Knowledge fuels change - Support energypedia!
For over 10 years, energypedia has been connecting energy experts around the world — helping them share knowledge, learn from each other, and accelerate the global energy transition.
Today, we ask for your support to keep this platform free and accessible to all.
Even a small contribution makes a big difference! If just 10–20% of our 60,000+ monthly visitors donated the equivalent of a cup of coffee — €5 — Energypedia would be fully funded for a whole year.
Is the knowledge you’ve gained through Energypedia this year worth €5 or more?
Your donation keeps the platform running, helps us create new knowledge products, and contributes directly to achieving SDG 7.
Thank you for your support, your donation, big or small, truly matters!
Difference between revisions of "Guatemala Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
= Introduction<br/> = | = Introduction<br/> = | ||
| + | |||
| + | Guatemala is located in Central America<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref>. It shares its borders with Mexico in the north, Belize and Honduras in the east, and El Salavador in the south<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref><ref name="https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf">https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf</ref>. On the west, the country borders the Pacific, with a much shorter northeastern Caribbean coastline<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref><ref name="https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf">https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf</ref>. <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">The country's major cities are: Guatemala city -the capital-, Quetzaltenango, Escuintla, Livingston and Puerto Barrios</span><ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref><span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">. </span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Guatemala is divided topographily into four general regions: central-western highlands, southern volcanic regions of the Sierra Madre, tropical coastal lowlands, and the low northern plateau, which is mainly jungle<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref><ref name="https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf">https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gua 01.PNG|thumb|center|850px|Fig.1: Guatemalan Borders]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Predominantly, Guatemala is an agricultural socitey, where farming is the major economic activiy, with forestry and mining close behind<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref>. The best soils suitable for farming are located on the Pacific coastal line, while the soil in the Peten tends to erode quickly, and highland soils are better protected because of coffee cultivation<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Guatemalan climate varies with accordance to the altitude of the region, and the proximity to the coasts<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref><ref name="https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf">https://eneken.ieej.or.jp/data/4474.pdf</ref>. The '''tierra caliente''' (hot country), which extends from the sea level into 750m above sea level, and its temperature is around 29°-32°C<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref>. The '''tierra templada''' (temperate country) extends from 750-1660m above sea level, with day temperature 24<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">°</span>-26<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">°C, and night temperatures 15.5<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">°-21<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">°C<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref><ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref>.The '''tierra fria''' (cold country) extends above 1660m above sea level with an average temperature of 26<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">°C</span> at day, and 10<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">°C</span> at night<ref name="https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf">https://info.publicintelligence.net/MCIA-GuatemalaHandbook.pdf</ref>.</span></span></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
= Energy Situation<br/> = | = Energy Situation<br/> = | ||
| Line 26: | Line 44: | ||
= References = | = References = | ||
| + | |||
| + | <references /><br/> | ||
[[Category:Latin_America]] | [[Category:Latin_America]] | ||
Revision as of 09:43, 15 October 2018
Capital:
Guatemala City
Region:
Coordinates:
14.38°N, 90.30°W
Total Area (km²): It includes a country's total area, including areas under inland bodies of water and some coastal waterways.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.
Population: It is based on the de facto definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship--except for refugees not permanently settled in the country of asylum, who are generally considered part of the population of their country of origin.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Rural Population (% of total population): It refers to people living in rural areas as defined by national statistical offices. It is calculated as the difference between total population and urban population.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
GDP (current US$): It is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. It is calculated without making deductions for depreciation of fabricated assets or for depletion and degradation of natural resources.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.2 ()
GDP Per Capita (current US$): It is gross domestic product divided by midyear population
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Access to Electricity (% of population): It is the percentage of population with access to electricity.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Energy Imports Net (% of energy use): It is estimated as energy use less production, both measured in oil equivalents. A negative value indicates that the country is a net exporter. Energy use refers to use of primary energy before transformation to other end-use fuels, which is equal to indigenous production plus imports and stock changes, minus exports and fuels supplied to ships and aircraft engaged in international transport.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption (% of total): It comprises coal, oil, petroleum, and natural gas products.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Introduction
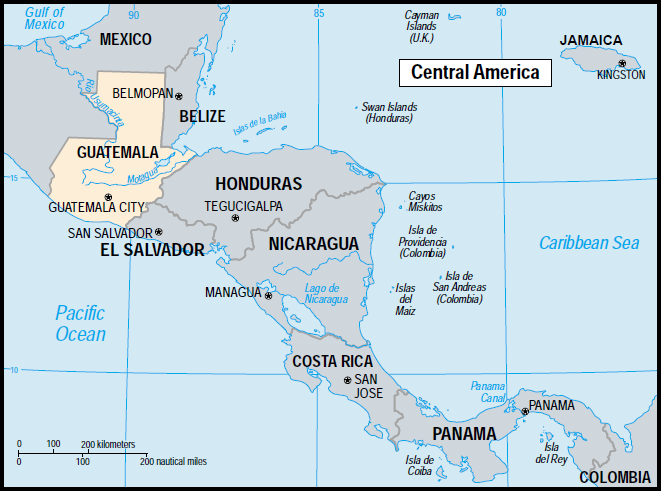
Guatemala is located in Central America[1]. It shares its borders with Mexico in the north, Belize and Honduras in the east, and El Salavador in the south[1][2]. On the west, the country borders the Pacific, with a much shorter northeastern Caribbean coastline[1][2]. The country's major cities are: Guatemala city -the capital-, Quetzaltenango, Escuintla, Livingston and Puerto Barrios[1].
Guatemala is divided topographily into four general regions: central-western highlands, southern volcanic regions of the Sierra Madre, tropical coastal lowlands, and the low northern plateau, which is mainly jungle[1][2].
Predominantly, Guatemala is an agricultural socitey, where farming is the major economic activiy, with forestry and mining close behind[1]. The best soils suitable for farming are located on the Pacific coastal line, while the soil in the Peten tends to erode quickly, and highland soils are better protected because of coffee cultivation[1].
Guatemalan climate varies with accordance to the altitude of the region, and the proximity to the coasts[1][2]. The tierra caliente (hot country), which extends from the sea level into 750m above sea level, and its temperature is around 29°-32°C[1]. The tierra templada (temperate country) extends from 750-1660m above sea level, with day temperature 24°-26°C, and night temperatures 15.5°-21°C[1][1].The tierra fria (cold country) extends above 1660m above sea level with an average temperature of 26°C at day, and 10°C at night[1].