Difference between revisions of "Basics and SWOT Analysis of SPIS"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 430: | Line 430: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
= Case Studies = | = Case Studies = | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
| Line 451: | Line 452: | ||
<u>Further Country Case Studies</u>: | <u>Further Country Case Studies</u>: | ||
| + | |||
{| style="width:100%;" | {| style="width:100%;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 469: | Line 471: | ||
*[[Advanced Solar Irrigation Scheduling for Sustainable Rural Development: A Case of India|Advanced Solar Irrigation Scheduling for Sustainable Rural Development: A Case of India]] | *[[Advanced Solar Irrigation Scheduling for Sustainable Rural Development: A Case of India|Advanced Solar Irrigation Scheduling for Sustainable Rural Development: A Case of India]] | ||
| − | |||
*[[Techno-Economic Feasibility of PV Irrigation in Egypt|Techno-Economic Feasibility of PV Irrigation in Egypt]] | *[[Techno-Economic Feasibility of PV Irrigation in Egypt|Techno-Economic Feasibility of PV Irrigation in Egypt]] | ||
*[https://energypedia.info/images/4/46/Potential_of_Solar_Irrigation_Water_Pumps_in_Pakistan.pdf Potential of Solar Irrigation Water Pumps in Pakistan] | *[https://energypedia.info/images/4/46/Potential_of_Solar_Irrigation_Water_Pumps_in_Pakistan.pdf Potential of Solar Irrigation Water Pumps in Pakistan] | ||
| + | *[https://creately.com/diagram-community/examples/t/swot SWOT Analysis Example for Energy Sector] | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 10:07, 9 September 2020
Overview
In a Solar Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) water can be extracted from different sources by a motor pump to water crops on a farmer’s field. The energy needed for this process comes from a solar generator which converts solar irradiation into electricity.
Among the renewables, solar Photovoltaic (PV) is often the most attractive option. It features a near-absence of running costs, little maintenance requirements and ease of use. In terms of CO2 emissions, an off-grid solar pumping system that replaces a typical diesel generator unit will save about 1 kg of CO2 per kilowatt-hour of output (GIZ, forthcoming). Due to falling costs for the components necessary for a PV pump, the renewable powered systems have become increasingly attractive from an economic perspective. However, many farmers in remote areas of the world do not know of these advantages of solar powered pumps, or if they do, non-technical barriers such as access to finance hinder an increased adoption of the systems.
Nevertheless, as prices for solar modules have fallen substantially in recent years, governments, extension services and technical cooperation are reconsidering PV water pumps to be employed in agricultural production and beyond. However, demand in this regard will have to be largely generated from the rural farm households themselves.
Basics of SPIS
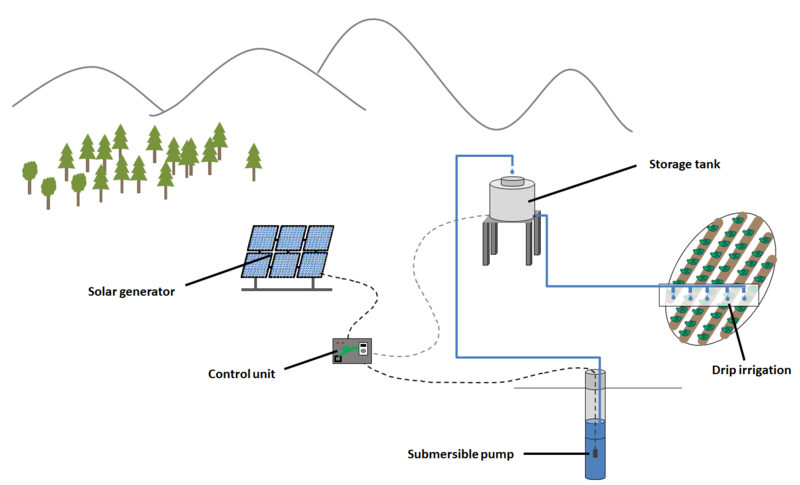
The SPIS mainly consists of the following parts: Solar generator, control unit, storage tank, motor pump and the irrigation system. Some parts of the system can be modified, depending on different parameters such as solar irradiation, hydraulic lift or water output.
