Nepal - Energy Efficiency in Industry
Overview
Although, Nepal has the second largest hydropower resources in the world, it is still suffering from high energy shortage since several years. This power crisis has resulted in scheduled power outages (called load shedding) up to 12 hours per day in the dry season when the run-off-the-river hydropower plant cannot meet the electricity demand.
Particularly, industry is suffering because they have to shut down during load shedding or to run costly fuel based backup systems. The import of petroleum product has increased sharply during the last decade resulting in a trade deficit with India.
However, energy is scarce and expensive it is often not used efficiently and wasted. This article gives an overview about energy saving potentials in eight energy-intensive sectors of Nepal.[1]
Industrial Sectors
Brick Sector
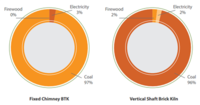
Sector highlightsBrick is a primary construction material in Nepal. Around 575 Brick kilns are in operations (Status 2006/2007) having a production capacity from 15,000 to 50,000 brick per day. Most of them operates only during dry season from December to June. Clay is the main raw material used in this industry and is available at very low cost. However, brick making is an energy and labour intensive industrial process. Hand moulding of green brick is mostly used. The predominant kiln technology in Nepal is the Fixed Chimney Bull Trench Kiln (FC-BTK). Apart from BTKs, Clamp Hoffmann and Vertical Shift Brick Kiln (VSBK) can be also found.
Energy use
Coal is the main energy source used in the brick kilns in Nepal and is mostly imported from India. Small amount of sawdust, fire wood and bagasse are sometimes also used as fuel. The energy cost on product value is 32% for FC-BTK and 14% for VSBK.
Energy Saving Potential
Thermal energy savings in Nepal’s brick sector is estimated to be 34% for the FC-BTK kiln technology and 4% for VSBK. It is estimated that brick kiln owners could save a total amount of NPR 3.45 Million every year by implementing energy efficiency measures.
Cement Sector
Cement is a commonly used as a basic building material in the country. About 70% of the cement used in the construction sector is manufactured in Nepal. There are two types of cement factories, namely, limestone-based and clinker-based. Limestone-based industry use the raw material limestone, that is abundantly available in Nepal, and burn the clinker and process the clinker to cement. Clinker-based factories import the clinker from India and process it to cement. There are more than 60 cement industries in Nepal; most of them clinker-based. Few new large units have a production capacity between 900 to 1,000 tons per day are in pipeline.
Energy Use
Main source of energy used in Cement factories is electricity and coal. Limestone-based units use coal for calcination. Clinker-based units use mainly electricity for grinding. Limestone-based cement plants is very energy-intensive with about 48% of energy cost on production value. In clinker-based units on 5% of the cost is due to energy.
Energy Saving Potential
Saving potentials are estimated to be around 41% and 49%, respectively for limestone and clinker-based industry. In total Nepalese cement units could annually save about NPR 1.5 Billion by using energy-efficient technologies.
Cold Storage Sector
Sector highlights
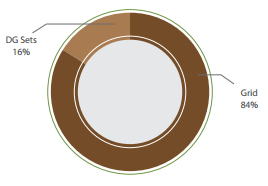
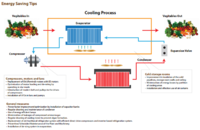
Cold storage units in Nepal are mainly used to store agriculture products such as potatoes, fruits, etc. Few of them store also meat items. There are about 35 cold storage units running in the country with an average size of 3,000 metric tons. The electricity price for cold storage is subsidized by 50%.Energy Use
Cold storage units use only electricity that is provided by Nepal Electricity Authority (NEA). During power outage (load shedding) power is supplied through Diesel based backup systems. Electricity is mainly consumed for the cooling process. Energy cost on product value in cold storage sector is estimated to be 38%.
Energy Saving Potential
Energy Saving potentials are around 20% which is equivalent to 1,800 Megawatt hours annually. By going energy-efficient cold storage units could save about NPR 13 Million on energy cost every year.
Hotel Sector
Sector highlights
Energy Use
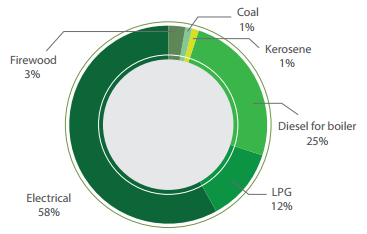
Hotels in Nepal use electricity as well as thermal energy in form of diesel, and LPG. Major energy is consumed for refrigeration, air conditioning, lighting, steam and hot water and cooking. Increased hours of scheduled power outage (called load shedding) has increased the energy costs in hotels due to the fact that they have to run diesel-based backup systems. Small and no-star hotels are unable to provide air conditioning service during power outage resulting in lower occupancy. Main source of energy is still electricity followed by diesel, and LPG.
Energy Saving Potential
About 8% of product value is spend on energy in hotels. Saving potentials are estimated to be 39% whereas 65% for electrical and 16% for thermal energy. In total the hotel sector could save a total amount of NPR 360 Million every year by implementing energy efficiency measures.
Pulp and Paper Sector
Energy use
Energy saving potentials
Soap Sector
Energy use
Energy saving potentials
Steel and Metal Sector
Energy use
Energy saving potentials
Dairy Sector
Energy use
Energy saving potentials
References
- ↑ NEEP, 2012: Baseline Study of Selected Sector Industries to assess The Potentials for more Efficient use of Energy. Prepared by PACE Nepal for Nepal Energy Efficiency Programme (NEEP) of the Water and Energy Commission Secretariat (WECS), supported by German Development Cooperation GIZ. Retrieved from: http://wecs-neep.gov.np/downloadthis/120220_baseline_report.pdf