Mali Energy Situation
Situation analysis and framework conditions
The energy supply in Mali is very low. The newest offical energy balance available shows that only 2,929 ktoe were consumed in 2000. Thereof 85% are used as traditional sources (e.g. firewood), 14% are oil and petrol products and the electricity consumption only accounts 1% of the total energy consumption.
Energy situation especially in rural areas
Energy demand and supply in the household sector
Households (mostly rural poor) consume 86% of Mali’s energy, (road) transport 10%, industry (mainly mining) 3% and agriculture 1% (2003 figures). 80 % of total energy consumption is based on firewood and charcoal (increasing by 3% and 10% annually, respectively). Oil products account for 16% (annual increase 10%), placing a heavy financial burden on the national economy which is wholly dependent on oil imports. Electricity accounts for only 3% of Mali’s energy consumption and less than 20% of the total population are connected to the national grid. Mali's power grid covers only a few urban areas, leaving more than 97% of the rural population without access to electricity. However, only fractions of Mali’s huge renewable power generating potential (hydro, solar) are exploited. In recent years, the necessity of tapping these resources for rural electrification was clearly identified.
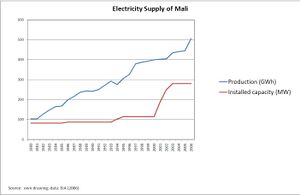
The total electricity generation in 2006 was about 505 GWh and the installed capacity was 280 MW. Since 1980 the consumption increased constantly, while the installed capacity of all plants remained in the 1980s and 1990s at the same level. Recently at the beginning of the new century the pattern changed and new production facilities were build (see graph).
EDM, the state energy utility, is expected to reach only 60 urban locations through the national grid.
Rural electricity supply
The existing national electrification policies are not yet ready to close the existing energy gap: EDM, the state energy utility, is expected to reach only 60 urban locations through the national grid. Mali's Agency for Domestic Energy and Rural Electrification (AMADER), whose rural electrification strategy focuses on the creation of a private sector in which public/private partnerships on a local level should take a lead role in the rural electrification process, seems to be completely surpassed by the task to provide the off-grid majority of over 700 rural communes (11.000 villages) with access to electricity.
Both central state institutions have neither the capacity nor the resources to achieve their national goal. Most remote rural areas will not be targeted and even if there are no local capacities available who could implement the ambitious programmes. They also insufficiently interlink electricity provision with decentralisation politics and; fail to involve the local municipalities in planning and running the energy facilities which is crucially important to ensure their long-term sustainability. Without tapping this potential of participatory communal development, the national goal of reaching 12% rural electrification rate by 2012 and 55 % by 2015 will be out of reach.
The national goal of reaching 12% rural electrification rate by 2012 and 55 % by 2015 is out of reach.
Institutional set up and actors in the energy sector
Public institutions
Electricity companies
Non governmental service providers for rural areas in the field of energy
Micro-Finance Institutions:
Policy framework
Poverty reduction strategy
The Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper (PRSP) was adopted by the previous Government in May 2002 and then reconfirmed by the new Government (GoM) in October 2002. The paper names three main as well as one pre-requisite pillar:
- Pre-Requisite Pillar: Accelerated and Re-Distributive Growth
- Pillar 1: Promote institutional development while improving governance and participation.
- Pillar 2: Develop human resources and improve access to quality basic services.
- Pillar 3: Develop basic infrastructure and productive sectors.
Energy policy
In 1999, the Government of Mali (GoM) issued a policy letter with the following goals:
- sector liberalization, allowing initiatives from communities and the private sector;
- institutional reforms to orient the State’s responsibility to activities of strategic and regulatory nature; *valorization of national energy resources (renewable energy, hydroelectricity);
- protection of forestry resources through sustainable exploitation benefiting rural populations;
- pursuing petroleum research. The goal is improved sector efficiency, a withdrawal of the public sector from operations, and to extend service coverage.
To that end, the GoM has restructured the sector by adopting a new Electricity Law and its implementation texts, which ends EDM’s monopoly and has openedn the sector to competition, under a regime of transparent regulation by an independent agency. Reform processes and institutions need to be strengthened to foster a lasting competitive business environment attractive to private investors and operators. The imperative to provide energy services to the poor calls for a spectrum of energy services, innovative service delivery mechanisms, with participation by communities, NGOs and the private sector.