (US$), South African rand (R), Botswana pula (P), Pound sterling (£) and Euro (€) are now used instead.[9] The United States dollar has been adopted as the official currency for all government transactions. Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zimbabwe
- ↑ U.S. Energy Information Administration. Available at: http://www.eia.gov/countries/country-data.cfm?fips=ZI#elec
- ↑ IRENA. RENEWABLE ENERGY COUNTRY PROFILE Zimbabwe. Available at: http://www.irena.org/REmaps/countryprofiles/africa/Zimbabwe.pdf#zoom=75
- ↑ CIA. The World Factbook Zimbabwe: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/zi.html
- ↑ Reegle. Zimbabwe Energy Profile. http://www.reegle.info/countries/zimbabwe-energy-profile/ZW
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 African Union/African Energy Commission. "African Energy Statistics 2012". Available at: http://www.afrec-energy.org/Docs/FR/PDF/2012/AEIS_FR_EN.pdf



















