Click here to register!
Difference between revisions of "Egypt Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| (156 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{CES Country|CES Country Name=Egypt | {{CES Country|CES Country Name=Egypt | ||
|CES Country Capital=Cairo | |CES Country Capital=Cairo | ||
| − | |CES Country Region=Middle East & North Africa | + | |CES Country Region Middle East and North Africa=Middle East & North Africa |
|CES Country Coordinates=26.0000° N, 30.0000° E | |CES Country Coordinates=26.0000° N, 30.0000° E | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == Energy | + | <br/> |
| + | |||
| + | = Introduction = | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Arab Republic of Egypt is located in North Africa and borders with Libya in the West, Sudan in the South and Palestinian territories and Israel in the East, while in the North, it is washed by the Mediterranean. Its population is mainly concentrated along the river Nile, as the rest of the country's territory is largely desert. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Most parts of the country have a hot desert climate with extreme heat occurring during summer. An exception is the northern Mediterranean coast which receives more rainfall during winter and has a generally more moderate climate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Egypt's Map.png|thumb|center|600px|Fig.1: Map of Egypt showing Examples of N.G. & C.O. Pipelines, Ports, Fields..etc (EIA, 2018)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypty is a country with a high potential of natural resources: precious stones, natural gas, oil, coal and large reserves of fossil fuel enery sources; approximately 4189 billion barrels of oil reserves and an estimated 77200 billion cubic meters of natural gas resreves, as the reserves are in the form of both mainland and coastal deposits<ref name="Obukhov. S. & Ibrahim A. (2017). Analysis of the Energy Potential of Renewable Energy Sources Egypt. MATEC Web Conference 141, 01035. Retrieved From: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2017/55/matecconf_smartgrids2017_01035.pdf">Obukhov. S. & Ibrahim A. (2017). Analysis of the Energy Potential of Renewable Energy Sources Egypt. MATEC Web Conference 141, 01035. Retrieved From: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2017/55/matecconf_smartgrids2017_01035.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | While more than 90% of the Egyptian generated electricity comes only from oil and natural gas, the major problem that Egypt encounters, especially in the energy-sector is the dynamic growth of population, which is estimated by around 1.3% per year, consequently increasing demand, which eventually fastens the rate of depleting the country's major resources<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref><ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Obukhov. S. & Ibrahim A. (2017). Analysis of the Energy Potential of Renewable Energy Sources Egypt. MATEC Web Conference 141, 01035. Retrieved From: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2017/55/matecconf_smartgrids2017_01035.pdf">Obukhov. S. & Ibrahim A. (2017). Analysis of the Energy Potential of Renewable Energy Sources Egypt. MATEC Web Conference 141, 01035. Retrieved From: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2017/55/matecconf_smartgrids2017_01035.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), it is the largest non-OPEC oil producer in Africa and the third largest dry natural gas producer on the continent, following Algeria & Nigeria<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The country also represents a vital role-player in the international energy market, as a major transit route, by operating the Suez Canal and the Suez Mediterranean Pipleline (SUMED)<ref name="http://www.iea.org/statistics/statisticssearch/report/?year=2011&country=EGYPT&product=Balances">http://www.iea.org/statistics/statisticssearch/report/?year=2011&country=EGYPT&product=Balances</ref>, through which the oil is shipped from the Persian Gulf to Europe and the United States<ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Energy Situation = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Historical Background and an Overview of the Main Energy Sources == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypt has been known to mainly depend, in all its energy-related activities, on three major sources: oil, natural gas and the hydroelectric power generated from the large dam projects over the Nile: the High Dam, Aswan I & Aswan II<ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref><ref name="United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). (2017). Energy Profile: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/20490/Energy_profile_Egypt.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y">United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). (2017). Energy Profile: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/20490/Energy_profile_Egypt.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y</ref>.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
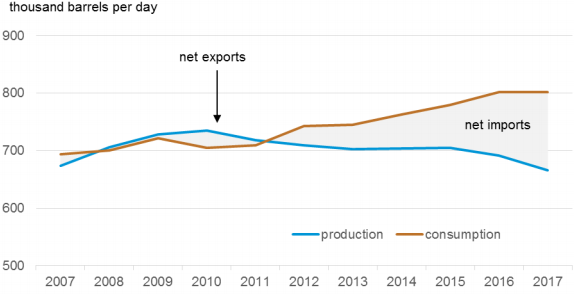
| + | Despite being a major producer and net exporter of oil, especially in the 1990s, when its oil production peaked, reaching approximately over 900000 bbl/day, Egypt has become a net oil importer around 2009/2010<ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref>. Thus can be traced back to both economic and population accelerated growth, which accompanied the beginning of the new millennium, leading to an increase in consumption by about 3% per year, resulting in growing of demand, and falling in production, that could roughly meet consumption requirements, resulting in a significant drop in the country’s oil refinery output since 2009<ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | During the period of the late 1990s/early 2000s, Egypt has witnessed a state of proliferation of discovering and exploiting huge natural gas reserves around the country, which drove the country to emerge as a key role player in the region as a natural gas producer and exporter<ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref>. Mainly, due to the same reason as in oil, consumption of natural gas has approximately increased by 7% per year during the first decade of 2000s, and production has noticeably decreased by around 3% yearly during the period of 2009-2013, consequently limiting its natural gas exporting capacity to only 5% of its total production by 2013, and eventually driving the country to start signing importing agreements in the following years of 2014 and 2015<ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref>.<br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.1: General Statistics on Oil & Natural Gas Situation in Egypt<ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:757px;" align="center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | <span style="font-weight: 700; text-align: center; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Oil</span><br/> | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | <span style="font-weight: 700; text-align: center; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Natural Gas</span><br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Total Production | ||
| + | | 680,000 bbl/day | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | 2 trillion cubic feet/day | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Global Production-Share<br/> | ||
| + | | 0.72%<br/> | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | 1.7%<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Proven Reserves<br/> | ||
| + | | 3,900,000,000 bbl<br/> | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | 65.3 trillion cubic feet<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Global Proven Reserves-Share<br/> | ||
| + | | 0.2%<br/> | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | 1% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | % Total Domestic Consumption<br/> | ||
| + | | 41% | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | 53% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Imports | ||
| + | | 80,000 bbl/day<br/> | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | To Be Updated | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Exports | ||
| + | | 189,000 bbl/day<br/> | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | 0.1 trillion cubic feet/year<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | | ||
| + | Export Destinations | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | EU (56%), India (28%), China (13%), Others (3%) | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="width: 276px;" | | ||
| + | EU (56%), India (28%), China (13%), Others (3%) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to reports from American Security Project (ASP) and United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), Egypt has produced approximately 13.2-13.7 billion kilowatt-hours (KWh) of electricity, using hydropower in the period 2012/2013<ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref><ref name="United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). (2017). Energy Profile: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/20490/Energy_profile_Egypt.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y">United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). (2017). Energy Profile: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/20490/Energy_profile_Egypt.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y</ref>.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hydropower accounts for about 9% of the total country’s power generation, and around 3% of the country’s total energy consumption, however, the majority of the Nile hydropower’s capacity in Egypt has already been exploited and is declining<ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref><ref name="United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). (2017). Energy Profile: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/20490/Energy_profile_Egypt.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y">United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). (2017). Energy Profile: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/20490/Energy_profile_Egypt.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Energy Access == | ||
| + | |||
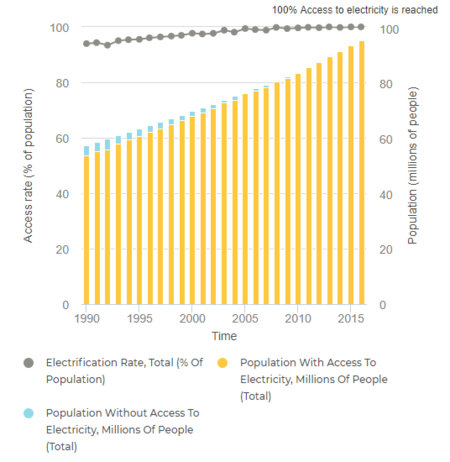
| + | According to the latest Tracking SDG7 Report on The Energy Progress, that was jointly prepared by:International Energy Agency (IEA), International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), United Nations Statistics Division, World Bank Group and World Health Organization, the state of energy access through Egypt is illustrated through the following table and figures<ref name="Tracking SDG7. (2018). The Energy Progress Report. Retrieved From: https://trackingsdg7.esmap.org/data/files/download-documents/tracking_sdg7-the_energy_progress_report_full_report.pdf">Tracking SDG7. (2018). The Energy Progress Report. Retrieved From: https://trackingsdg7.esmap.org/data/files/download-documents/tracking_sdg7-the_energy_progress_report_full_report.pdf</ref>:<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Egypt Electricity Access (Total).png|thumb|center|450px|Fig.2: Total Energy Access in Egypt 1990-2015 (Tracking SDG7, 2018)|alt=Fig.2: Total Energy Access in Egypt 1990-2015 (Tracking SDG7, 2018)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The report shows that since around 2014/2015, the total Egyptian population has had access to reliable energy sources, and only 2% of the whole population has no access to clean cooking<ref name="Tracking SDG7. (2018). The Energy Progress Report. Retrieved From: https://trackingsdg7.esmap.org/data/files/download-documents/tracking_sdg7-the_energy_progress_report_full_report.pdf">Tracking SDG7. (2018). The Energy Progress Report. Retrieved From: https://trackingsdg7.esmap.org/data/files/download-documents/tracking_sdg7-the_energy_progress_report_full_report.pdf</ref>.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
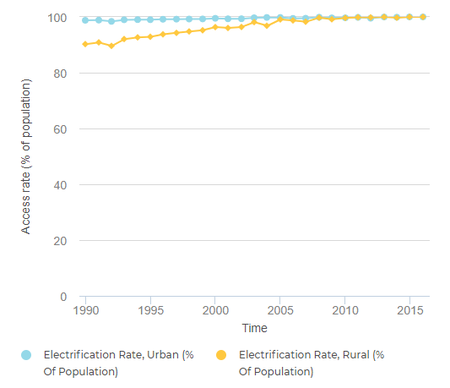
| + | [[File:Egypt Electricity Access (Urban & Rural).png|thumb|center|450px|Fig.3: Urban & Rural Energy Access in Egypt 1990-2015 (Tracking SDG7, 2018)|alt=Fig.3: Urban & Rural Energy Access in Egypt 1990-2015 (Tracking SDG7, 2018)]]<br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.2: Percentage of Egyptian Population's Access to Electricity & Clean Cooking<ref name="Tracking SDG7. (2018). The Energy Progress Report. Retrieved From: https://trackingsdg7.esmap.org/data/files/download-documents/tracking_sdg7-the_energy_progress_report_full_report.pdf">Tracking SDG7. (2018). The Energy Progress Report. Retrieved From: https://trackingsdg7.esmap.org/data/files/download-documents/tracking_sdg7-the_energy_progress_report_full_report.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" colspan="1" scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! rowspan="1" colspan="2" scope="col" | Access to | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Electricity | ||
| + | ! rowspan="1" colspan="2" | Clean Cooking<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | % of Population | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center;" | 100% | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center;" | 98% | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span style="background-color: initial; font-size: 19.04px;">Production </span>== | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.3: Egypt’s Production of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe<ref name="African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf">African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2012 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2013 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2014 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Coal | ||
| + | | 20 | ||
| + | | 14 | ||
| + | | 0 | ||
| + | | 0 | ||
| + | | 0 | ||
| + | | 0 | ||
| + | | 0 | ||
| + | | 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Crude Oil | ||
| + | | 33189 | ||
| + | | 30111 | ||
| + | | 32142 | ||
| + | | 29537 | ||
| + | | 32825 | ||
| + | | 33210 | ||
| + | | 30835 | ||
| + | | 31885 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Natural gas | ||
| + | | 18555 | ||
| + | | 35901 | ||
| + | | 54839 | ||
| + | | 50143 | ||
| + | | 39084 | ||
| + | | 34763 | ||
| + | | 34763 | ||
| + | | 35362 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Electricity from Fossil Fuels | ||
| + | | 5302 | ||
| + | | 8211 | ||
| + | | 12250 | ||
| + | | 12250 | ||
| + | | 13431 | ||
| + | | 14355 | ||
| + | | 14514 | ||
| + | | 14679 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Hydro Electricity | ||
| + | | 1260 | ||
| + | | 1087 | ||
| + | | 1112 | ||
| + | | 1113 | ||
| + | | 1188 | ||
| + | | 1155 | ||
| + | | 1171 | ||
| + | | 1187 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Electricity from Renewables | ||
| + | | 12 | ||
| + | | 47 | ||
| + | | 139 | ||
| + | | 139 | ||
| + | | 145 | ||
| + | | 137 | ||
| + | | 150 | ||
| + | | 165 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Refinery/Oil Porducts | ||
| + | | 23449 | ||
| + | | 28561 | ||
| + | | 24754 | ||
| + | | 21836 | ||
| + | | 25348 | ||
| + | | 25676 | ||
| + | | 26357 | ||
| + | | 270565 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Installed Capacity == | ||
| + | |||
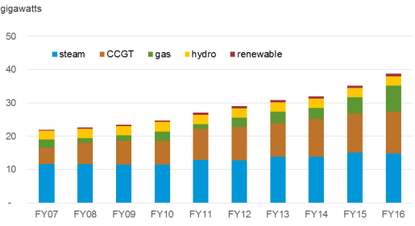
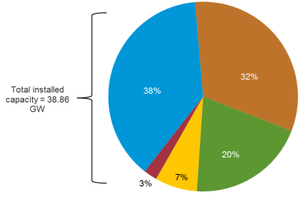
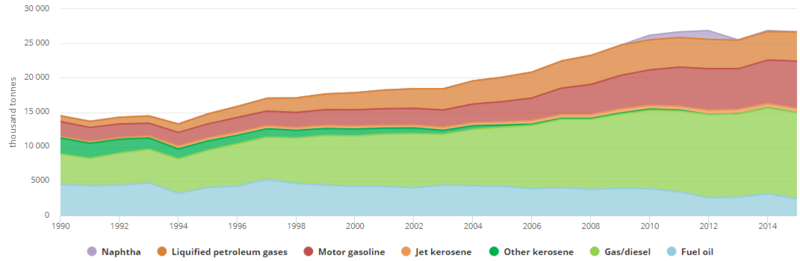
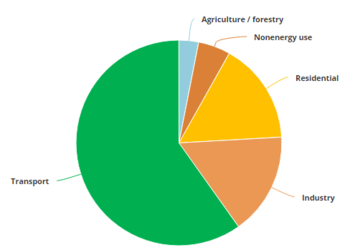
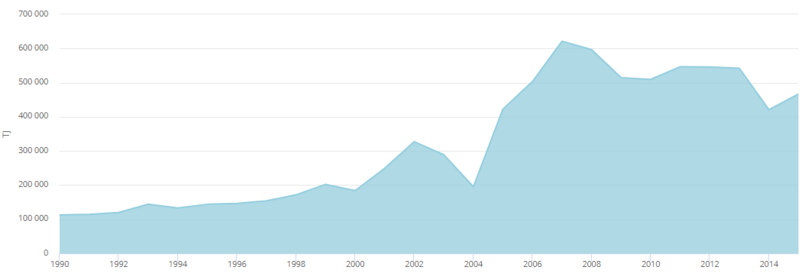
