Wind Turbine Technology
 |
This article needs to be revised. Please rewrite the article according to the specifications below. Only remove this maintenance box after a thorough revision of this article. See the discussion page for more details or start a discussion there. In particular the following aspects and passages have been specified to be in need for a revision: |
Introduction
Wind Turbine Control Concepts
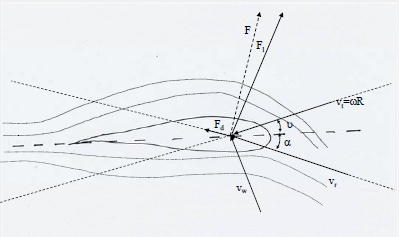
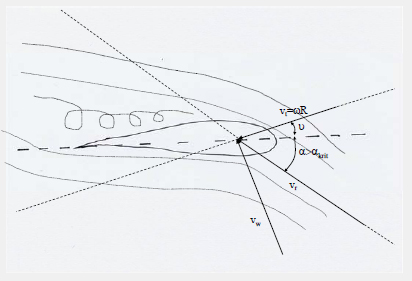
Aerodynamics
Stall
Stall Control:
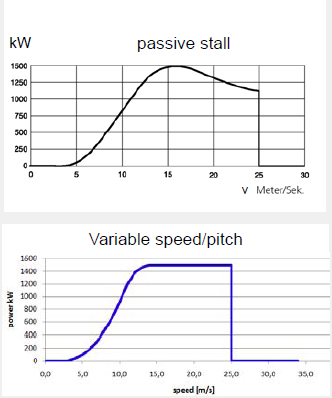
Passive Stall
Power of the wind turbine is limited by the aerodynamic characteristics of the turbine.
Active Stall
Power of the wind turbine is limited additionally by decreasing the pitch angle (increasing the inflow angle ).
Pitch
Pitch Control:
- Power of the wind turbine is limited by increasing the pitch angle (decreasing the inflow angle α)
Wind Turbine Operation
Operation of Fix Speed Wind Turbine (Passive Stall)
- Start up (with open breaker) if wind speed > cut-in wind speed
- Close breaker
- Operation at constant blade angle over the whole wind speed range
- In case of large wind speeds: Power limited by aerodynamic profile.
Operation of Variable Speed Wind-Turbines
Start up (with open breaker) if wind speed > cut-in wi
nd speed
• Close breaker
• Below rated wind-speed
– Maximum power coefficient (Max. Power Tracking)
– Evt: Speed Limitation
• Above rated wind-speed:
– P=Pr
ated (Limited by power electronics converter)
– Pitching
• Advantages of variable speed operation:
– Lower cut-in wind speeds
– Higher efficiency, especially at low wind speeds
– Lower power variations (compared to fixed speed turbines)
• Disadvantage: More expensive!
