Sierra Leone Energy Situation
Capital:
Freetown
Region:
Coordinates:
8.4844° N, 13.2344° W
Total Area (km²): It includes a country's total area, including areas under inland bodies of water and some coastal waterways.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.
Population: It is based on the de facto definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship--except for refugees not permanently settled in the country of asylum, who are generally considered part of the population of their country of origin.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Rural Population (% of total population): It refers to people living in rural areas as defined by national statistical offices. It is calculated as the difference between total population and urban population.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
GDP (current US$): It is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. It is calculated without making deductions for depreciation of fabricated assets or for depletion and degradation of natural resources.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.2 ()
GDP Per Capita (current US$): It is gross domestic product divided by midyear population
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Access to Electricity (% of population): It is the percentage of population with access to electricity.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Energy Imports Net (% of energy use): It is estimated as energy use less production, both measured in oil equivalents. A negative value indicates that the country is a net exporter. Energy use refers to use of primary energy before transformation to other end-use fuels, which is equal to indigenous production plus imports and stock changes, minus exports and fuels supplied to ships and aircraft engaged in international transport.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption (% of total): It comprises coal, oil, petroleum, and natural gas products.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Introduction
Very few people have access to electricity in Sierra Leone: Approximately 10% to 12% of the urban population and only around 2% of the rural population. Petrol or diesel generators are often used because most of the region lacks a stable public power supply. Kerosene, battery lamps or candles are mainly used for lighting. Many people cook with firewood or charcoal. There is significant potential for the use of renewable energy, particularly solar energy and hydroelectric power.
Energy Situation/Statistics
“Energy statistics are difficult to obtain in Sierra Leone, especially for renewable energy. Although the conventional thermal energy production and consumption patterns have been reported, no consolidated set of statistics exists for the total Energy situation of Sierra Leone. The figures presented in this document should be regarded as indicative of the orders of magnitude rather than as precise consumption figures.” [1]
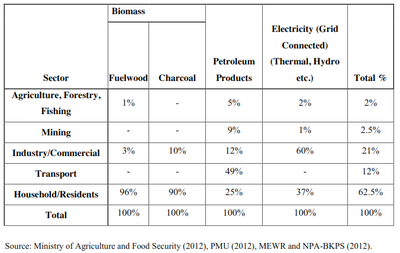
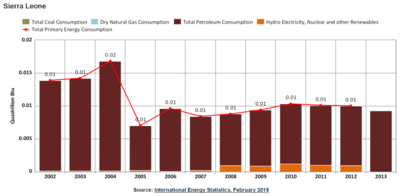
Overall Energy
- 80% Biomass (mainly for cooking)
- Wood Fuel
- Charcoal
- Wood Fuel
- 13% Petroleum products (mainly for transport, lighting and private energy generation)
- All petroleum is impohttps://energypedia.info/skins/common/images/button_bold.pngrted
- All petroleum is impohttps://energypedia.info/skins/common/images/button_bold.pngrted
- Grid connected energy accounts for the remaining energy
- Most of the energy is used in households