| + | With accordance to the EIA's report on Egypt (2018), the following graph and pie-chart highlight the installed capacity of different energ sources in the country from 2007-2016 in terms of fiscal years. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="width: 100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width: 423.078px;" | [[File:Installed Capacity of different fuels per fiscal years' Graph.png|thumb|center|415px|Fig.4: Egyptian Installed Capacity of Different Energy Sources per Fiscal Year 2007-2016 (EIA, 2018)|alt=Fig.4: Egyptian Installed Capacity of Different Energy Sources per Fiscal Year 2007-2016 (EIA, 2018)]]<br/> | ||
| + | | style="width: 7px;" | | ||
| + | | style="width: 321px;" | [[File:Installed Capacity of different fuels in the fy 2015-16 piechart.png|thumb|center|301px|Fig.5: Egyptian Installed Capacity of Different Energy Sources by the Fiscal Year 2015-2016 (EIA, 2018)|alt=Fig.5: Egyptian Installed Capacity of Different Energy Sources by the Fiscal Year 2015-2016 (EIA, 2018)]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Consumption == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypt is by far the largest consumer of oil and natural gas in Africa, showing 22% of petroleum and other liquids of the continent's total consumption and 37% of its dry natural gas consumption<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The main drivers of the rapid growth of the country's consumption of oil and natural gas can be summarized in the follwoing<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>: | ||
| + | |||
| + | #The increased industrial output. | ||
| + | #Economic growth. | ||
| + | #Intense extraction projects of oil and natural gas. | ||
| + | #Population growth. | ||
| + | #The inclining rate of private and commercial vehicle sales. | ||
| + | #The generous subsidy policy, that is focused on energy products. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Through this sub-chapter, different consumption data will be presented, using different sources, to get a holistic view as possible of the energy consumption situation in the country. | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.4: Egypt’s Primary Energy Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Rate | ||
| + | | 7.8 | ||
| + | | 10.5 | ||
| + | | 28 | ||
| + | | 37.3 | ||
| + | | 48.4 | ||
| + | | 60.5 | ||
| + | | 78.4 | ||
| + | | 84.4 | ||
| + | | 88.2 | ||
| + | | 91.6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.5: Egypt’s Primary Energy Consumption by Fuel 2016-2017 Mtoe<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Oil | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Natural Gas | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Coal | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Nuclear | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Hydro-Electric | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Renewables | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Total | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | 2016 | ||
| + | | 42 | ||
| + | | 42.4 | ||
| + | | .2 | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | 3 | ||
| + | | .6 | ||
| + | | 88.2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | 2017 | ||
| + | | 39.7 | ||
| + | | 48.1 | ||
| + | | .2 | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | 3 | ||
| + | | .6 | ||
| + | | 91.6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.6: Egypt’s Final Consumption of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe<ref name="African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf">African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2012 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2013 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2014 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Coal | ||
| + | | 453 | ||
| + | | 203 | ||
| + | | 204 | ||
| + | | 188 | ||
| + | | 188 | ||
| + | | 200 | ||
| + | | 211 | ||
| + | | 224 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Oil | ||
| + | | 17898 | ||
| + | | 20156 | ||
| + | | 27009 | ||
| + | | 22573 | ||
| + | | 26333 | ||
| + | | 35213 | ||
| + | | 36086 | ||
| + | | 37028 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Natural Gas | ||
| + | | 4274 | ||
| + | | 9182 | ||
| + | | 12719 | ||
| + | | 18202 | ||
| + | | 19505 | ||
| + | | 20956 | ||
| + | | 21446 | ||
| + | | 21960 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Electricity | ||
| + | | 5559 | ||
| + | | 7918 | ||
| + | | 12060 | ||
| + | | 12324 | ||
| + | | 12306 | ||
| + | | 12668 | ||
| + | | 13134 | ||
| + | | 13630 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.7: Egypt’s Industrial Consumption of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe<ref name="African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf">African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2012 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2013 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2014 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Oil | ||
| + | | 5461 | ||
| + | | 5548 | ||
| + | | 3716 | ||
| + | | 3279 | ||
| + | | 3133 | ||
| + | | 6369 | ||
| + | | 6713 | ||
| + | | 7080 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Natural Gas | ||
| + | | 2072 | ||
| + | | 5567 | ||
| + | | 6649 | ||
| + | | 6789 | ||
| + | | 8002 | ||
| + | | 9083 | ||
| + | | 9303 | ||
| + | | 9536 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Electricity | ||
| + | | 2111 | ||
| + | | 2812 | ||
| + | | 3430 | ||
| + | | 3500 | ||
| + | | 3288 | ||
| + | | 369 | ||
| + | | 3488 | ||
| + | | 3612 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Coal | ||
| + | | 453 | ||
| + | | 203 | ||
| + | | 204 | ||
| + | | 188 | ||
| + | | 188 | ||
| + | | 200 | ||
| + | | 211 | ||
| + | | 224 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.8: Egypt’s Transport Consumption of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe<ref name="African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf">African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2012 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2013 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2014 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Oil | ||
| + | | 9060 | ||
| + | | 9371 | ||
| + | | 15547 | ||
| + | | 12362 | ||
| + | | 16416 | ||
| + | | 16892 | ||
| + | | 17098 | ||
| + | | 17312 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Electricity | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | 44 | ||
| + | | 44 | ||
| + | | 45 | ||
| + | | 46 | ||
| + | | 46 | ||
| + | | 47 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | + | ||
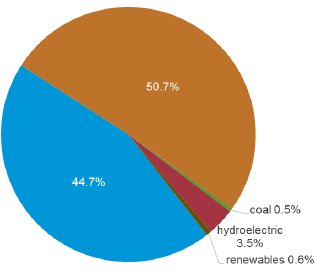
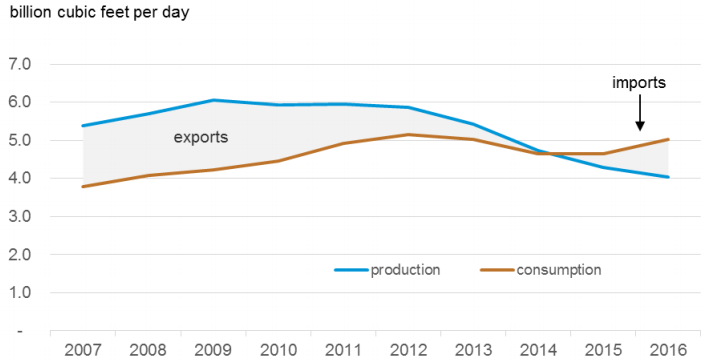
| − | === | + | [[File:Egyptian Primary Energy Consumption by 2016 accoding to EIA's Report.png|thumb|center|316px|Fig.6: A Pie-Chart of the Egyptian Primary Energy Consumption in the Year 2016 (EIA, 2018)]] |
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Import and Export == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypt is a net exporter of crude oil and natural gas, however, the combination of increasing consumption and declining production has led to a decline in natural gas exports since 2009, as the government started to divert natural gas supplies from exports, in order to satisfy domestic demand, eventually turning the country into a natural gas importer since 2015<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In terms of coal and peat, Egypt is a net importer, and coal imports are even expected to increase in the short-medium term, since the Egyptian government has approved the industrial use of coal in April 2014, and in the same year signed a construction deal for the first coal-fired power in the country. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Subsidies === | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 2013, the Egyptian government spent 120 billion Egyptian pounds (about 13.8 billion EUR) on fuel subsidies, which equals 7% of the GDP<ref name="http://www.iisd.org/GSI/sites/default/files/ffs_egypt_update_august_2014.pdf">http://www.iisd.org/GSI/sites/default/files/ffs_egypt_update_august_2014.pdf</ref>. These costs in combination with economic stagnation have contributed to the increasing deficit, which reached about 12% of GDP in 2013. In order to alleviate this burden, the Egyptian government announced spending cuts on energy subsidies in June 2014. The Financial Times reported that these subsidies are going to be cut by almost a third <ref name="http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/9da3cb08-007d-11e4-a3f2-00144feab7de.html#axzz3PwcopOCd">http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/9da3cb08-007d-11e4-a3f2-00144feab7de.html#axzz3PwcopOCd</ref>.<br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Electricity == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === General Data === | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><span style="text-align: -webkit-center; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Table.9: The General Electricity Situation in Egypt<ref name="Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (2018). The World FactBook: Africa: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html">Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (2018). The World FactBook: Africa: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html</ref></span><br/></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! rowspan="2" colspan="1" scope="row" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! rowspan="1" colspan="10" scope="col" | Electricity<br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Production | ||
| + | ! <span style="font-weight: 700; text-align: center; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Consumption</span><br/> | ||
| + | ! Exports | ||
| + | ! <span style="font-weight: 700; text-align: center; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Imports</span><br/> | ||
| + | ! <span style="font-weight: 700; text-align: center; background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Installed Generating Capacity</span><br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Rate | ||
| + | | 171.9 billion kWh | ||
| + | | 150.4 billion kWh | ||
| + | | 1.158 billion kWh | ||
| + | | 43 million kWh | ||
| + | | 38.88 million kWh | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | World Ranking | ||
| + | | 24 | ||
| + | | 25 | ||
| + | | 57 | ||
| + | | 106 | ||
| + | | 27 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Electricity Access === | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)'s 2018 report, only around 300,000 people of the whole Egyptian population is currently without access to electricity. | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.10: Electrification Percentages in Egypt<ref name="Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (2018). The World FactBook: Africa: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html">Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (2018). The World FactBook: Africa: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | rowspan="2" colspan="1" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! rowspan="1" colspan="3" | Electrification | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Total Population | ||
| + | ! Urban Areas | ||
| + | ! Rural Areas | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! % | ||
| + | | 99.6 | ||
| + | | 100 | ||
| + | | 99.3 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Installed Capacity and Generation === | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.11: Percentages of Different Electricity-Generating Energy-Sources in Egypt<ref name="Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (2018). The World FactBook: Africa: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html">Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (2018). The World FactBook: Africa: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | rowspan="2" colspan="1" | <br/> | ||
| + | ! rowspan="1" colspan="4" | Electricity Generated From: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width: 146px;" | '''Fossil Fuels''' | ||
| + | | style="width: 148px;" | | ||
| + | '''Nuclear Fuels''' | ||
| − | + | ! Hydroelectric Plants | |
| − | + | ! Other Renewables | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | ! % of the Total Installed Capacity |
| + | | style="width: 146px;" | 90.5 | ||
| + | | style="width: 148px;" | 0 | ||
| + | | 7.3 | ||
| + | | 2.2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | ! World Ranking |
| − | + | | style="width: 146px;" | 58 | |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 148px;" | 83 |
| + | | 125 | ||
| + | | 115 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Between 2011/2012 and 2012/2013, the total installed capacity increased about 6 %, reaching 30,803 MW, due to added thermal plants. The installed capacity development by type of generation since 2008 is outlined in table 12.<br/><br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center"><u>Table 12: Installed capacity development by type of generation (in MW) 2008-2013</u><u><ref name="http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf">http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf</ref></u><br/></p> | ||
| + | {| style="width: 674.39px" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 205.39px" | <br/> |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 147.6px" | 2008/2009 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 84px" | 2009/2010 |
| + | | style="width: 76px" | 2010/2011 | ||
| + | | style="width: 74px" | 2011/2012 | ||
| + | | style="width: 135px" | 2012/2013 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 670px" colspan="6" | MW |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 205.39px" | Renewables |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 147.6px" | 425 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 84px" | 249 |
| + | | style="width: 76px" | 687 | ||
| + | | style="width: 74px" | 687 | ||
| + | | style="width: 135px" | 687 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style="width: 205.39px" | Steam |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 147.6px" | 11,458 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 84px" | 11,458 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 76px" | 12,859 |
| + | | style="width: 74px" | 12,684 | ||
| + | | style="width: 135px" | 13,808 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style="width: 205.39px" | Hydro |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 147.6px" | 2,800 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 84px" | 2,800 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 76px" | 2,800 |
| + | | style="width: 74px" | 2,800 | ||
| + | | style="width: 135px" | 2,800 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style="width: 205.39px" | Combined Cycle |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 147.6px" | 7,178 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 84px" | 7,137 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 76px" | 9,327 |
| + | | style="width: 74px" | 10,077 | ||
| + | | style="width: 135px" | 10,080 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style="width: 205.39px" | Gas |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 147.6px" | 1,641 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 84px" | 2,841 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 76px" | 1,376 |
| + | | style="width: 74px" | 2,826 | ||
| + | | style="width: 135px" | 3,428 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 670px" colspan="6" | <br/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 205.39px" | Total |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 147.6px" | 23,502 |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width: 84px" | 24,762 |