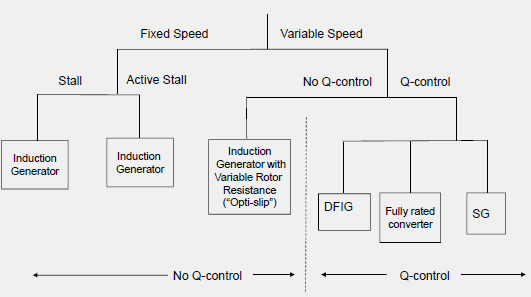
Generator Concepts
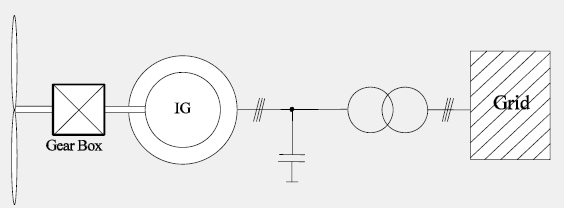
Fixed Speed Induction Generator
Only fix speed operation possible (stall control required)
• Reactive power compensation required
• No reactive power control capability. Additional devices required:
– TSCs (Thyristor switched capacitors)
– STATCOMs
• Risk of dynamic voltage collapse
GTZ Expert Workshop 2010: Grid and System Integration of Wind Energy, 22/23.11.2010, Berlin/Germany
y g p
– > Typically, wind generators based on induction generators are asked to
disconnect in case of voltage dips
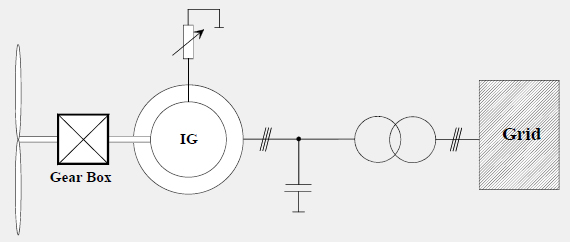
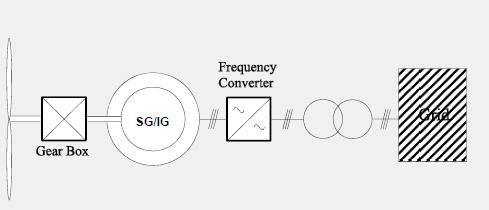
Induction Generator with Variable Rotor Resistance
Simple concept for variable speed operation.
• Reactive power compensation required.
• No reactive power control capability. Additional devices required:
– TSCs (Thyristor switched capacitors)
– STATCOMs
• Limited LVRT capability. Dynamic voltage collapse problems have to
GTZ Expert Workshop 2010: Grid and System Integration of Wind Energy, 22/23.11.2010, Berlin/Germany
be mitigated by:
– Fast increase of rotor resistance during faults
– Additional reactive power compensation devices (typically TSCs)
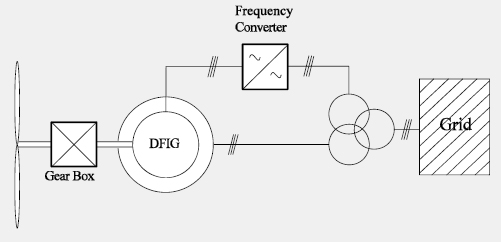
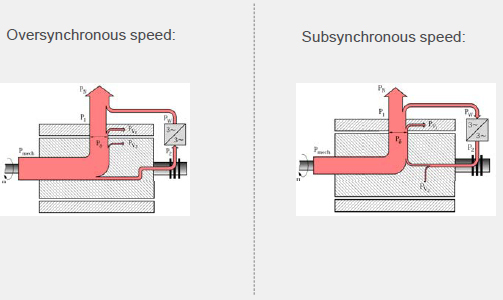
Doubly-Fed Induction Generator
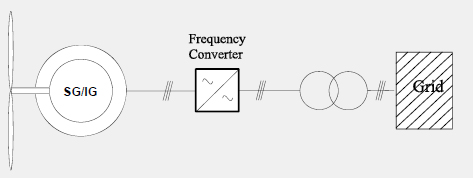
Generator with Fully Rated Converter
Generator with Fully Rated Converter and Direct Drive
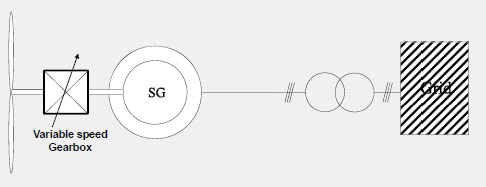
Directly Coupled Synchronous Generator with Variable Gear Box
References
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[1]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[2]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[3]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[4]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[5]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[6]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[7]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[8]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[9]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[10]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[11]]
- ↑ Weigel S., Poeller M. (2010) Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs) Physical Principals and Generator Concepts, Presentation prepared by DigSILENT GmbH for the Wind Energy and Development Dialogue 2010, retrieved 27.8.2011 [[12]]