Difference between revisions of "Germany Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| (57 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{CES Country|CES Country Name=Germany | |
| + | |CES Country Capital=Berlin | ||
| + | |CES Country Region Europe and Central Asia = Europe & Central Asia | ||
| + | |CES Country Coordinates=52.5167° N, 13.3833° E | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | = Introduction = | ||
| − | This article first briefly discusses the present energy situation in Germany in general terms, before adressing in more detail the electricity sector and recent political endeavours that link climate protection and long-term sustainable energy supply. | + | When looking at the energy/electricity situation of developing countries around the world it is always helpful to have in mind a reference point for a better understanding, analysis and judgement of the respective challenges in the case at hand. The country situation Germany should help to provide this critical positioning.<br/>This article first briefly discusses the present energy situation in Germany in general terms, before adressing in more detail the electricity sector and recent political endeavours that link climate protection and long-term sustainable energy supply. |
| − | + | [[Germany_Energy_Situation#toc|►Go to Top]] | |
| − | + | = Energy Situation = | |
| − | + | == Primary Energy Consumption == | |
| − | Primary energy denotes the state of energy before any conversion or transformation process towards a more valuable energy form has taken place (e. g. solar energy, wind energy, fossil fuels, hydro power, nuclear fuels, biomass etc.). Primary energy consumption relates to the entire amount of primary energy used by an economy in a certain time period (usually a year). | + | Primary energy denotes the state of energy before any conversion or transformation process towards a more valuable energy form has taken place (e. g. solar energy, wind energy, fossil fuels, hydro power, nuclear fuels, biomass etc.). Primary energy consumption relates to the entire amount of primary energy used by an economy in a certain time period (usually a year). |
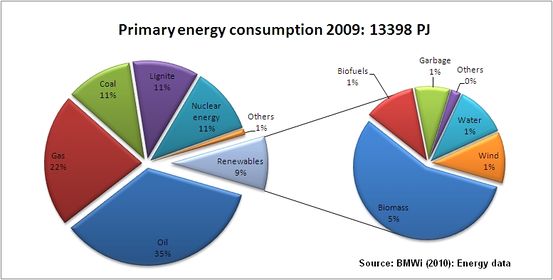
| − | In Germany, primary energy consumption in 2009 amounted to 13398 PJ (= 3720 TWh). (As a yard stick: this is about 2-3 times the value of countries like Saudi-Arabia, Mexico, South Africa, Nigeria or Thailand; or about half the amount of primary energy consumption of the entire African continent.)<ref>cf. International Energy Agency (2010): Key World Energy Statistics, pp. 48-57.</ref> Although there has been a sharp decline in petroleum product consumption since 1995 (-14,4%), it still remains the most important primary energy carrier representing about a third of total primary energy consumption. Similarily, coal consumption has been decreasing during the last 10-15 years, but remains an important primary energy carrier. A substitution process in the direction of an increasing gas consumption has accompanied the decrease in consumption of the beforementioned energy sources. | + | In Germany, primary energy consumption in 2009 amounted to 13398 PJ (= 3720 TWh). (As a yard stick: this is about 2-3 times the value of countries like Saudi-Arabia, Mexico, South Africa, Nigeria or Thailand; or about half the amount of primary energy consumption of the entire African continent.)<ref>cf. International Energy Agency (2010): Key World Energy Statistics, pp. 48-57.</ref> Although there has been a sharp decline in petroleum product consumption since 1995 (-14,4%), it still remains the most important primary energy carrier representing about a third of total primary energy consumption. Similarily, coal consumption has been decreasing during the last 10-15 years, but remains an important primary energy carrier. A substitution process in the direction of an increasing gas consumption has accompanied the decrease in consumption of the beforementioned energy sources. |