| + | | style="width: 76px" | 27,049 | ||
| + | | style="width: 74px" | 29,074 | ||
| + | | style="width: 135px" | 30,803 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition, Egypt has 30 decentralized power plants, mostly diesel and gas turbine units which are not connected to the national grid. The combined installed capacities of these plants added up to 224 MW in 2012/2013. Approximately 234.5 GWh of electricity were supplied to local users including tourist resorts.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypt is a net exporter of electricity, importing 77 GWh while exporting 474 GWh of electricity in 2012. In 2012/2013, the average percentage of network losses were 11.02%.<ref name="http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf">http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf</ref><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
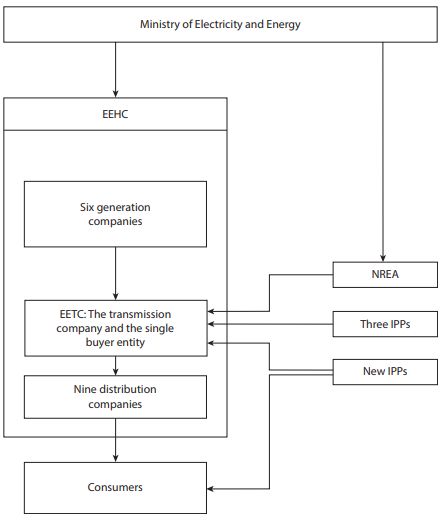
| + | Between 2001 and 2012, electricity production rose from 83,282 GWh to 164,364 GWh. The main source for the production of electricity is gas (66%) followed by hydro (18.2%) and oil (15.6%).<ref name="http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf">http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf</ref> The Egyptian Electricity Holding Company (EEHC) operates with five-year plans. The current one (2012-2017) foresees the installation of 15.000 MW additional capacity. However, due to the increasing demand, the reserve margin is still expected to remain tight.<ref>https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1</ref><br/> | ||
| + | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
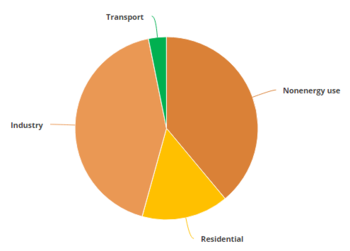
| − | === | + | === Consumption === |
| − | + | ||
| − | <p style="text-align: center | + | The main consumer of electricity in Egypt is the residential sector which accounts for 42% of the total consumption, followed by the industrial sector (28%). The consumption of the residential sector has been steadily increasing in the recent years. According to the Ministry of Electricity and Energy, this is due to two factors: the expansion of residential compounds and new communities as well as the use of domestic appliances, air conditioners in particular, during hot weather. The development of the electricity consumption per sector is outlined in table 13.<br/> |
| − | {| style="width: | + | <p style="text-align: center"><u>Table 13: Electricity consumption by sector (GWh) 2008-2013</u> <ref name="http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf">http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf</ref><br/></p> |
| + | {| style="width: 100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Sector |
| − | + | | 2008/2009 | |
| − | + | | 2009/2010 | |
| − | + | | 2010/2011 | |
| − | + | | 2011/2012 | |
| − | + | | 2012/2013 | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | colspan="6" | GWh |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Industries |
| − | | | + | | 37,273 |
| − | | | + | | 38,916 |
| − | | | + | | 40,702 |
| − | | | + | | 42,098 |
| − | | | + | | 39,887 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Agriculture |
| − | | | + | | 4,617 |
| − | | | + | | 4,834 |
| − | | | + | | 4,927 |
| − | | | + | | 5,560 |
| − | | | + | | 6,230 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Utilities |
| − | | | + | | 4,714 |
| − | | | + | | 5,555 |
| − | | | + | | 5,759 |
| − | | | + | | 6,010 |
| − | | | + | | 5,904 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Public lighting |
| − | | | + | | 6,982 |
| − | + | | 7,050 | |
| − | | | + | | 6,186 |
| − | | | + | | 6,537 |
| − | | | + | | 6,210 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Governmental entities |
| − | | | + | | 5,563 |
| − | | | + | | 5,443 |
| − | | | + | | 5,977 |
| − | | | + | | 6,385 |
| − | | | + | | 7,664 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Residential |
| + | | 43,811 | ||
| + | | 47,431 | ||
| + | | 51,370 | ||
| + | | 56,664 | ||
| + | | 59,757 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Commercial & others |
| − | | | + | | 8,754 |
| − | | | + | | 9,674 |
| − | | | + | | 10,238 |
| − | | | + | | 10,715 |
| − | | | + | | 14,605 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="6" | <br/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Total | ||
| + | | 111,714 | ||
| + | | 118,903 | ||
| + | | 125,159 | ||
| + | | 133,969 | ||
| + | | 140,257 | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | === Grid === |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In 2012/2013, the carrier grid consisted of 43,634 km total transmission lines and cables. The grid is subdivided into six geographical zones, namely Cairo, Canal, Delta, Alexandria and West Delta, Middle Egypt and Upper Egypt. The country’s entire territory is covered. The network is interconnected with the grids of Libya, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon. There are ongoing studies<ref name="http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf">http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf</ref> for interconnections with Saudi Arabia, Sudan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Eastern Nile Basin (Sudan and Ethiopia) and Greece.<br/> | |
| − | + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.14: Indicators of Egyptian Grid<ref name="Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf">Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf</ref></p> | |
| − | + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | ! scope="row" | Category | |
| − | The | + | ! scope="col" | Installed Capacity |
| − | + | ! scope="col" | Max Load | |
| − | + | ! scope="col" | Transmission Grid | |
| − | + | ! scope="col" | Generated Energy | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | ! scope="row" | Indicator | |
| − | + | | 45192 MW | |
| − | + | | 30400 MW | |
| − | + | | 45000 Km | |
| − | + | | 186320 GWh | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | == | + | === Electricity prices === |
| − | Egypt | + | |
| − | + | The prices of electricity in Egypt range among the lowest in the world. The prices are fixed by the Egyptian and are highly subsidized. The tariff structure varies according to the type of consumption (i.e. residential, commercial, industrial) and amount consumed. Since the tariff is higher for higher consumption, there is an incentive to consume less. The lowest category of the residential tariff, up to 50 KWh/month, has remained unchanged since 1993 at 5 piasters (approximately 0.6 €-ct) per KWh.<br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Since 2007, the government has been trying to cut costs for subsidies. In July 2014, electricity prices were increased as part of a five-year plan which aims to start generating profits from electricity, which is currently sold for less than half its production cost<ref name="http://english.alarabiya.net/en/business/2014/07/04/Minister-Egypt-raises-electricity-prices-.html">http://english.alarabiya.net/en/business/2014/07/04/Minister-Egypt-raises-electricity-prices-.html</ref>.<br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | = Further Information | + | <br/> |
| + | |||
| + | == Energy Security == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Egypt's_Energy_Security_-_Challenges_&_Possible_Futuristic_Scenarios|read more about Energy Security]] | ||
| + | Despite the lack of profound resources and information, and the ambiguity of available data regarding energy security in Egypt, yet Atlam & Rapiea (2016)’s study on “''Assessing the Future Energy Security in Egypt''” can be used as a firm basis for investigating the energy security situation in the country.<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref>.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Renewable Energy = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == General Data == | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.15: Egyptian Renewable Energy Production since 1965 in Twh<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Produced Capacity | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .5 | ||
| + | | 1.4 | ||
| + | | 1.9 | ||
| + | | 2.6 | ||
| + | | 2.7 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.16: Egyptian Renewable Energy Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Consumed Capacity | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .3 | ||
| + | | .4 | ||
| + | | .6 | ||
| + | | .6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
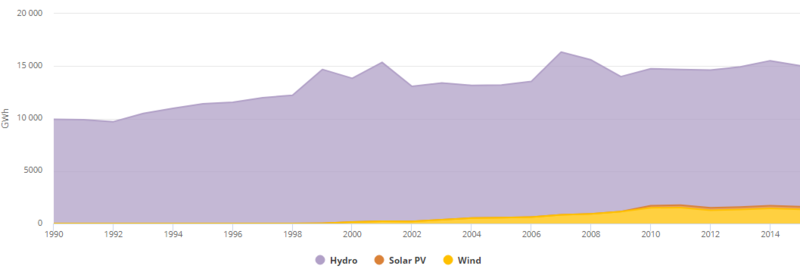
| + | [[File:Egyptian Electricity Generation from Renewables by Source (2015,IEA).png|thumb|center|800px|Fig.7: Egyptian Electricity Generation from Renewables by Source (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
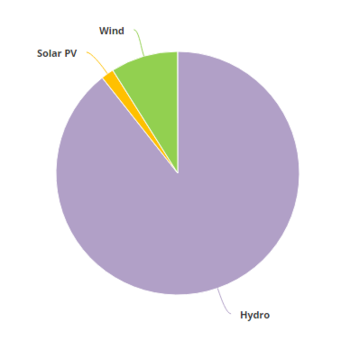
| + | [[File:Generation-Share of Different Renewable Energy Sources in Egypt in 2015.PNG|thumb|center|350px|FIg.8: Generation-Share of Different Renewable Energy Sources in Egypt in 2015 (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 2012, electricity production from renewable energy sources reached 14,855 GWh<ref name="http://www.iea.org/statistics/statisticssearch/report/?year=2012&country=EGYPT&product=ElectricityandHeat">http://www.iea.org/statistics/statisticssearch/report/?year=2012&country=EGYPT&product=ElectricityandHeat</ref>, which is a share of 9.04% of the total electricity production. While 13,358 GWh (8.13%) were produced by hydropower installations, wind power contributed another 1,260 GWh (0.77%) and solar PV 237 GWh (0.14%).<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Hydro == | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.17: Egyptian Hydro-Generation since 1965 in Twh<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Generated Capacity | ||
| + | | 1.7 | ||
| + | | 6.8 | ||
| + | | 9.1 | ||
| + | | 11.2 | ||
| + | | 14.2 | ||
| + | | 12.6 | ||
| + | | 13 | ||
| + | | 13.7 | ||
| + | | 13.3 | ||
| + | | 13.4 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.18: Egyptian Hydro-Consumption from since 1965 in Mtoe<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Consumed Capacity | ||
| + | | .4 | ||
| + | | 1.5 | ||
| + | | 2.1 | ||
| + | | 2.5 | ||
| + | | 3.2 | ||
| + | | 2.9 | ||
| + | | 2.9 | ||
| + | | 3.1 | ||
| + | | 3 | ||
| + | | 3 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Egyptian Hydro-Generation (IEA, 2017).png|thumb|center|800px|Fig.9: Egyptian Hydro-Generation (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The latest estimates of the hydropower installed capacity are approximately 2842 MW, accounting for about 7.2-9% of the total generated mix<ref name="Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf">Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf</ref><ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. Also, the ongoing implementation of 32 MW hydropower project in Assiut governorate and a 2400 MW pumping and storage plant in Attaqa-Suez, that is supposed to be operating by 2022, according to the Egyptian Ministry of Electricity and Renewable Energy & the Egyptian Holding Electricity Company<ref name="Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf">Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.19: Egypt's Hydroelectric Plants<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Operator | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Comissioning Date | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Installed Capacity (MW) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | High Dam | ||
| + | | 1967 | ||
| + | | 2100 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Aswan Dam 1 | ||
| + | | 1960 | ||
| + | | 280 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Aswan Dam 2 | ||
| + | | 1985/86 | ||
| + | | 270 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Esna | ||
| + | | 1993 | ||
| + | | 86 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Nag' Hamadi | ||
| + | | 2008 | ||
| + | | 64 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Wind == | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.20: Egyptian Wind-Power Generation since 1965 in Twh<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Generation Capacity | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .5 | ||
| + | | 1.4 | ||
| + | | 1.9 | ||
| + | | 2.5 | ||
| + | | 2.5 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.21: Egyptian Wind-Energy Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Consumed Capacity | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .3 | ||
| + | | .4 | ||
| + | | .6 | ||
| + | | .6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
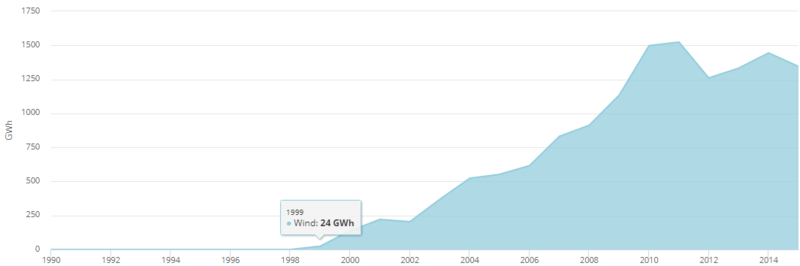
| + | [[File:Egyptian Wind-Energy Generation (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.10: Egyptian Wind-Energy Generation (IEA, 2017)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Egypt is endowed with abundant wind energy resources, with many coastal regions, where high and stable wind speeds are frequent, especially in the Gulf of Suez and the Nile Valley, as wind speed could reach 10.5 m/s at 50m height<ref name="Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf">Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf</ref><ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.22: Egyptian Wind Indicators<ref name="Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf">Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf</ref><ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Indicator | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Installed Capacity | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Generated Energy | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Fuel Savings | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | CO<sub>2</sub> Reductions | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Potential Capacities | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Value | ||
| + | | 750-753 MW | ||
| + | | 12600 GWh | ||
| + | | 2.7 Mtoe | ||
| + | | 6.8 Million Tons | ||
| + | | 30000 MW | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.23: Egyptian Major Wind Farms<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Farm | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Za'farana | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Gebel El-Zeit | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Hurghada | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Generated Capacity | ||
| + | | 547 MW | ||
| + | | 200 MW | ||
| + | | 5 MW | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Solar == | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.24: Egyptian Solar Production since 1965 in Twh<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Procution Capacity | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .2 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"><br/>Table.25: Egyptian Solar Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Consumption Capacity | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | - | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
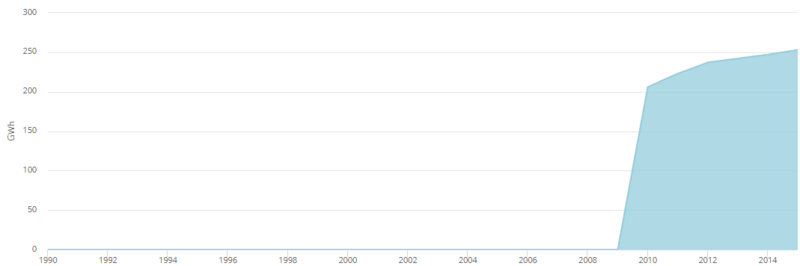