Solar Generator
The solar generator converts sun energy (sunlight, including sun ultra violet radiation) directly into electricity.
The sizing depends of the power requirements of the motor pump and the solar irradiation: The higher the power requirements and the lower the solar irradiation, the sizing of the solar panels increases. Panels can be connected in parallel or in series in order to fulfill the specific power requirements.
The orientation and tilt angle depend on the construction site. In the southern hemisphere the panels should point north, while in the northern hemisphere they should point south. The panel’s tilt angle should be approximately equal to the site's latitude, taking into account the angle of the sun over the entire year. Sometimes it may be advantageous to tilt the PV panel at an angle that optimizes the performance in the winter, when solar radiation is likely to be the lowest.
Especially in dry regions, dust on the surface of the solar panels can lead to power losses up to 10 %. Panels have to be cleaned regularly in order to maximize the system efficiency (Mertens, 2015).
Other points which lead to power losses are shading and bad air circulation. Panels should be installed in a way that other objects (trees, buildings, …) don’t leave a shadow during the sun path. A good air circulation is important as the solar generator efficiency decreases with a rising temperature.
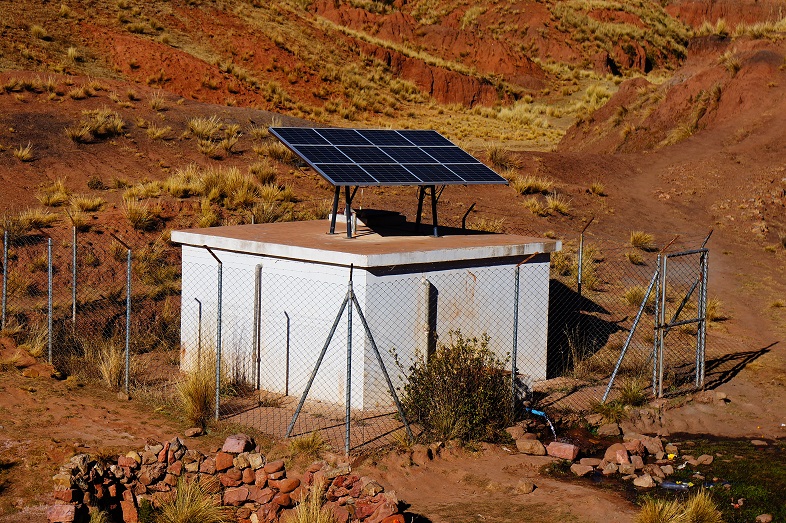
When installed away from buildings, theft of the solar panels or other components is a common problem, especially in rural areas. Constructions on a mounted structure, a surrounding fence or special screws are ways to raise the threshold and reduce the risk of theft.
Control Unit
The pump controller is installed between the solar generator and the motor pump to regulate the power supply of the pump and the operation of the whole system.
During the day, different parameters vary, such as solar irradiation (especially on cloudy days), the water level in the well, the water level in the storage or the time and amount of irrigation.
Most control units have an integrated Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) which maximizes the power use from the PV generator under changing irradiation conditions to provide the required amount of power needed by the pump.
Connected sensors in well and tank measure the water level and prevent dry operation of the pump. The controller also ensures, that an adjusted amount of water is distributed to irrigate the crops at a given time (e.g. during the morning / evening where a low irradiation leads to fewer evaporation losses).
Motor Pump
The pump moves the water by mechanical action. Water is lifted out of the water source into a tank or directly to the fields.
