Difference between revisions of "Kazakhstan Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
There is a discrepancy between rural and urban population income. While 32% of the rural population lives below the poverty line, the urban rate is 16%. <br> | There is a discrepancy between rural and urban population income. While 32% of the rural population lives below the poverty line, the urban rate is 16%. <br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == National Energy Situation == | |
| − | + | Kazakhstan is rich in reserves of fossil fuel. It owns about 0.5% of the world´s mineral energy resources, equaling 90 billion tons of oil equivalent. This number includes 70% coal, 22% oil, and 8% gas. 99% of its energy needs is covered from fossil sources. The fuel energy sector production contributes about 17% of the GDP. | |
| − | + | '''Primary energy''' in Kazakhstan are fossil fuel resources with the following share in 2006: 19% oil, 49% coal, and 31% gas. The share of renwable of renewable energy, mainly hydro power, is about 1%. Data on the use of traditional fuel sources such as firewood for domestic use were not available. | |
| − | + | In 2006, the '''electricity generation''' in Kazakhstan was 71.6 billion kWh. About 70% of the total generation comes from coal, 10.6% from gas, 4.9% from oil, and 14.6% from hydro power. The share of power consumer is: 68.7 industry, 9.3 households, 8% service sector, 5.6% transportation, and 1.2% agriculture. Electricity prices are 0.067US$/kWh for private consumers and 0.052US$ for the industrial sector. | |
| − | + | The mayority of of the '''distribution network''' has not yet been privatized, even the Kazakhstan Electricity Grid Operating Company (KEGOC) has granted several management rights to private companies. The policy is focused on energy saving and optimizatioon of current electric plants with fossil energy sources. The main problem people are facing with regard to energy and electricity is the low capacity of the centralized power stations in the south of the country. High transmission losses (25 - 50%) and the deterioration of transmission lines cause electricity shortage in remote rural areas. Only a small fraction of around 3,5% of rural settlements do not have access to energy and electricity. About 1% of the population ist not connected to the grid in rural areas. | |
| − | + | The present share of using '''renewable energies''' in Kazakhstan is very small due to the low prices for fossil energy. But the potential is estimated to be high, as estimations from Dukenbaev in 1996 show: | |
| + | |||
| + | | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" width="200" border="1" | ||
| + | |+ Renewable Energy Potential | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | | ||
| − | + | Wind energy: Kazakhstan has enormous wind resources due the location in the northern hemisphere´s wind belt, but only a small part of the wind potential is used; 500kv out of a potential of 1.3 trillion kWh of electric energy per year at the Jungar Gates is used. | |
| − | + | Solar energy: Kazakhstan has 2,200 - 3,000 sunshine houres anually, which equals to 1,300 - 1,800 kWm² energy. Despite the very favourable conditions for solar energy, there is little use of the resource. | |
| − | + | | |
| − | == | + | == Household energy situation == |
| − | ==== Share of Fuel Types ==== | + | ==== Share of Fuel Types ==== |
Percentage of energy types used for cooking in urban areas <ref name="WHO 2010">fckLRWHO 2010: WHO Household Energy Database</ref> | Percentage of energy types used for cooking in urban areas <ref name="WHO 2010">fckLRWHO 2010: WHO Household Energy Database</ref> | ||
| Line 200: | Line 236: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | === Share of Solid Fuels === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The percentage of the population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy: | |
| − | + | National: 11.6%, Urban: 5.5%, Rural: 25.2% <ref name="WHO 2007">WHO 2007</ref> | |
| − | + | However, the energy demand for heating is as well assumed to be high due to the cold winters, but quantitative data are not available so far. | |
| − | + | ==== Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health ==== | |
| − | + | • Total annual deaths attributable to solid fuel use: < 100 persons <ref name="WHO 2006">WHO (2006): Fuel for Life - Household Energy and Health</ref><br>• Percentage of national burden of diseases attributable to solid fuel use: 0%<br> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | & | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | ||
| − | + | === Potentials === | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Private households mainly in rural areas use solar-thermal energy. A market for the equipment is not existent. | |
| − | + | == Policy framework == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == Market risks == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Relevant institutions and organisation == | |
| − | = | + | == References<br> == |
| − | + | The information refer to the following sources: | |
| − | + | *WHO | |
| + | *CIA factbook | ||
| + | *GIZ (2009): Regional Reports on Renewable Energies - 30 Country Analysis on Potentials and markets in West Africa (17), East Africa (5) and Central Asia (8) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| | ||
[[Category:Kazakhstan]] | [[Category:Kazakhstan]] | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 25 November 2011
| Kazakhstan | |||
| |
| ||
|
Capital |
Astana (51°10′N 71°25′E) | ||
|
Official language(s) |
Kazakh (1st)/Russian (2nd) | ||
|
Government |
Presidential republic | ||
|
President |
Nursultan Nazarbayev | ||
|
Prime Minister |
Karim Massimov | ||
|
Total area |
2,724,900 km2 | ||
|
Population |
16,600,000 (2011 estimate) | ||
|
Population - Rural |
41% (6.4 million | ||
|
Population - Urban |
59% (9.1 million) | ||
|
Population Density |
6 people/ km² (one of lowest in the world) | ||
|
Avg. Household Size |
6 members | ||
|
Literacy Rate |
99.5% | ||
|
GDP (nominal) |
$180.147 billion | ||
|
GDP per Capita |
$10,951 | ||
|
GNI per Capita |
$ 7769.40 | ||
|
Currency |
Tenge (KZT) | ||
|
Time Zone |
(UTC+5/6) | ||
|
Calling Code |
+7-6xx, +7-7xx | ||
Geography and Climatic Conditions
The Republic of Kazakhstan is located in Central Asia. The neighbooring countries are Russia in the North and West, China China in the East, Kyrgyztan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan in the South. The capital of Kazakhstan is Astana and the country is administratively divided into 14 regions.