| + | [[File:Egyptian Solar Generation (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.11: Egyptian Solar Generation (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Though solar energy use in the country is still in its infancy, yet the country has a great potential in the solar sector. With accordance to the EIA's latest report, the country only has 30 MW of installed solar capacity so far<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. Additionally, there is one solar thermal project, an integrated solar combined-cycle power plant. Here, the solar power partially replaces fossil fuel. The plant has an overall capacity of 140 MW, of which the solar input is 20 MW. More PV projects are in the pipeline, one in Hurghada (20 MW, expected start of operation 2016), and one in Kom Ombo (20 MW, expected the start of operation 2016).<ref>https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1</ref><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Also, the Egyptian government has a huge scheme to boost the solar sector by installing a 1.8 GW solar park, which to be developed in Benban<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. As part of reaching that goal, the Egyptian government has closed two deals on two different fronts; the 1st is with Norway's Scatec Solar to build six solar photovoltaic plants with a combined capacity of 400 MW, while the 2nd is with Saudi firma Acwa for another three solar photovoltaic plants with a capacity of 120 MW<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.26: Egyptian Solar Potential Indicators<ref name="Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf">Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Indicator | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Direct Solar Radiaton | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Sunshine Duration | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Potential Capacities | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Value | ||
| + | | 2000-3000 kWh/m<sup>2</sup>/year | ||
| + | | 9-11 hours/day | ||
| + | | >50000 MW | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Fossil Fuels = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Oil == | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.27: Egyptian Proved Oil Reserves since 1980 in Barrels<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1980 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1990 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Reserves (Thosuand million barrel) | ||
| + | | 2.9 | ||
| + | | 3.5 | ||
| + | | 3.6 | ||
| + | | 4.5 | ||
| + | | 3.5 | ||
| + | | 3.4 | ||
| + | | 3.3 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.28: Egyptian Oil Production in Barrels since 1965<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Prduction (1000 barrels/day) | ||
| + | | 126 | ||
| + | | 228 | ||
| + | | 882 | ||
| + | | 924 | ||
| + | | 779 | ||
| + | | 672 | ||
| + | | 725 | ||
| + | | 726 | ||
| + | | 691 | ||
| + | | 660 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.29: Egyptian Oil Consumption since 1965<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Consumption (1000 barrels/day) | ||
| + | | 131 | ||
| + | | 159 | ||
| + | | 406 | ||
| + | | 463 | ||
| + | | 552 | ||
| + | | 617 | ||
| + | | 766 | ||
| + | | 833 | ||
| + | | 854 | ||
| + | | 816 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.30: Egyptian Refinery/Oil Products' Production since 1980<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1980 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1990 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Output (1000 barrels/day) | ||
| + | | 277 | ||
| + | | 489 | ||
| + | | 497 | ||
| + | | 580 | ||
| + | | 530 | ||
| + | | 509 | ||
| + | | 508 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;">Table.31: Egyptian Refinery/Oil Products' Production Capacity since 1965<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref></p> | ||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Capacity (1000 barrels/day) | ||
| + | | 181 | ||
| + | | 201 | ||
| + | | 433 | ||
| + | | 633 | ||
| + | | 654 | ||
| + | | 810 | ||
| + | | 810 | ||
| + | | 810 | ||
| + | | 810 | ||
| + | | 810 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:00- Egyptian Annual Petroleum & Other Oil-Products Production, Consumption, Net Exports & Net Imports (EIA, 2018).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.12: Egyptian Annual Petroleum & Other Oil-Products Production, Consumption, Net Exports & Net Imports (EIA, 2018)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:01- Egyptian Production of Crude Oil & Other Oil-Products (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.13: Egyptian Production of Crude Oil & Other Oil-Products (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:02- Final Egyptian Consumption of Oil & Oil-Products (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.14: Final Egyptian Consumption of Oil & Oil-Products (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:03- Egyptian Oil-Products Consumption By Sector (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|350px|Fig.15: Egyptian Oil-Products Consumption By Sector]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Natural Gas == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |+ Table.32: Egyptian Proved Natural Gas Reserves since 1980 in Tcm<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1980 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1990 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Estimated Reserves | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | .4 | ||
| + | | 1.4 | ||
| + | | 2.1 | ||
| + | | 1.8 | ||
| + | | 1.8 | ||
| + | | 1.8 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |+ Table.33: Egyptian Natural Gas Production in Bcm since 1970<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1970 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1980 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1990 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Production Capacity | ||
| + | | .1 | ||
| + | | 2.1 | ||
| + | | 7.8 | ||
| + | | 20.2 | ||
| + | | 59 | ||
| + | | 42.6 | ||
| + | | 40.3 | ||
| + | | 49 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |+ Table.34: Egyptian Natural Gas Consumption since 1965<ref name="BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html">BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Year | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1965 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1975 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1985 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 1995 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2000 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2005 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2010 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2015 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2016 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | 2017 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Consumption Capacity (Bcm) | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | <.1 | ||
| + | | 4.7 | ||
| + | | 12.1 | ||
| + | | 19.3 | ||
| + | | 30.4 | ||
| + | | 43.4 | ||
| + | | 46 | ||
| + | | 49.4 | ||
| + | | 56 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NG 01- Egyptian Natural Gas Production, Consumption, Net Exports, Net Imports (EIA, 2018).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.16: Egyptian Natural Gas Production, Consumption, Net Exports, Net Imports (EIA, 2018)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NG 02- Egyptian Natural Gas Production (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig,17: Egyptian Natural Gas Production (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NG 03- Egyptian Natural Gas Consumption (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.18: Egyptian Natural Gas Consumption (IEA, 2017)]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NG 04- Egyptian Sectorial Natural Gas Consumption (IEA, 2017).PNG|thumb|center|350px|Fig.19: Egyptian Sectorial Natural Gas Consumption (IEA, 2017)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Key Problems of the Energy Sector = | ||
| + | |||
| + | The main and utmost challenge that Egypt currently faces, that is mentioned in almost any literature that is related to energy in Egypt, is the un-controlable and continuously increasing population growth. Yet, the Egyptian energy sector has few other challenges that need to be dealt with adequately and seriously, otherwise Egypt will have to deal with a catastrophic energy situation within the few years to come. These challenges can be summarized in the following points: | ||
| + | |||
| + | #The decline of Egyptian oil and natural gas reserves; as proved oil reserves have decreased from 4.5 million barrels in 2009 to 4.2 million barrels in 2013, while natural gas reserves have decreased from 78 trillion cubic feet in 2010 to 77.2 trillion cubic feet in 2014<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref><ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref><ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | #The fact that the current Egyptian energy mixture is not properly diversified, as Egypt, heavily and mainly depends on oil, natural gas and the hydroelectric power from the Nile, with the third being close to nothing and even descending more, then Egypt is left with only both oil and natural gas representing approximately 90.4-94.4% of the total primary energy consumption till 2014<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref><ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | #The gap between supply and demand of oil, since the supply ratio is about 52.7% of the demand<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref><ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| + | #The majority of the Egyptian imported oil (~4.9 million tons), comes only from three suppliers: Kuwait, Iraq and Oman –according to the Egyptian Ministry of Petroleum- in 2014<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref>. <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Such a low variety of oil importers increases the probability of the risk of Egypt being negatively affected by any geopolitical instabilities in one or all of these importers, consequently affecting its ability to secure domestic demands in such situations<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref>.</span> | ||
| + | #<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">The low percentage of private investment in the energy sector (~16% in 2014/15), which in a way confines and hinders the technological aspects of energy production, distribution and consumption<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref><ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref>.</span> | ||
| + | #<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">The aging, un-maintained, low to non-efficient, mal-planned Egyptian infrastructure, especially in the energy sectors, which when faced with any sign of major problem, would lead to catastrophic outcomes, as for example, the daily blackouts of 2013 and 2014 summers, where electricity used to be completely absent allover Egypt for 6-8 hours/day through different times of the day<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref><ref name="Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf">Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf</ref><ref name="Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf">Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf</ref>.</span> | ||
| + | #<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">The non-existence of clear, to the point and profound strategies to be properly integrated in the Egyptian energy sector, and the un-clarity and complete randomness of the existent mixed ones, which are mostly unreliable, un-applicable strategies designed by totally different and varied institutions and energy-suppliers with different agendas and mentalities, eventually hindering any possible appropriate application or planning a proper solution(s) to secure energy supply<ref name="Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930">Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930</ref>.</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Policy Framework, Laws and Regulations</span> = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">General Information</span>== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">The combination of increasing demand, decreasing production and high subsidies for fuel have put a strain on the Egyptian energy sector and led to an enormous public deficit. As of June 2014, Egypt owed 7.5 billion USD and counting to foreign oil and gas companies alone <ref name="http://www.eia.gov/countries/cab.cfm?fips=eg">http://www.eia.gov/countries/cab.cfm?fips=eg</ref>. In order help meeting the energy demand and to prevent an Egyptian energy crisis, Gulf countries have been providing financial aid to Egypt. However, this kind of aid is expected to decrease as the Gulf countries are impacted by the falling oil prices of 2015.</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/><span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">One topic dominating energy policy debates in Egypt is the use of coal. In April 2014, the government approved the industrial use of coal. This is especially relevant for cement factories, as these are particularly energy intensive and have occasionally been cut off from the energy supply as the government's priority was to preserve gas for power generation<ref name="http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/11/05/egypt-cement-coal-idUSL6N0SU2YB20141105">http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/11/05/egypt-cement-coal-idUSL6N0SU2YB20141105</ref>.</span><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Renewable Energy Policy</span>== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">In February 2008, the Egyptian government adopted a New National Renewable Energy Strategy. It sets out the ambitious goal to achieve a generation of 20% of the country’s electricity from renewable resources by 2020. 12 percentage points (7,200 MW) are supposed to be covered by wind energy. One-third of the planned RE capacity will be state-owned projects financed through public investments by the New and Renewable Energy Agency (NREA) in cooperation with international financing institutions. Two thirds will be private sector projects, which will be supported by policies structured in three phases:</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Phase 1 will adopt competitive bids through issuing tenders requesting the private sector to supply electricity from renewable energy sources.</span><br/> | ||
| + | *<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">In Phase 2, a feed-in-tariff will be implemented, in particular for medium and small size projects.</span><br/> | ||
| + | *<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Phase 3 allows investors to build and operate renewable energy power plants to satisfy their electricity needs or to sell electricity to other consumers through the national grid.</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Also, an RE support fund is supposed to be established to cover the feed-in tariff payments.</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">In September 2014, the government approved the issuance of feed-in tariffs for solar PV and wind projects.<br/>The new Presidential Decree 1947/2014 of October 2014 provides for fixed feed-in-tariffs over 25 years for PV and over 20 years for wind. These tariffs will be adjusted as soon as the following ceilings are reached: 300 MW of small PV (< 500 kW), 2000 MW of medium PV (500 kW – 50 MW), and 2000 MW of wind. The tariffs are going to be paid according to plant capacity. The details are outlined in a [http://egyptera.org/Downloads/taka guiding document published by the Egyptian Electric Utility for Consumer Protection and Regulatory Agency (EgyptERA)].</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/><span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">The FIT scheme is complemented by Law 203/2014 of 22 December 2014 whereby the Egyptian TSO (EETC) and the local distribution companies are obliged to connect a RES project to the grid. The costs of the connection shall be borne by the producer, while the government shall fund any extension of the grid. They are also obliged to purchase the electricity generated by qualifying projects and, if this is not feasible, compensate the producer.</span><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Energy Efficiency Policy</span> == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Egypt has adopted a National Energy Efficiency Action Plan (NEEAP) (2012-2015) with cumulative energy efficiency targets of 5%. At the Council of Minister's secretariat, there is an EE unit which is the mandated entity for developing and implementing this plan. However, there is no designated energy efficiency agency and no general legal framework for EE measures<ref name="http://www.rcreee.org/sites/default/files/egypt_ee_fact_sheet_print.pdf">http://www.rcreee.org/sites/default/files/egypt_ee_fact_sheet_print.pdf</ref>.<br/>Some steps have been taken to improve energy efficiency:</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Mandatory EE codes for residential buildings (2006), commercial buildings (2009), and government buildings (2011) have been adopted.</span><br/> | ||