| − | Germany is a net importer of primary energy with an increase of imports from 57% in 1990 to 70% in 2008.<ref name="null">cf. ewi/gws/prognos (2010): Studie – Energieszenarien für ein Energiekonzept der Bundesregierung, p. 257.</ref> This situation underlines the high degree of energy dependence the German state faces. The rising import quotas can largely be attributed to a rising demand of gas and substitution processes of German coal through coal from international markets. | + | Germany is a net importer of primary energy with an increase of imports from 57% in 1990 to 70% in 2008.<ref name="null">cf. ewi/gws/prognos (2010): Studie – Energieszenarien für ein Energiekonzept der Bundesregierung, p. 257.</ref> This situation underlines the high degree of energy dependence the German state faces. The rising import quotas can largely be attributed to a rising demand of gas and substitution processes of German coal through coal from international markets. |
| − | The following diagram offers an overview of the share of different energy carriers in primary energy consumption: | + | The following diagram offers an overview of the share of different energy carriers in primary energy consumption: |
| − | <br> | + | <br/> |
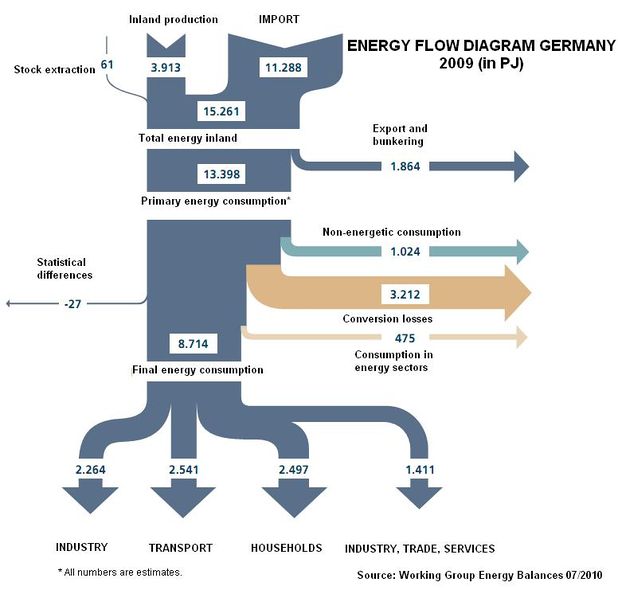
| − | [[ | + | [[File:Primary energy consumption.neu.JPG|thumb|right|553px|Primary energy consumption.neu.JPG]]The following energy flow diagram offers insight into the shares of different sectors in total primary energy consumption in 2009. Very prominently, it visualizes the high degree of dependence on energy imports (~70%). Furthermore, it shows that approximately 25% of primary energy consumption are lost in conversion processes. Out of the 13398 PJ of primary energy consumption only 8714 PJ are available for final energy consumption. Final energy consumption is quite evenly distributed among the three sectors industry, transport and households. Only trade and services represent a minor share. |
| − | <br> | + | <br/> |
| − | + | [[File:Energy Flow.JPG|thumb|center|618px]] | |
| − | [[ | + | [[Germany_Energy_Situation#toc|►Go To Top]] |
| − | + | = Electricity Situation = | |
| − | Needless to say, in comparison to developing and even emerging countries the German electricity sector is very proficient and works reliably. Power outage rates rank among the lowest in the world. Power outages affecting German customers totaled only 23 minutes on average in 2004. Therefore, Germany has the most secure power supply system in Europe. | + | Needless to say, in comparison to developing and even emerging countries the German electricity sector is very proficient and works reliably. Power outage rates rank among the lowest in the world. Power outages affecting German customers totaled only 23 minutes on average in 2004. Therefore, Germany has the most secure power supply system in Europe. |
| − | + | [[Germany_Energy_Situation#toc|►Go To Top]] | |
| − | + | == Electricity Supply == | |
| − | + | Currently, the installed capacity of German power plants lies in the range of 143,3 GW electrical power. This means if capacity factors were assumed to be 100% (i. e. all power plants are in use throughout the whole year) the maximum amount of electricity generation would be 1255.3 TWh/year (143,3 GW x 8760h). Clearly, this is unrealistic due to high variable costs of power plants that are specifically designed to serve intermediate and peak loads only. Additionally, power plants depending on renewable energies like wind or solar radiation cannot decide when to generate. | |
| − | + | In reality, German electricity generation amounted to 597 billions kWh (= 597 TWh) in 2009 which lies in the range of emerging countries like Brazil or India.<ref>cf. International Energy Agency (2010): Key World Energy Statistics, pp. 48-57.</ref> This shows that the true value of the aggregated average capacity factor lies around 50%. Whereas nuclear, lignite and hydro power plants virtually run all the time to supply the base load, other electricity plants (such as coal and gas) only serve intermediate load. Peak load is mainly provided for by pumped-storage power plants and oil-fired power plants. To produce the abovementioned amount of electricity, fuels with an energy content of 5227 PJ were used in German power plants (~39% of primary energy consumption). | |
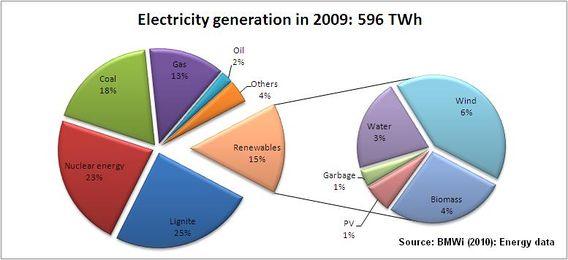