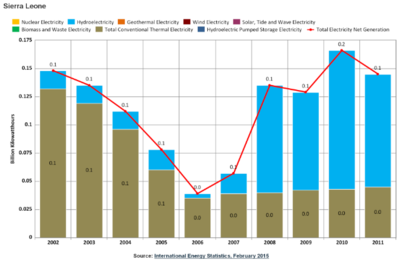
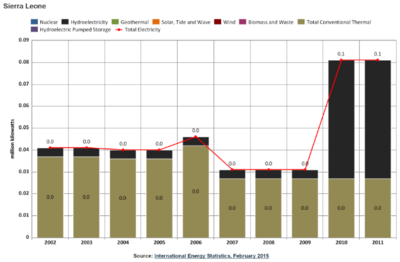
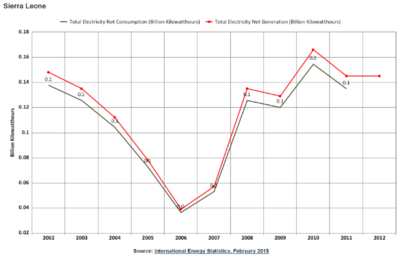
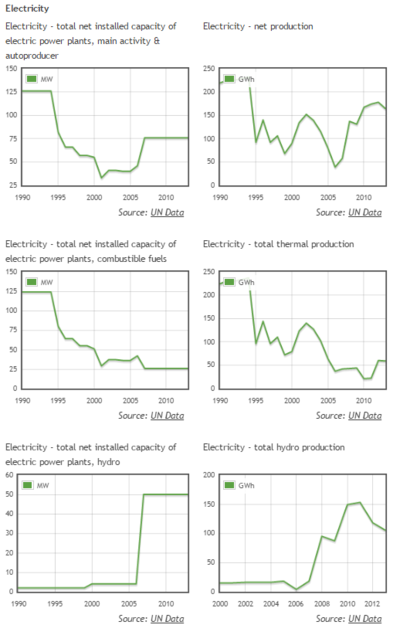
Electricity Generation
- 81,000 kW installed capacity (2012)
- Zero imports, zero exports
- 33.3% Fissile Fuels (44 MW from Oil)
- 66.7% Hydro Power (56 MW)
- Only 12% of the population has access to electricity (in rural areas only around 2%)
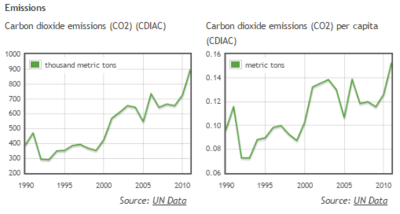
Graphics
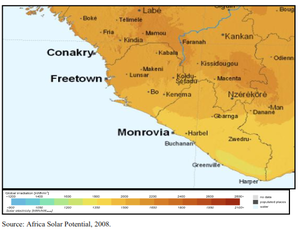
Renewable Energy
“The country possesses vast potential in renewable energy in the form of biomass from agricultural wastes, hydro and solar power, which remain virtually untapped.” [7]
Hydro Power:
- Current capacity: 56 MW
- Capacity still available for expansion: 755 MW
Biomass
Capacity still available for expansion: 115 MW
- Agrocultural resedues
- Palm Oil Products
- Ethanol
Solar
|
Fossil Fuel
Key Problems of the Energy Sector
- Financing/Investment
- Building up Infrastructure (Transmission and Distribution Networks)
- Many parts of the country have no grid access
- Network is very old (50 years) and many distribution lines were destroyed during the civil war
- This has led to large private sector generation, especially in industry. Many companies are forced to rely on diesel generators
- Generation capacity does not cover the demand
- Poor Energy Efficiency (both in terms of electricity generation and distribution as well as with biofuels/kerosene used for cooking and lighting)
- Old equipment
- No energy audits/benchmarking
- Inefficient cooking stoves + kerosene lights
Policy Framework, Laws and Regulations
“Improving the country’s energy sector is one of the Government’s foremost objectives …The Government is committed to working with the private sector, International Energy Development Programmes and the donor community to achieve these essential improvements.” [12]
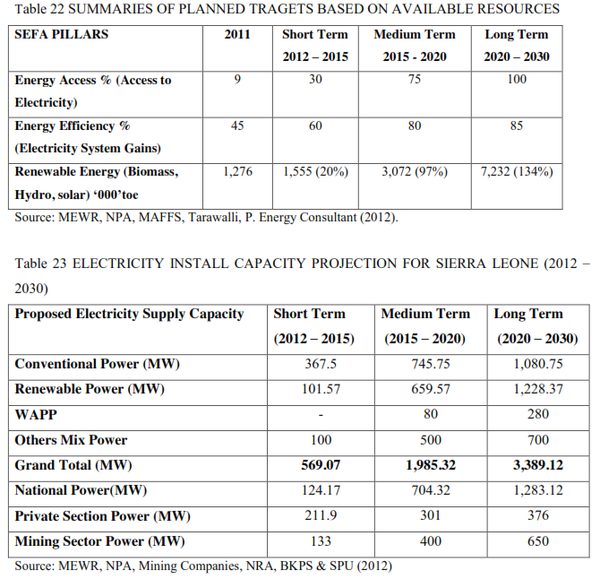
Future Targets
Institutional Set up in the Energy Sector
Further Information
- A much more detailed report on the energy situation is provided in the National Energy Profile of Sierra Leone, published by the UN in 2012
- For a full overview of energy policies see: Sierra Leone Energy Africa Compact, published by Energy Africa
- Useful IRENA mapping tool for seeing the wind and solar potential in Sierra Leone
References
- ↑ UNDP, 2012. National Energy Profile pf Sierra Leone, s.l.: UNDP.
- ↑ UNDP, 2012. National Energy Profile pf Sierra Leone, s.l.: UNDP.
- ↑ Taylor, S. & Buya-Kamara, Z., 2013. Sierra Leone Energy Africa Compact, Freetown: Energy Africa.
- ↑ UNDP, 2012. National Energy Profile pf Sierra Leone, s.l.: UNDP.
- ↑ U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2015. International Energy Statistics. [Online] fckLRAvailable at: http://sierraleone.opendataforafrica.org/search?query=energyfckLR[Accessed 17 June 2016].
- ↑ UNDP, 2012. National Energy Profile pf Sierra Leone, s.l.: UNDP.
- ↑ UNDP, 2012. National Energy Profile pf Sierra Leone, s.l.: UNDP.
- ↑ Miketa, A. & Bruno Merven, B., 2013. West African Power Pool: Planning and Prospects for Renewable Energy, s.l.: IRENA.
- ↑ Miketa, A. & Bruno Merven, B., 2013. West African Power Pool: Planning and Prospects for Renewable Energy, s.l.: IRENA.
- ↑ Miketa, A. & Bruno Merven, B., 2013. West African Power Pool: Planning and Prospects for Renewable Energy, s.l.: IRENA.
- ↑ UNDP, 2012. National Energy Profile pf Sierra Leone, s.l.: UNDP.
- ↑ UNDP, 2012. National Energy Profile pf Sierra Leone, s.l.: UNDP.