| + | *<span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Minimum performance standards with mandatory labeling schemes have been adopted for refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, air conditioners, CFLs, and electric water heaters.</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">By 2012, 750,000 m2 of Solar Water Heaters had been installed and 10.25 million Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs) had been distributed. However, there are no buildings which are built according to EE building code and no demonstration projects for energy-efficient buildings.</span><br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Institutional Set up in the Energy Sector</span> = | ||
| + | |||
| + | == <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">Governmental Bodies, Agencies & Utilities</span>== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |+ Table.35: Egyptian Energy-Sector Governmental Bodies/Agencies<ref name="Meier, P. Vagliasindi, M. Imran, M. Eberhard, A. & Siyambalapitiya, T. (2015). The Design and Sustainability of Renewable Energy Incentives: An Economic Analysis. Retrieved From: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1">Meier, P. Vagliasindi, M. Imran, M. Eberhard, A. & Siyambalapitiya, T. (2015). The Design and Sustainability of Renewable Energy Incentives: An Economic Analysis. Retrieved From: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Body/Agency | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Abbreviation | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Establishment | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Role | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Ministry of Electricity and Energy | ||
| + | | MOEE | ||
| + | | 1964 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Supervising all activities related to energy projects<br/> | ||
| + | *Suggesting electricity prices<br/> | ||
| + | *Publishing data and statistics relating to electricity production<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);"> </span>'''New and Renewable Energy Authority'''<br/> | ||
| + | | NREA | ||
| + | | 1986, by MOEE | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Bundling activities aiming to promote both renewable energy soures and energy efficiency<br/> | ||
| + | *Acts as the national focal point for expanding efforts to introduce and develop renewable technologies in Egypt<br/> | ||
| + | *Implementation of related energy conservation programs<br/> | ||
| + | *Responsible for development, ownership and operation of governmental wind projects | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency | ||
| + | | EEAA | ||
| + | | 1982, and restructured in 1994 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Executive arm of the Ministry of Environment<br/> | ||
| + | *Formulation of environmental policies<br/> | ||
| + | *Development and monitoring of projects<br/> | ||
| + | *Implementation of pilot projects<br/> | ||
| + | *Tha national autority in charge of promoting environmental topics<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian Electric Utility and Consumer Protection Regulatory Agency | ||
| + | | EgyptERA | ||
| + | | 1997, upon decree | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Balance the interests of electricity producers, providers and end users<br/> | ||
| + | *Ensure reliable long term supply of electriciy<br/> | ||
| + | *Promoting and supervising environmental protection and operational reliability in the energy sector<br/> | ||
| + | *Licensing the construction and operation of electricity generation, transmission and distribution facilities<br/> | ||
| + | *Electricity trading<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian Electricity Holding Company | ||
| + | | EEHC | ||
| + | | 2000, As a result of major institutional reform tha took place through law 164 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Coordinates, supervises and monitors the activities of its affiliated companies in the fields of production, transmission and distribution of electric energy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian Energy Transmission Company | ||
| + | | EETC | ||
| + | | 1976 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Responsible for the country-wide transmission of electricity to regional and local distributors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The current Egyptian electricity market is completely composed of governmental owned utilities, which can be divided into: 6 for generation, 1 for transmission and 9 for distribution<ref name="Meier, P. Vagliasindi, M. Imran, M. Eberhard, A. & Siyambalapitiya, T. (2015). The Design and Sustainability of Renewable Energy Incentives: An Economic Analysis. Retrieved From: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1">Meier, P. Vagliasindi, M. Imran, M. Eberhard, A. & Siyambalapitiya, T. (2015). The Design and Sustainability of Renewable Energy Incentives: An Economic Analysis. Retrieved From: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1</ref>, which all are operating under the direct management of the EEHC, as shown in the following figure (Fig.20)<ref name="Meier, P. Vagliasindi, M. Imran, M. Eberhard, A. & Siyambalapitiya, T. (2015). The Design and Sustainability of Renewable Energy Incentives: An Economic Analysis. Retrieved From: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1">Meier, P. Vagliasindi, M. Imran, M. Eberhard, A. & Siyambalapitiya, T. (2015). The Design and Sustainability of Renewable Energy Incentives: An Economic Analysis. Retrieved From: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Egypt Sectorial Structure.PNG|thumb|center|800px|Fig.20: Egypt Sectorial Structure (Peter et al., 2015)]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255);">On the other hand, the whole petroleum sector in Egypt is run by main five state-owned enterprises, with accordance to the latest EIA's Egypt's analysis brief (2018), which can be summarized in the following table.</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" style="width:100%;" | ||
| + | |+ Table.36: Egypt's Petroleum Sector Main Enterprises<ref name="U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf">U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Enterprise | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Abbreviaton | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Establishment | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Role | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation | ||
| + | | EGPC | ||
| + | | 1956 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Manage upstream oil activities<br/> | ||
| + | *Issue upstream licenses<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Focus on activities the country, except Southern)<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian Natural Gas Holding Company | ||
| + | | EGAS | ||
| + | | 2001 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Oversees the development, production and marketing of natural gas<br/> | ||
| + | *Organizing international exploration bid rounds<br/> | ||
| + | *Awarding natural gas exploration licenses<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian Petrochemicals Holding Company | ||
| + | | ECHEM | ||
| + | | 2002 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Developing the petrochemical sector | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Egyptian Mineral Resources Authority | ||
| + | | EMRA | ||
| + | | 1896 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Mineral resources assessment<br/> | ||
| + | *Geological mapping of the country<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Ganoub El-Wadi Holding Company | ||
| + | | Ganope | ||
| + | | 2003 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | *Manage upstream oil activities<br/> | ||
| + | *Issue upstream licenses<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Focus on activities in the Southern Region) <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Others == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="font-size: 0.85em">In the area of fossil power plants, Egypt already works with Independent Power Producers (IPPs). The first contract under a power purchase agreement (PPA) was signed in 1998.</span><ref>https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1</ref><span style="font-size: 0.85em">In 2012/13, the following IPPs feed a total 33 GWh into the Egyptian electricity grid: </span>'''Petrochemicals '''<span style="font-size: 0.85em">(15 GWh), </span>'''Carbon Black '''<span style="font-size: 0.85em">(1 GWh), </span>'''Talkha Fertilizer'''<span style="font-size: 0.85em">and </span>'''Ghazl El-Mahaala '''<span style="font-size: 0.85em">(17 GWh)</span><ref name="http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf">http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf</ref><span style="font-size: 0.85em">.</span><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/>The private sector is also involved via the “Build-Own-Operate-Transfer” (BOOT) scheme. Four steam power plants were operated with the BOOT model in 2012/13 and provided a total of 14,264 GWh. According to EgyptERA<ref name="http://egyptera.org/en/curr_egy.aspx">http://egyptera.org/en/curr_egy.aspx</ref>, the companies under the BOOT model are '''Suez Gulf Power Company '''(4,576 GWh), '''Port Said East Power Company''' (4,983 GWh) and '''Sidi Krir Generating Company''' (4,705 GWh). The power plants operated by these companies were built in 2001-2003, with an installed capacity of 682.5 MW each. All three BOOT companies were acquired by the Malaysian Powertek Energy in 2006/2007<ref name="http://www.powertek.com.my/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=60&Itemid=70">http://www.powertek.com.my/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=60&Itemid=70</ref>.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/>The '''Egyptian Wind Energy Association ([http://eaee-eg.com/ EGWEA])''' is the umbrella organisation, representing the wind energy sector in Egypt. It assists interaction and co-operation between all relevant players with professional involvement in the field of wind energy. The EGWEA is organised in a global network of wind associations. It aims at promoting and supporting the development of wind energy in Egypt by providing the means to facilitate the exchange of technical information, expertise and experience in the wind energy sector. It conducts studies, provides information on tenders and conferences and organises workshops for interested parties. EGWEA is particularly interested in bringing forward wind energy interests of Egypt.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, the association is also engaged in the promotion of wind energy in developing countries in general.<br/><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | = Energy Cooperation = | ||
| + | |||
| + | At the European level, a [http://www.enpi-info.eu/library/sites/default/files/attachments/mou_energy_eu-egypt_en.pdf Memorandum of Understanding to enhance EU-Egypt energy cooperation] was signed in December 2008. The priority areas covered are, among others, the development of the Egyptian energy strategy, including the market reform, the convergence of Egypt’s energy market with that of the EU, the promotion of renewable energy and energy efficiency, the development of energy grids as well as technological and industrial cooperation.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Bilateral Energy Cooperation with Germany == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Along with the World Bank, the African Development Bank, the United States, France, the EU and Japan, Germany is Egypt’s leading partner in terms of official development assistance. Egypt is one of the priority partner countries of the German development policy. Since 1963, Egypt has received approximately 6 billion EUR of aggregate commitments from Germany. The current focus areas of the bilateral cooperation are water management, renewable energies, energy efficiency and climate change.<ref name="http://www.auswaertiges-amt.de/EN/Aussenpolitik/Laender/Laenderinfos/01-Nodes/Aegypten_node.html">http://www.auswaertiges-amt.de/EN/Aussenpolitik/Laender/Laenderinfos/01-Nodes/Aegypten_node.html</ref><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/>Within the framework of the German development cooperation, two initiatives to promote renewable energies and energy efficiency were launched in 2008:<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The Regional Center for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency (RCREEE), based in Cairo. Besides Egypt, other Arab members of the RCREEE are Algeria, Bahrain, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Palestine, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia and Yemen. RCREEE formulates and disseminates policies in support of RE and EE in the region and provides a platform for the regional exchange on policy issues and technological questions. In addition, RCREEE encourages the participation of the private sector to promote the establishment of a regional RE and EE industry.<br/> | ||
| + | *The Egyptian-German High-Level Committee on Renewable Energy, Energy Efficiency and Environmental Protection JCEE, is a bilateral Egyptian-German initiative. The JCEE is a platform for energy policy discussion, for developing initiatives for investment as well as institutional projects, awareness, and capacity building activities and establishing contacts and exchange between the two countries. The project is financed by the Egyptian Ministry of Electricity and Energy and the German Federal Ministry of Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). The implementing partners of the cooperation are NREA and GIZ. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Other Key Actors / Activities of Donors, Implementing Agencies, Civil Society Organisations = | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Further Information = | ||
*[http://www.egypt.gov.eg/english/ Egypt's Government Services Portal]<br/> | *[http://www.egypt.gov.eg/english/ Egypt's Government Services Portal]<br/> | ||
*[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html Egypt's entry at The World Factbook] | *[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html Egypt's entry at The World Factbook] | ||
| − | + | *<br/> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | = References = | ||
| − | [[ | + | <references /><br/>[[Egypt Energy Situation#toc|►Go to Top]]<br/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 09:44, 7 November 2022
Capital:
Cairo
Region:
Coordinates:
26.0000° N, 30.0000° E
Total Area (km²): It includes a country's total area, including areas under inland bodies of water and some coastal waterways.