| − | + | Electricity generation in Germany is still based to a very large extent on coal. The generation mix in 2009 consisted of 28% from nuclear power plants, 26% from lignite, 18% from coal, 11% from gas and about 16% from renewable energies. The following diagram provides a brief overview of the situation. It should be noted that the share of renewable energies in electricity generation is considerably greater than in primary energy consumption. This can largely be attributed to the incentives created by the German Renewable Energy Law of 2000. | |
| − | [[ | + | <br/>[[File:Electricity generation.neu.JPG|thumb|center|568px|Electricity generation.neu.JPG]]<br/><br/>The webpage of SMA publishes a [http://www.sma.de/en/news-infos/pv-leistung-in-deutschland.html life view on the projected, current power output in Germany only based on PV Systems] in Germany. |
| − | + | [[Germany_Energy_Situation#toc|►Go To Top]] | |
| − | + | = Policy Framework, Laws, Regulations = | |
| − | + | == Energy and Environmental Policy == | |
| − | In Germany, energy and environmental politics are strongly intertwined. The combined energy and climate protection program is only one obvious example. Many other regulations in the | + | In Germany, energy and environmental politics are strongly intertwined. The combined energy and climate protection program is only one obvious example. Many other regulations in the past to cut down the use of energy explicitly aimed at reducing environmental pollution at the same time. |
| − | In the political debate on costs and benefits of the promotion of renewable energy technologies the macro-economic and employment effects of the renewable energy industry became an important line of argumentation in favor of the legal framework set by the Renewable Energy Law. The Federal Ministry of Environment (BMU) | + | In the political debate on costs and benefits of the promotion of renewable energy technologies the macro-economic and employment effects of the renewable energy industry became an important line of argumentation in favor of the legal framework set by the Renewable Energy Law. The Federal Ministry of Environment (BMU) regularly monitors these effects and reports that the employment contribution of renewable energies rose to 340.000 jobs in 2009 ([http://www.erneuerbare-energien.de/inhalt/47015/40289/ Report on Short and Long-term Employment Effects of Renewable Energy Promotion in Germany, 02/2011 - in German]). |
| − | + | [[Germany_Energy_Situation#toc|►Go To Top]] | |
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | + | == <br/>Renewable Energy Law<br/> == | |
| − | + | Most prominently, the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/German_Renewable_Energy_Act German Renewable Energy Act of 2000] aims at considerably increasing the contribution of renewable energies in the electricity generation mix.<br/>In 2014 the german Federal Ministry for Economics Affairs and Energy published the latest version and additional documents of the RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES ACT here: [http://www.bmwi.de/EN/Topics/Energy/Renewable-Energy/2014-renewable-energy-sources-act.html http://www.bmwi.de/EN/Topics/Energy/Renewable-Energy/2014-renewable-energy-sources-act.html]<br/>[[Germany_Energy_Situation#toc|►Go To Top]] | |
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | + | == Energy Concept 2050 == | |
| − | + | The [[Energy_Concept_2050|Energy Concept 2050]] is the latest political endeavour of the present German coalition government between CDU/CSU and FDP concerning a clean, reliable and affordable future energy supply. | |
| − | + | = Further Information = | |
| − | + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_in_Germany Wikipedia, Energy in Germany]<br/> | |
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renewable_energy_in_Germany Wikipedia, Renewable Energy in Germany] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electricity_sector_in_Germany Wikipedia, Electricity Sector in Germany] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_power_in_Germany Wikipedia, Wind power in Germany] | ||
| + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_power_in_Germany Wikipedia, Solar power in Germany] | ||
| + | *[[:File:Renewable_Energies_Act_(EEG).pdf|Renewable Energy Act]]<br/> | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | + | [[Germany_Energy_Situation#toc|►Go To Top]] | |
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | + | = References = | |
| − | + | '''<references />'''<br/> | |