Forest/steppe and steppe land areas comprise 10% of the territory, 60% semi-desert and desert land and about 5% are categorized as highlands. The land covered by forest is 1,2% with decreasing forest coverage by approx. -0,17% annually[1]. The percentage of land and water is 98% to 2%.
The climate is continental with cold dry winters (below -50°C) and hot dry summers (more than 53°C). The perception ranges between 15 to 320 mm annually. The average minimum is 3.8°C and the average maximum temperature is about 14.6°C with regional differences in the north, south and west [2].
Kazakhstan has 220 million hectares of agricultural land, which comprises 10,8% arable land, 2,2% of haying land, and 85%pasturable land.
Socio-economic Development
15.5 million is the population of Kazakhstan. The population density is 5.7 people per square meter, which is one of the lowest in the world. The percentage of urban and rural population is 52.6% to 47.7%. The literacy (age 15+) is 99,5%.
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) until 2008 was around 141 billion US$, refering to 9,075 US$ per capita. The GDP consits out of 5,4% agriculture, 42,8% industry, and 51,8% services share. The annual growth rate of the GDP was about in 7% 2010, 1.2% in 2009, and 3.2% in 2008. Main agricultural export products are grain, flour, cotton (15%), and leather as well as wool (25%).
There is a discrepancy between rural and urban population income. While 32% of the rural population lives below the poverty line, the urban rate is 16%.
National Energy Situation
Kazakhstan is rich in reserves of fossil fuel. It owns about 0.5% of the world´s mineral energy resources, equaling 90 billion tons of oil equivalent. This number includes 70% coal, 22% oil, and 8% gas. 99% of its energy needs is covered from fossil sources. The fuel energy sector production contributes about 17% of the GDP.
Primary energy in Kazakhstan are fossil fuel resources with the following share in 2006: 19% oil, 49% coal, and 31% gas. The share of renwable of renewable energy, mainly hydro power, is about 1%. Data on the use of traditional fuel sources such as firewood for domestic use were not available.
In 2006, the electricity generation in Kazakhstan was 71.6 billion kWh. About 70% of the total generation comes from coal, 10.6% from gas, 4.9% from oil, and 14.6% from hydro power. The share of power consumer is: 68.7 industry, 9.3 households, 8% service sector, 5.6% transportation, and 1.2% agriculture. Electricity prices are 0.067US$/kWh for private consumers and 0.052US$ for the industrial sector.
The mayority of of the distribution network has not yet been privatized, even the Kazakhstan Electricity Grid Operating Company (KEGOC) has granted several management rights to private companies. The policy is focused on energy saving and optimizatioon of current electric plants with fossil energy sources. The main problem people are facing with regard to energy and electricity is the low capacity of the centralized power stations in the south of the country. High transmission losses (25 - 50%) and the deterioration of transmission lines cause electricity shortage in remote rural areas. Only a small fraction of around 3,5% of rural settlements do not have access to energy and electricity. About 1% of the population ist not connected to the grid in rural areas.
The present share of using renewable energies in Kazakhstan is very small due to the low prices for fossil energy. But the potential is estimated to be high, as estimations from Dukenbaev in 1996 show:
Wind energy: Kazakhstan has enormous wind resources due the location in the northern hemisphere´s wind belt, but only a small part of the wind potential is used; 500kv out of a potential of 1.3 trillion kWh of electric energy per year at the Jungar Gates is used.
Solar energy: Kazakhstan has 2,200 - 3,000 sunshine houres anually, which equals to 1,300 - 1,800 kWm² energy. Despite the very favourable conditions for solar energy, there is little use of the resource.
Household energy situation
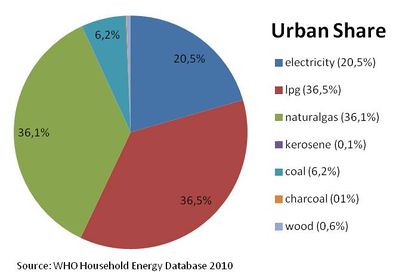
Percentage of energy types used for cooking in urban areas [3]
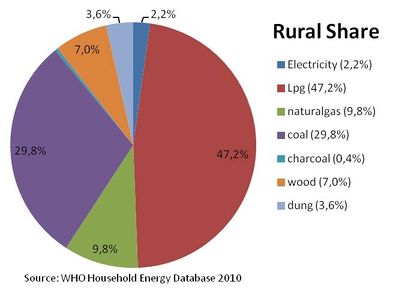
Percentage of energy types used for cooking in rural areas[3]
The percentage of the population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy:
National: 11.6%, Urban: 5.5%, Rural: 25.2% [4]
However, the energy demand for heating is as well assumed to be high due to the cold winters, but quantitative data are not available so far.
Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health
• Total annual deaths attributable to solid fuel use: < 100 persons [5]
• Percentage of national burden of diseases attributable to solid fuel use: 0%
Potentials
Private households mainly in rural areas use solar-thermal energy. A market for the equipment is not existent.
Policy framework
Market risks
Relevant institutions and organisation
References
The information refer to the following sources:
- WHO
- CIA factbook
- GIZ (2009): Regional Reports on Renewable Energies - 30 Country Analysis on Potentials and markets in West Africa (17), East Africa (5) and Central Asia (8)
- ↑ http://rainforests.mongabay.com/deforestation/
- ↑ http://data.un.org/CountryProfile.aspx?crName=Kazakhstan
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 fckLRWHO 2010: WHO Household Energy Database Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "WHO 2010" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ WHO 2007
- ↑ WHO (2006): Fuel for Life - Household Energy and Health