Pumps can mainly be grouped into:
- submersible
- surface
- floating
as well as into their technology:
positive displacement (e.g. helical rotor, diaphragm )
- centrifugal
with their own characteristics:
| Pump Type |
Pumping head |
Volume flow |
|---|---|---|
| Positive displacement |
High |
Low |
| Centrifugal |
Low |
High |
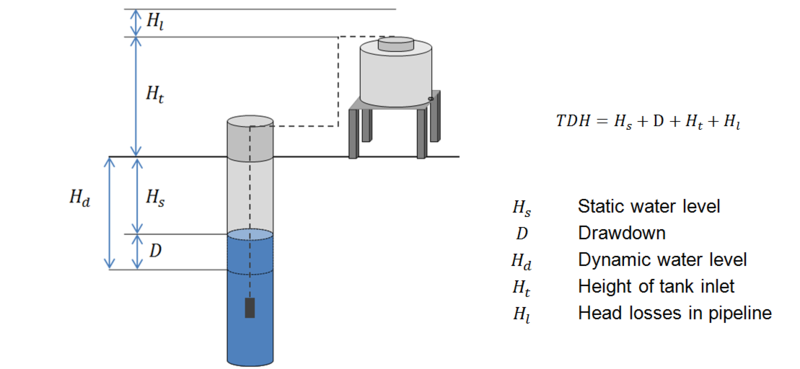
While the pump type mainly depends on the water source, sizing is dependent of the pumping head (altitude between water level and tank) and the flow rate.
Submersible pumps are mostly installed in (deep) wells. They push the water to the surface and have a high efficiency. Due to their subsurface installation they are safe from frost, dust or UV-radiation.
Surface pumps are installed on the ground and are mainly used for shallow sources as rivers, tanks or wells. They pull the water to the surface and push it further into a tank or to the irrigation site.
Floating pumps are mainly used for water sources with a strongly varying water level such as tanks or rivers. They float on the surface and pull/push the water to the tank or irrigation site.
For small and medium irrigation applications, water pumps are mostly direct current (DC) powered and can directly use the output of the solar generator. High-performance pumps often run with alternating current (AC) and therefore need a power inverter installed within the system.
While the flow rate is determined by the crop’s water need, the pumping head depends on the site conditions and construction:
Storage Tank
The tank contains water pumped by the system and serves as energy storage and for a longer autonomy of the SPIS.
- The sizing depends of the days of autonomy required, a volume of three times the daily need is recommended.
- Closed or covered tanks decrease evaporation and contamination of the stored water.
- Sun resisting materials (examples) or a UV protection (examples) increase the tank‘s lifespan.
- Putting the tank on a higher level platform leads to a higher pressure when distributing the water.
- The tank serves as energy storage (like a battery), water can so be distributed despite cloudy days or within the night.
- Reservoirs can be used to mix in soluble fertilizers when used for crop irrigation only.
Irrigation System
There are various methods that can be used for irrigation, each method needs an experienced farmer to determine the quantity of water to apply and the timing of the irrigation.
Surface Irrigation is the application of water by gravity flow to the surface of the field. Either the entire field is flooded (basin irrigation as i.e. for cultivating paddy rice) or the water is fed into small channels (furrows) or strips of land (borders). Surface irrigation can be operated without any high-tech applications but is often more labor intensive than other irrigation methods.
Sprinkler Irrigation is a method of providing rainfall-like irrigation to the crops. Water is distributed through a system of pipes usually by pumping. Spray heads at the outlets distribute the water over the entire soil surface.
A typical sprinkler irrigation system consists of the following components: Pump unit; Mainline; Lateral lines; Sprinklers.
Drip irrigation involves dripping water onto the soil at very low rates. Water is applied close to plants so that only part of the soil in which the roots grow is wetted.
A typical drip irrigation system consists of the following components: Pump unit; Control head; Mainlines and sub-mainlines; Lateral lines; Emitters or drippers.