| − | + | [[Category:Europe_and_Central_Asia]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Germany]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | ||
Latest revision as of 21:22, 10 July 2018
Capital:
Berlin
Region:
Coordinates:
52.5167° N, 13.3833° E
Total Area (km²): It includes a country's total area, including areas under inland bodies of water and some coastal waterways.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.
Population: It is based on the de facto definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship--except for refugees not permanently settled in the country of asylum, who are generally considered part of the population of their country of origin.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Rural Population (% of total population): It refers to people living in rural areas as defined by national statistical offices. It is calculated as the difference between total population and urban population.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
GDP (current US$): It is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. It is calculated without making deductions for depreciation of fabricated assets or for depletion and degradation of natural resources.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.2 ()
GDP Per Capita (current US$): It is gross domestic product divided by midyear population
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Access to Electricity (% of population): It is the percentage of population with access to electricity.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Energy Imports Net (% of energy use): It is estimated as energy use less production, both measured in oil equivalents. A negative value indicates that the country is a net exporter. Energy use refers to use of primary energy before transformation to other end-use fuels, which is equal to indigenous production plus imports and stock changes, minus exports and fuels supplied to ships and aircraft engaged in international transport.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption (% of total): It comprises coal, oil, petroleum, and natural gas products.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Introduction
When looking at the energy/electricity situation of developing countries around the world it is always helpful to have in mind a reference point for a better understanding, analysis and judgement of the respective challenges in the case at hand. The country situation Germany should help to provide this critical positioning.
This article first briefly discusses the present energy situation in Germany in general terms, before adressing in more detail the electricity sector and recent political endeavours that link climate protection and long-term sustainable energy supply.
Energy Situation
Primary Energy Consumption
Primary energy denotes the state of energy before any conversion or transformation process towards a more valuable energy form has taken place (e. g. solar energy, wind energy, fossil fuels, hydro power, nuclear fuels, biomass etc.). Primary energy consumption relates to the entire amount of primary energy used by an economy in a certain time period (usually a year).
In Germany, primary energy consumption in 2009 amounted to 13398 PJ (= 3720 TWh). (As a yard stick: this is about 2-3 times the value of countries like Saudi-Arabia, Mexico, South Africa, Nigeria or Thailand; or about half the amount of primary energy consumption of the entire African continent.)[1] Although there has been a sharp decline in petroleum product consumption since 1995 (-14,4%), it still remains the most important primary energy carrier representing about a third of total primary energy consumption. Similarily, coal consumption has been decreasing during the last 10-15 years, but remains an important primary energy carrier. A substitution process in the direction of an increasing gas consumption has accompanied the decrease in consumption of the beforementioned energy sources.
Germany is a net importer of primary energy with an increase of imports from 57% in 1990 to 70% in 2008.[2] This situation underlines the high degree of energy dependence the German state faces. The rising import quotas can largely be attributed to a rising demand of gas and substitution processes of German coal through coal from international markets.