1,001,450
Population: It is based on the de facto definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship--except for refugees not permanently settled in the country of asylum, who are generally considered part of the population of their country of origin.
110,990,103 (2022)
Rural Population (% of total population): It refers to people living in rural areas as defined by national statistical offices. It is calculated as the difference between total population and urban population.
57 (2022)
GDP (current US$): It is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. It is calculated without making deductions for depreciation of fabricated assets or for depletion and degradation of natural resources.
476,747,720,365 (2022)
GDP Per Capita (current US$): It is gross domestic product divided by midyear population
4,295.41 (2022)
Access to Electricity (% of population): It is the percentage of population with access to electricity.
100.00 (2021)
Energy Imports Net (% of energy use): It is estimated as energy use less production, both measured in oil equivalents. A negative value indicates that the country is a net exporter. Energy use refers to use of primary energy before transformation to other end-use fuels, which is equal to indigenous production plus imports and stock changes, minus exports and fuels supplied to ships and aircraft engaged in international transport.
-7.39 (2014)
Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption (% of total): It comprises coal, oil, petroleum, and natural gas products.
97.93 (2014)
Introduction
The Arab Republic of Egypt is located in North Africa and borders with Libya in the West, Sudan in the South and Palestinian territories and Israel in the East, while in the North, it is washed by the Mediterranean. Its population is mainly concentrated along the river Nile, as the rest of the country's territory is largely desert.
Most parts of the country have a hot desert climate with extreme heat occurring during summer. An exception is the northern Mediterranean coast which receives more rainfall during winter and has a generally more moderate climate.
Egypty is a country with a high potential of natural resources: precious stones, natural gas, oil, coal and large reserves of fossil fuel enery sources; approximately 4189 billion barrels of oil reserves and an estimated 77200 billion cubic meters of natural gas resreves, as the reserves are in the form of both mainland and coastal deposits[1].
While more than 90% of the Egyptian generated electricity comes only from oil and natural gas, the major problem that Egypt encounters, especially in the energy-sector is the dynamic growth of population, which is estimated by around 1.3% per year, consequently increasing demand, which eventually fastens the rate of depleting the country's major resources[2][3][1][4].
According to the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), it is the largest non-OPEC oil producer in Africa and the third largest dry natural gas producer on the continent, following Algeria & Nigeria[5].
The country also represents a vital role-player in the international energy market, as a major transit route, by operating the Suez Canal and the Suez Mediterranean Pipleline (SUMED)[6], through which the oil is shipped from the Persian Gulf to Europe and the United States[3][5].
Energy Situation
Historical Background and an Overview of the Main Energy Sources
Egypt has been known to mainly depend, in all its energy-related activities, on three major sources: oil, natural gas and the hydroelectric power generated from the large dam projects over the Nile: the High Dam, Aswan I & Aswan II[3][4][7].
Despite being a major producer and net exporter of oil, especially in the 1990s, when its oil production peaked, reaching approximately over 900000 bbl/day, Egypt has become a net oil importer around 2009/2010[4]. Thus can be traced back to both economic and population accelerated growth, which accompanied the beginning of the new millennium, leading to an increase in consumption by about 3% per year, resulting in growing of demand, and falling in production, that could roughly meet consumption requirements, resulting in a significant drop in the country’s oil refinery output since 2009[3][4].
During the period of the late 1990s/early 2000s, Egypt has witnessed a state of proliferation of discovering and exploiting huge natural gas reserves around the country, which drove the country to emerge as a key role player in the region as a natural gas producer and exporter[3]. Mainly, due to the same reason as in oil, consumption of natural gas has approximately increased by 7% per year during the first decade of 2000s, and production has noticeably decreased by around 3% yearly during the period of 2009-2013, consequently limiting its natural gas exporting capacity to only 5% of its total production by 2013, and eventually driving the country to start signing importing agreements in the following years of 2014 and 2015[3][4].
Table.1: General Statistics on Oil & Natural Gas Situation in Egypt[4]
| Oil |
Natural Gas | |
|---|---|---|
| Total Production | 680,000 bbl/day | 2 trillion cubic feet/day |
| Global Production-Share |
0.72% |
1.7% |
| Proven Reserves |
3,900,000,000 bbl |
65.3 trillion cubic feet |
| Global Proven Reserves-Share |
0.2% |
1% |
| % Total Domestic Consumption |
41% | 53% |
| Imports | 80,000 bbl/day |
To Be Updated |
| Exports | 189,000 bbl/day |
0.1 trillion cubic feet/year |
|
Export Destinations |
EU (56%), India (28%), China (13%), Others (3%) |
EU (56%), India (28%), China (13%), Others (3%) |
According to reports from American Security Project (ASP) and United Nations Environment Program (UNEP), Egypt has produced approximately 13.2-13.7 billion kilowatt-hours (KWh) of electricity, using hydropower in the period 2012/2013[4][7].
Hydropower accounts for about 9% of the total country’s power generation, and around 3% of the country’s total energy consumption, however, the majority of the Nile hydropower’s capacity in Egypt has already been exploited and is declining[4][7].
Energy Access
According to the latest Tracking SDG7 Report on The Energy Progress, that was jointly prepared by:International Energy Agency (IEA), International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), United Nations Statistics Division, World Bank Group and World Health Organization, the state of energy access through Egypt is illustrated through the following table and figures[8]:
The report shows that since around 2014/2015, the total Egyptian population has had access to reliable energy sources, and only 2% of the whole population has no access to clean cooking[8].
Table.2: Percentage of Egyptian Population's Access to Electricity & Clean Cooking[8]
| Access to | ||
|---|---|---|
| Electricity | Clean Cooking | |
| % of Population | 100% | 98% |
Production
Table.3: Egypt’s Production of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe[9]
| 2000 | 2005 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 20 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Crude Oil | 33189 | 30111 | 32142 | 29537 | 32825 | 33210 | 30835 | 31885 |
| Natural gas | 18555 | 35901 | 54839 | 50143 | 39084 | 34763 | 34763 | 35362 |
| Electricity from Fossil Fuels | 5302 | 8211 | 12250 | 12250 | 13431 | 14355 | 14514 | 14679 |
| Hydro Electricity | 1260 | 1087 | 1112 | 1113 | 1188 | 1155 | 1171 | 1187 |
| Electricity from Renewables | 12 | 47 | 139 | 139 | 145 | 137 | 150 | 165 |
| Refinery/Oil Porducts | 23449 | 28561 | 24754 | 21836 | 25348 | 25676 | 26357 | 270565 |
Installed Capacity
With accordance to the EIA's report on Egypt (2018), the following graph and pie-chart highlight the installed capacity of different energ sources in the country from 2007-2016 in terms of fiscal years.
Consumption
Egypt is by far the largest consumer of oil and natural gas in Africa, showing 22% of petroleum and other liquids of the continent's total consumption and 37% of its dry natural gas consumption[5].
The main drivers of the rapid growth of the country's consumption of oil and natural gas can be summarized in the follwoing[5]:
- The increased industrial output.
- Economic growth.
- Intense extraction projects of oil and natural gas.
- Population growth.
- The inclining rate of private and commercial vehicle sales.
- The generous subsidy policy, that is focused on energy products.
Through this sub-chapter, different consumption data will be presented, using different sources, to get a holistic view as possible of the energy consumption situation in the country.
Table.4: Egypt’s Primary Energy Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate | 7.8 | 10.5 | 28 | 37.3 | 48.4 | 60.5 | 78.4 | 84.4 | 88.2 | 91.6 |
Table.5: Egypt’s Primary Energy Consumption by Fuel 2016-2017 Mtoe[10]
| Oil | Natural Gas | Coal | Nuclear | Hydro-Electric | Renewables | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 42 | 42.4 | .2 | - | 3 | .6 | 88.2 |
| 2017 | 39.7 | 48.1 | .2 | - | 3 | .6 | 91.6 |
Table.6: Egypt’s Final Consumption of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe[9]
| 2000 | 2005 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 453 | 203 | 204 | 188 | 188 | 200 | 211 | 224 |
| Oil | 17898 | 20156 | 27009 | 22573 | 26333 | 35213 | 36086 | 37028 |
| Natural Gas | 4274 | 9182 | 12719 | 18202 | 19505 | 20956 | 21446 | 21960 |
| Electricity | 5559 | 7918 | 12060 | 12324 | 12306 | 12668 | 13134 | 13630 |
Table.7: Egypt’s Industrial Consumption of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe[9]
| 2000 | 2005 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | 5461 | 5548 | 3716 | 3279 | 3133 | 6369 | 6713 | 7080 |
| Natural Gas | 2072 | 5567 | 6649 | 6789 | 8002 | 9083 | 9303 | 9536 |
| Electricity | 2111 | 2812 | 3430 | 3500 | 3288 | 369 | 3488 | 3612 |
| Coal | 453 | 203 | 204 | 188 | 188 | 200 | 211 | 224 |
Table.8: Egypt’s Transport Consumption of Different Energy Sources during the 2000s in Ktoe[9]
| 2000 | 2005 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | 9060 | 9371 | 15547 | 12362 | 16416 | 16892 | 17098 | 17312 |
| Electricity | - | - | 44 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 46 | 47 |
Import and Export
Egypt is a net exporter of crude oil and natural gas, however, the combination of increasing consumption and declining production has led to a decline in natural gas exports since 2009, as the government started to divert natural gas supplies from exports, in order to satisfy domestic demand, eventually turning the country into a natural gas importer since 2015[5].