|
Application System |
Irrigation Efficiency[1] |
|
Drip Systems |
90 % |
|
Micro Sprinkler Systems |
80 % |
|
Permanent Sprinkler Systems |
75 % |
|
Moving Sprinkler Systems |
80 % |
|
Movable Quick Coupling Sprinkler Systems |
70 % |
|
Travelling Sprinkler Systems |
65 % |
|
Surface Irrigation Systems (Piped Supply) |
80 % |
|
Surface Irrigation Systems (Earth Channel Supply) |
60 % |
|
Irrigation Type |
Initial costs |
Land leveling |
Efficiency |
Adding of fertilizers |
Labor requirements |
|
Surface |
Low |
Requiered |
Low |
No |
Intensive |
|
Sprinkler |
High |
Not requiered |
Middle |
Economical |
Low |
|
Drip |
High |
Not requiered |
High |
Highly efficient |
Low |
Based on : Solar Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS)
SWOT Analysis of SPIS
|
Strengths
|
|
Weaknesses
|
|
Opportunities
|
|
Threats
|
Comparison PV – Diesel
When choosing between a SPIS and a diesel pump, a cost comparison is a good way to check the economical aspect. Comparing the two technologies shows, that SPIS needs higher investment costs as the solar panels and the electric pump are more expensive than a diesel pump. Operating costs, however, are much higher in the diesel system due to its fuel need and higher maintenance costs. The following points have to be taken into consideration when creating the cost comparison:
|
|
Diesel system |
Solar powered irrigation system |
|
Investment costs |
|
|
|
Operating costs |
|
|
Environmental Effects of Irrigation
The way of irrigation has different impacts on the environment with its available natural resources, such as water or soil.
The extraction of water out of the ground, whether by solar or diesel pumps, can have serious impacts and even lead to groundwater depletion, if the amount of pumped water is higher than the natural refreshment rate.
Some irrigation methods, especially surface irrigation can lead to high soil salinities, since almost all water (even natural rainfall) contains dissolved salts. When the plants use the water or when the water evaporates to fast, salts are left behind in the soil and begin to accumulate. This process can have detrimental effects on plant growth and yield.
Leaching of nutrients is another problem caused by wrong irrigation.
Further Information
Case Studies
Solar-Powered Pumps for Improved Irrigation in Honduras, Nepal and Zambia: iDE’s Clean Irrigation Solution (CIS) can compete with fossil fuel pumps both in terms of cost and enhancing agricultural productivity. CIS’s universal piston pump can run on a variety of power sources (solar steam power, photovoltaic power, and grid-connected alternating current (AC) where available). The system accesses groundwater from deeper depths than conventional pumps, and maintains a slow, steady discharge rate. iDE will work with local businesses to sell and service the CIS. Recently, field testing of pumps have been started in Nepal.
►Read more here.
Micro-Solar Utilities for Small-Scale Irrigation in Senegal: Earth Institute’s solution will enable a small group of farmers to use a central Solar Energy unit to power multiple AC pumps for irrigation. The proposed solution takes advantage of the benefits of solar without the high costs associated with DC-powered pumps and battery storage. This power will be accessed by farmers with prepaid electricity cards issued by a micro-utility, and sold through local vendors who will benefit from a small commission. Recognizing that a major obstacle to technology adoption is Portal:Financing and Funding, a tariff-based financing model will allow customers to cover their appliance loans in small payments added into their micro-utility bills.
►Read more Micro-Solar Utilities for Small-Scale Irrigation.
Solar Powered Irrigation Systems in Egypt and the initiative "RaSeed": This initiative aims to promote the use of Photovoltaic (PV) systems in drip irrigation farming in order to support cost-effective and sustainable agriculture. Therefore, the aim is to introduce high capacity solar operated water pumps - of up to a pump size of 100kW - to the Egyptian agricultural sector. Furthermore, soil in the “New Lands” is mostly sandy, and water used for irrigation is ground water. Hence, it is crucial to use water efficient irrigation systems. RaSeed targets farm specific optimization of drip irrigation systems that enable maximum fuel savings and water efficiency by taking into account soil compositions and environmental conditions. In order to further the initiative, a Private Public Partnership (PPP) was established with a solar energy firm that is supported by the multi-donor initiative: Powering Agriculture: An Energy Grand Challenge for Development. Together with its partners, RaSeed establishes a network, providing high quality solar energy technology and training in Egypt.
►Read more Solar Powered Irrigation Systems in Egypt.
Further Country Case Studies:

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
Further Case Studies
- ↑ http://www.sabi.co.za/01.pdf/SABI Norms 12 March 2014.pdf