The following diagram offers an overview of the share of different energy carriers in primary energy consumption:
The following energy flow diagram offers insight into the shares of different sectors in total primary energy consumption in 2009. Very prominently, it visualizes the high degree of dependence on energy imports (~70%). Furthermore, it shows that approximately 25% of primary energy consumption are lost in conversion processes. Out of the 13398 PJ of primary energy consumption only 8714 PJ are available for final energy consumption. Final energy consumption is quite evenly distributed among the three sectors industry, transport and households. Only trade and services represent a minor share.
Electricity Situation
Needless to say, in comparison to developing and even emerging countries the German electricity sector is very proficient and works reliably. Power outage rates rank among the lowest in the world. Power outages affecting German customers totaled only 23 minutes on average in 2004. Therefore, Germany has the most secure power supply system in Europe.
Electricity Supply
Currently, the installed capacity of German power plants lies in the range of 143,3 GW electrical power. This means if capacity factors were assumed to be 100% (i. e. all power plants are in use throughout the whole year) the maximum amount of electricity generation would be 1255.3 TWh/year (143,3 GW x 8760h). Clearly, this is unrealistic due to high variable costs of power plants that are specifically designed to serve intermediate and peak loads only. Additionally, power plants depending on renewable energies like wind or solar radiation cannot decide when to generate.
In reality, German electricity generation amounted to 597 billions kWh (= 597 TWh) in 2009 which lies in the range of emerging countries like Brazil or India.[3] This shows that the true value of the aggregated average capacity factor lies around 50%. Whereas nuclear, lignite and hydro power plants virtually run all the time to supply the base load, other electricity plants (such as coal and gas) only serve intermediate load. Peak load is mainly provided for by pumped-storage power plants and oil-fired power plants. To produce the abovementioned amount of electricity, fuels with an energy content of 5227 PJ were used in German power plants (~39% of primary energy consumption).
Electricity generation in Germany is still based to a very large extent on coal. The generation mix in 2009 consisted of 28% from nuclear power plants, 26% from lignite, 18% from coal, 11% from gas and about 16% from renewable energies. The following diagram provides a brief overview of the situation. It should be noted that the share of renewable energies in electricity generation is considerably greater than in primary energy consumption. This can largely be attributed to the incentives created by the German Renewable Energy Law of 2000.
The webpage of SMA publishes a life view on the projected, current power output in Germany only based on PV Systems in Germany.
Policy Framework, Laws, Regulations
Energy and Environmental Policy
In Germany, energy and environmental politics are strongly intertwined. The combined energy and climate protection program is only one obvious example. Many other regulations in the past to cut down the use of energy explicitly aimed at reducing environmental pollution at the same time.
In the political debate on costs and benefits of the promotion of renewable energy technologies the macro-economic and employment effects of the renewable energy industry became an important line of argumentation in favor of the legal framework set by the Renewable Energy Law. The Federal Ministry of Environment (BMU) regularly monitors these effects and reports that the employment contribution of renewable energies rose to 340.000 jobs in 2009 (Report on Short and Long-term Employment Effects of Renewable Energy Promotion in Germany, 02/2011 - in German).
Renewable Energy Law
Most prominently, the German Renewable Energy Act of 2000 aims at considerably increasing the contribution of renewable energies in the electricity generation mix.
In 2014 the german Federal Ministry for Economics Affairs and Energy published the latest version and additional documents of the RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES ACT here: http://www.bmwi.de/EN/Topics/Energy/Renewable-Energy/2014-renewable-energy-sources-act.html
►Go To Top
Energy Concept 2050
The Energy Concept 2050 is the latest political endeavour of the present German coalition government between CDU/CSU and FDP concerning a clean, reliable and affordable future energy supply.
Further Information
- Wikipedia, Energy in Germany
- Wikipedia, Renewable Energy in Germany
- Wikipedia, Electricity Sector in Germany
- Wikipedia, Wind power in Germany
- Wikipedia, Solar power in Germany
- Renewable Energy Act