In terms of coal and peat, Egypt is a net importer, and coal imports are even expected to increase in the short-medium term, since the Egyptian government has approved the industrial use of coal in April 2014, and in the same year signed a construction deal for the first coal-fired power in the country.
Subsidies
In 2013, the Egyptian government spent 120 billion Egyptian pounds (about 13.8 billion EUR) on fuel subsidies, which equals 7% of the GDP[11]. These costs in combination with economic stagnation have contributed to the increasing deficit, which reached about 12% of GDP in 2013. In order to alleviate this burden, the Egyptian government announced spending cuts on energy subsidies in June 2014. The Financial Times reported that these subsidies are going to be cut by almost a third [12].
Electricity
General Data
Table.9: The General Electricity Situation in Egypt[13]
| Electricity | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production | Consumption |
Exports | Imports |
Installed Generating Capacity | ||||||
| Rate | 171.9 billion kWh | 150.4 billion kWh | 1.158 billion kWh | 43 million kWh | 38.88 million kWh | |||||
| World Ranking | 24 | 25 | 57 | 106 | 27 | |||||
Electricity Access
According to the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)'s 2018 report, only around 300,000 people of the whole Egyptian population is currently without access to electricity.
Table.10: Electrification Percentages in Egypt[13]
| Electrification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Population | Urban Areas | Rural Areas | |
| % | 99.6 | 100 | 99.3 |
Installed Capacity and Generation
Table.11: Percentages of Different Electricity-Generating Energy-Sources in Egypt[13]
| Electricity Generated From: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fossil Fuels |
Nuclear Fuels |
Hydroelectric Plants | Other Renewables | |
| % of the Total Installed Capacity | 90.5 | 0 | 7.3 | 2.2 |
| World Ranking | 58 | 83 | 125 | 115 |
Between 2011/2012 and 2012/2013, the total installed capacity increased about 6 %, reaching 30,803 MW, due to added thermal plants. The installed capacity development by type of generation since 2008 is outlined in table 12.
Table 12: Installed capacity development by type of generation (in MW) 2008-2013[14]
| 2008/2009 | 2009/2010 | 2010/2011 | 2011/2012 | 2012/2013 | |
| MW | |||||
| Renewables | 425 | 249 | 687 | 687 | 687 |
| Steam | 11,458 | 11,458 | 12,859 | 12,684 | 13,808 |
| Hydro | 2,800 | 2,800 | 2,800 | 2,800 | 2,800 |
| Combined Cycle | 7,178 | 7,137 | 9,327 | 10,077 | 10,080 |
| Gas | 1,641 | 2,841 | 1,376 | 2,826 | 3,428 |
| Total | 23,502 | 24,762 | 27,049 | 29,074 | 30,803 |
In addition, Egypt has 30 decentralized power plants, mostly diesel and gas turbine units which are not connected to the national grid. The combined installed capacities of these plants added up to 224 MW in 2012/2013. Approximately 234.5 GWh of electricity were supplied to local users including tourist resorts.
Egypt is a net exporter of electricity, importing 77 GWh while exporting 474 GWh of electricity in 2012. In 2012/2013, the average percentage of network losses were 11.02%.[14]
Between 2001 and 2012, electricity production rose from 83,282 GWh to 164,364 GWh. The main source for the production of electricity is gas (66%) followed by hydro (18.2%) and oil (15.6%).[14] The Egyptian Electricity Holding Company (EEHC) operates with five-year plans. The current one (2012-2017) foresees the installation of 15.000 MW additional capacity. However, due to the increasing demand, the reserve margin is still expected to remain tight.[15]
Consumption
The main consumer of electricity in Egypt is the residential sector which accounts for 42% of the total consumption, followed by the industrial sector (28%). The consumption of the residential sector has been steadily increasing in the recent years. According to the Ministry of Electricity and Energy, this is due to two factors: the expansion of residential compounds and new communities as well as the use of domestic appliances, air conditioners in particular, during hot weather. The development of the electricity consumption per sector is outlined in table 13.
Table 13: Electricity consumption by sector (GWh) 2008-2013 [14]
| Sector | 2008/2009 | 2009/2010 | 2010/2011 | 2011/2012 | 2012/2013 |
| GWh | |||||
| Industries | 37,273 | 38,916 | 40,702 | 42,098 | 39,887 |
| Agriculture | 4,617 | 4,834 | 4,927 | 5,560 | 6,230 |
| Utilities | 4,714 | 5,555 | 5,759 | 6,010 | 5,904 |
| Public lighting | 6,982 | 7,050 | 6,186 | 6,537 | 6,210 |
| Governmental entities | 5,563 | 5,443 | 5,977 | 6,385 | 7,664 |
| Residential | 43,811 | 47,431 | 51,370 | 56,664 | 59,757 |
| Commercial & others | 8,754 | 9,674 | 10,238 | 10,715 | 14,605 |
| Total | 111,714 | 118,903 | 125,159 | 133,969 | 140,257 |
Grid
In 2012/2013, the carrier grid consisted of 43,634 km total transmission lines and cables. The grid is subdivided into six geographical zones, namely Cairo, Canal, Delta, Alexandria and West Delta, Middle Egypt and Upper Egypt. The country’s entire territory is covered. The network is interconnected with the grids of Libya, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon. There are ongoing studies[14] for interconnections with Saudi Arabia, Sudan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the Eastern Nile Basin (Sudan and Ethiopia) and Greece.
Table.14: Indicators of Egyptian Grid[16]
| Category | Installed Capacity | Max Load | Transmission Grid | Generated Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | 45192 MW | 30400 MW | 45000 Km | 186320 GWh |
Electricity prices
The prices of electricity in Egypt range among the lowest in the world. The prices are fixed by the Egyptian and are highly subsidized. The tariff structure varies according to the type of consumption (i.e. residential, commercial, industrial) and amount consumed. Since the tariff is higher for higher consumption, there is an incentive to consume less. The lowest category of the residential tariff, up to 50 KWh/month, has remained unchanged since 1993 at 5 piasters (approximately 0.6 €-ct) per KWh.
Since 2007, the government has been trying to cut costs for subsidies. In July 2014, electricity prices were increased as part of a five-year plan which aims to start generating profits from electricity, which is currently sold for less than half its production cost[17].
Energy Security
Despite the lack of profound resources and information, and the ambiguity of available data regarding energy security in Egypt, yet Atlam & Rapiea (2016)’s study on “Assessing the Future Energy Security in Egypt” can be used as a firm basis for investigating the energy security situation in the country.[2].
Renewable Energy
General Data
Table.15: Egyptian Renewable Energy Production since 1965 in Twh[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Produced Capacity | - | - | - | - | .1 | .5 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 2.7 |
Table.16: Egyptian Renewable Energy Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumed Capacity | - | - | - | - | - | .1 | .3 | .4 | .6 | .6 |
In 2012, electricity production from renewable energy sources reached 14,855 GWh[18], which is a share of 9.04% of the total electricity production. While 13,358 GWh (8.13%) were produced by hydropower installations, wind power contributed another 1,260 GWh (0.77%) and solar PV 237 GWh (0.14%).
Hydro
Table.17: Egyptian Hydro-Generation since 1965 in Twh[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generated Capacity | 1.7 | 6.8 | 9.1 | 11.2 | 14.2 | 12.6 | 13 | 13.7 | 13.3 | 13.4 |
Table.18: Egyptian Hydro-Consumption from since 1965 in Mtoe[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumed Capacity | .4 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3 | 3 |
The latest estimates of the hydropower installed capacity are approximately 2842 MW, accounting for about 7.2-9% of the total generated mix[16][5]. Also, the ongoing implementation of 32 MW hydropower project in Assiut governorate and a 2400 MW pumping and storage plant in Attaqa-Suez, that is supposed to be operating by 2022, according to the Egyptian Ministry of Electricity and Renewable Energy & the Egyptian Holding Electricity Company[16].
Table.19: Egypt's Hydroelectric Plants[5]
| Operator | Comissioning Date | Installed Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|
| High Dam | 1967 | 2100 |
| Aswan Dam 1 | 1960 | 280 |
| Aswan Dam 2 | 1985/86 | 270 |
| Esna | 1993 | 86 |
| Nag' Hamadi | 2008 | 64 |
Wind
Table.20: Egyptian Wind-Power Generation since 1965 in Twh[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generation Capacity | - | - | - | - | .1 | .5 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
Table.21: Egyptian Wind-Energy Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumed Capacity | - | - | - | - | - | .1 | .3 | .4 | .6 | .6 |
Egypt is endowed with abundant wind energy resources, with many coastal regions, where high and stable wind speeds are frequent, especially in the Gulf of Suez and the Nile Valley, as wind speed could reach 10.5 m/s at 50m height[16][5].
Table.22: Egyptian Wind Indicators[16][5]
| Indicator | Installed Capacity | Generated Energy | Fuel Savings | CO2 Reductions | Potential Capacities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 750-753 MW | 12600 GWh | 2.7 Mtoe | 6.8 Million Tons | 30000 MW |
Table.23: Egyptian Major Wind Farms[5]
| Farm | Za'farana | Gebel El-Zeit | Hurghada |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generated Capacity | 547 MW | 200 MW | 5 MW |
Solar
Table.24: Egyptian Solar Production since 1965 in Twh[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Procution Capacity | - | - | - | - | - | <.1 | .1 | .1 | .1 | .2 |
Table.25: Egyptian Solar Consumption since 1965 in Mtoe[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption Capacity | - | - | - | - | <.1 | <.1 | <.1 | <.1 | <.1 | <.1 |
Though solar energy use in the country is still in its infancy, yet the country has a great potential in the solar sector. With accordance to the EIA's latest report, the country only has 30 MW of installed solar capacity so far[5]. Additionally, there is one solar thermal project, an integrated solar combined-cycle power plant. Here, the solar power partially replaces fossil fuel. The plant has an overall capacity of 140 MW, of which the solar input is 20 MW. More PV projects are in the pipeline, one in Hurghada (20 MW, expected start of operation 2016), and one in Kom Ombo (20 MW, expected the start of operation 2016).[19]
Also, the Egyptian government has a huge scheme to boost the solar sector by installing a 1.8 GW solar park, which to be developed in Benban[5]. As part of reaching that goal, the Egyptian government has closed two deals on two different fronts; the 1st is with Norway's Scatec Solar to build six solar photovoltaic plants with a combined capacity of 400 MW, while the 2nd is with Saudi firma Acwa for another three solar photovoltaic plants with a capacity of 120 MW[5].
Table.26: Egyptian Solar Potential Indicators[16]
| Indicator | Direct Solar Radiaton | Sunshine Duration | Potential Capacities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 2000-3000 kWh/m2/year | 9-11 hours/day | >50000 MW |
Fossil Fuels
Oil
Table.27: Egyptian Proved Oil Reserves since 1980 in Barrels[10]
| Year | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reserves (Thosuand million barrel) | 2.9 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.3 |
Table.28: Egyptian Oil Production in Barrels since 1965[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prduction (1000 barrels/day) | 126 | 228 | 882 | 924 | 779 | 672 | 725 | 726 | 691 | 660 |
Table.29: Egyptian Oil Consumption since 1965[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption (1000 barrels/day) | 131 | 159 | 406 | 463 | 552 | 617 | 766 | 833 | 854 | 816 |
Table.30: Egyptian Refinery/Oil Products' Production since 1980[10]
| Year | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Output (1000 barrels/day) | 277 | 489 | 497 | 580 | 530 | 509 | 508 |
Table.31: Egyptian Refinery/Oil Products' Production Capacity since 1965[10]
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity (1000 barrels/day) | 181 | 201 | 433 | 633 | 654 | 810 | 810 | 810 | 810 | 810 |
Natural Gas
| Year | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Reserves | .1 | .4 | 1.4 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Year | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production Capacity | .1 | 2.1 | 7.8 | 20.2 | 59 | 42.6 | 40.3 | 49 |
| Year | 1965 | 1975 | 1985 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption Capacity (Bcm) | <.1 | <.1 | 4.7 | 12.1 | 19.3 | 30.4 | 43.4 | 46 | 49.4 | 56 |
Key Problems of the Energy Sector
The main and utmost challenge that Egypt currently faces, that is mentioned in almost any literature that is related to energy in Egypt, is the un-controlable and continuously increasing population growth. Yet, the Egyptian energy sector has few other challenges that need to be dealt with adequately and seriously, otherwise Egypt will have to deal with a catastrophic energy situation within the few years to come. These challenges can be summarized in the following points:
- The decline of Egyptian oil and natural gas reserves; as proved oil reserves have decreased from 4.5 million barrels in 2009 to 4.2 million barrels in 2013, while natural gas reserves have decreased from 78 trillion cubic feet in 2010 to 77.2 trillion cubic feet in 2014[2][3][4][5].
- The fact that the current Egyptian energy mixture is not properly diversified, as Egypt, heavily and mainly depends on oil, natural gas and the hydroelectric power from the Nile, with the third being close to nothing and even descending more, then Egypt is left with only both oil and natural gas representing approximately 90.4-94.4% of the total primary energy consumption till 2014[2][3][4].
- The gap between supply and demand of oil, since the supply ratio is about 52.7% of the demand[2][3][5].
- The majority of the Egyptian imported oil (~4.9 million tons), comes only from three suppliers: Kuwait, Iraq and Oman –according to the Egyptian Ministry of Petroleum- in 2014[2]. Such a low variety of oil importers increases the probability of the risk of Egypt being negatively affected by any geopolitical instabilities in one or all of these importers, consequently affecting its ability to secure domestic demands in such situations[2].
- The low percentage of private investment in the energy sector (~16% in 2014/15), which in a way confines and hinders the technological aspects of energy production, distribution and consumption[2][3][4].
- The aging, un-maintained, low to non-efficient, mal-planned Egyptian infrastructure, especially in the energy sectors, which when faced with any sign of major problem, would lead to catastrophic outcomes, as for example, the daily blackouts of 2013 and 2014 summers, where electricity used to be completely absent allover Egypt for 6-8 hours/day through different times of the day[2][3][4].
- The non-existence of clear, to the point and profound strategies to be properly integrated in the Egyptian energy sector, and the un-clarity and complete randomness of the existent mixed ones, which are mostly unreliable, un-applicable strategies designed by totally different and varied institutions and energy-suppliers with different agendas and mentalities, eventually hindering any possible appropriate application or planning a proper solution(s) to secure energy supply[2].
Policy Framework, Laws and Regulations
General Information
The combination of increasing demand, decreasing production and high subsidies for fuel have put a strain on the Egyptian energy sector and led to an enormous public deficit. As of June 2014, Egypt owed 7.5 billion USD and counting to foreign oil and gas companies alone [20]. In order help meeting the energy demand and to prevent an Egyptian energy crisis, Gulf countries have been providing financial aid to Egypt. However, this kind of aid is expected to decrease as the Gulf countries are impacted by the falling oil prices of 2015.
One topic dominating energy policy debates in Egypt is the use of coal. In April 2014, the government approved the industrial use of coal. This is especially relevant for cement factories, as these are particularly energy intensive and have occasionally been cut off from the energy supply as the government's priority was to preserve gas for power generation[21].
Renewable Energy Policy
In February 2008, the Egyptian government adopted a New National Renewable Energy Strategy. It sets out the ambitious goal to achieve a generation of 20% of the country’s electricity from renewable resources by 2020. 12 percentage points (7,200 MW) are supposed to be covered by wind energy. One-third of the planned RE capacity will be state-owned projects financed through public investments by the New and Renewable Energy Agency (NREA) in cooperation with international financing institutions. Two thirds will be private sector projects, which will be supported by policies structured in three phases:
- Phase 1 will adopt competitive bids through issuing tenders requesting the private sector to supply electricity from renewable energy sources.
- In Phase 2, a feed-in-tariff will be implemented, in particular for medium and small size projects.
- Phase 3 allows investors to build and operate renewable energy power plants to satisfy their electricity needs or to sell electricity to other consumers through the national grid.
Also, an RE support fund is supposed to be established to cover the feed-in tariff payments.
In September 2014, the government approved the issuance of feed-in tariffs for solar PV and wind projects.
The new Presidential Decree 1947/2014 of October 2014 provides for fixed feed-in-tariffs over 25 years for PV and over 20 years for wind. These tariffs will be adjusted as soon as the following ceilings are reached: 300 MW of small PV (< 500 kW), 2000 MW of medium PV (500 kW – 50 MW), and 2000 MW of wind. The tariffs are going to be paid according to plant capacity. The details are outlined in a guiding document published by the Egyptian Electric Utility for Consumer Protection and Regulatory Agency (EgyptERA).
The FIT scheme is complemented by Law 203/2014 of 22 December 2014 whereby the Egyptian TSO (EETC) and the local distribution companies are obliged to connect a RES project to the grid. The costs of the connection shall be borne by the producer, while the government shall fund any extension of the grid. They are also obliged to purchase the electricity generated by qualifying projects and, if this is not feasible, compensate the producer.
Energy Efficiency Policy
Egypt has adopted a National Energy Efficiency Action Plan (NEEAP) (2012-2015) with cumulative energy efficiency targets of 5%. At the Council of Minister's secretariat, there is an EE unit which is the mandated entity for developing and implementing this plan. However, there is no designated energy efficiency agency and no general legal framework for EE measures[22].
Some steps have been taken to improve energy efficiency:
- Mandatory EE codes for residential buildings (2006), commercial buildings (2009), and government buildings (2011) have been adopted.
- Minimum performance standards with mandatory labeling schemes have been adopted for refrigerators, freezers, washing machines, air conditioners, CFLs, and electric water heaters.
By 2012, 750,000 m2 of Solar Water Heaters had been installed and 10.25 million Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs) had been distributed. However, there are no buildings which are built according to EE building code and no demonstration projects for energy-efficient buildings.
Institutional Set up in the Energy Sector
Governmental Bodies, Agencies & Utilities
| Body/Agency | Abbreviation | Establishment | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Electricity and Energy | MOEE | 1964 |
|
| New and Renewable Energy Authority |
NREA | 1986, by MOEE |
|
| Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency | EEAA | 1982, and restructured in 1994 |
|
| Egyptian Electric Utility and Consumer Protection Regulatory Agency | EgyptERA | 1997, upon decree |
|
| Egyptian Electricity Holding Company | EEHC | 2000, As a result of major institutional reform tha took place through law 164 |
|
| Egyptian Energy Transmission Company | EETC | 1976 |
|
The current Egyptian electricity market is completely composed of governmental owned utilities, which can be divided into: 6 for generation, 1 for transmission and 9 for distribution[23], which all are operating under the direct management of the EEHC, as shown in the following figure (Fig.20)[23].
On the other hand, the whole petroleum sector in Egypt is run by main five state-owned enterprises, with accordance to the latest EIA's Egypt's analysis brief (2018), which can be summarized in the following table.
| Enterprise | Abbreviaton | Establishment | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation | EGPC | 1956 |
(Focus on activities the country, except Southern) |
| Egyptian Natural Gas Holding Company | EGAS | 2001 |
|
| Egyptian Petrochemicals Holding Company | ECHEM | 2002 |
|
| Egyptian Mineral Resources Authority | EMRA | 1896 |
|
| Ganoub El-Wadi Holding Company | Ganope | 2003 |
(Focus on activities in the Southern Region) |
Others
In the area of fossil power plants, Egypt already works with Independent Power Producers (IPPs). The first contract under a power purchase agreement (PPA) was signed in 1998.[24]In 2012/13, the following IPPs feed a total 33 GWh into the Egyptian electricity grid: Petrochemicals (15 GWh), Carbon Black (1 GWh), Talkha Fertilizerand Ghazl El-Mahaala (17 GWh)[14].
The private sector is also involved via the “Build-Own-Operate-Transfer” (BOOT) scheme. Four steam power plants were operated with the BOOT model in 2012/13 and provided a total of 14,264 GWh. According to EgyptERA[25], the companies under the BOOT model are Suez Gulf Power Company (4,576 GWh), Port Said East Power Company (4,983 GWh) and Sidi Krir Generating Company (4,705 GWh). The power plants operated by these companies were built in 2001-2003, with an installed capacity of 682.5 MW each. All three BOOT companies were acquired by the Malaysian Powertek Energy in 2006/2007[26].
The Egyptian Wind Energy Association (EGWEA) is the umbrella organisation, representing the wind energy sector in Egypt. It assists interaction and co-operation between all relevant players with professional involvement in the field of wind energy. The EGWEA is organised in a global network of wind associations. It aims at promoting and supporting the development of wind energy in Egypt by providing the means to facilitate the exchange of technical information, expertise and experience in the wind energy sector. It conducts studies, provides information on tenders and conferences and organises workshops for interested parties. EGWEA is particularly interested in bringing forward wind energy interests of Egypt.
However, the association is also engaged in the promotion of wind energy in developing countries in general.
Energy Cooperation
At the European level, a Memorandum of Understanding to enhance EU-Egypt energy cooperation was signed in December 2008. The priority areas covered are, among others, the development of the Egyptian energy strategy, including the market reform, the convergence of Egypt’s energy market with that of the EU, the promotion of renewable energy and energy efficiency, the development of energy grids as well as technological and industrial cooperation.
Bilateral Energy Cooperation with Germany
Along with the World Bank, the African Development Bank, the United States, France, the EU and Japan, Germany is Egypt’s leading partner in terms of official development assistance. Egypt is one of the priority partner countries of the German development policy. Since 1963, Egypt has received approximately 6 billion EUR of aggregate commitments from Germany. The current focus areas of the bilateral cooperation are water management, renewable energies, energy efficiency and climate change.[27]
Within the framework of the German development cooperation, two initiatives to promote renewable energies and energy efficiency were launched in 2008:
- The Regional Center for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency (RCREEE), based in Cairo. Besides Egypt, other Arab members of the RCREEE are Algeria, Bahrain, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Palestine, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia and Yemen. RCREEE formulates and disseminates policies in support of RE and EE in the region and provides a platform for the regional exchange on policy issues and technological questions. In addition, RCREEE encourages the participation of the private sector to promote the establishment of a regional RE and EE industry.
- The Egyptian-German High-Level Committee on Renewable Energy, Energy Efficiency and Environmental Protection JCEE, is a bilateral Egyptian-German initiative. The JCEE is a platform for energy policy discussion, for developing initiatives for investment as well as institutional projects, awareness, and capacity building activities and establishing contacts and exchange between the two countries. The project is financed by the Egyptian Ministry of Electricity and Energy and the German Federal Ministry of Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). The implementing partners of the cooperation are NREA and GIZ.
Other Key Actors / Activities of Donors, Implementing Agencies, Civil Society Organisations
Further Information
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Obukhov. S. & Ibrahim A. (2017). Analysis of the Energy Potential of Renewable Energy Sources Egypt. MATEC Web Conference 141, 01035. Retrieved From: https://www.matec-conferences.org/articles/matecconf/pdf/2017/55/matecconf_smartgrids2017_01035.pdf
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 Atlam, B. and Rapiea, A. (2016). Assessing the Future of Energy Security in Egypt. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy. Vol, 6(4): 684-700. Retrieved From: http://www.econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/2777/1930
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 Hegazy, K. (2015). Energy Charter Secretariat Knowledge Centre’s Occasional Paper on Egypt’s Energy Sector: Regional Cooperation Outlook and Prospects of Furthering Engagement with The Energy Charter. Retrieved From: https://energycharter.org/fileadmin/DocumentsMedia/Occasional/Egypt_and_the_Charter.pdf
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 Park, S. (2015). American Security Project (ASP)’s Report on Energy in Egypt: Background and Issues. Retrieved From: https://www.americansecurityproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Ref-0190-Energy-in-Egypt-Background-and-Issues.pdf
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). (2018). Country Analysis Brief: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.eia.gov/beta/international/analysis_includes/countries_long/Egypt/egypt.pdf
- ↑ http://www.iea.org/statistics/statisticssearch/report/?year=2011&country=EGYPT&product=Balances
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 United Nations Environment Program (UNEP). (2017). Energy Profile: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/20490/Energy_profile_Egypt.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Tracking SDG7. (2018). The Energy Progress Report. Retrieved From: https://trackingsdg7.esmap.org/data/files/download-documents/tracking_sdg7-the_energy_progress_report_full_report.pdf
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 African Energy Commission (AFREC). (2017). Africa Energy Database. Retrieved From: https://afrec-energy.org/Docs/En/PDF/2017/statistics_2017_afrec.pdf
- ↑ 10.00 10.01 10.02 10.03 10.04 10.05 10.06 10.07 10.08 10.09 10.10 10.11 10.12 10.13 10.14 10.15 10.16 10.17 BP. (2018). BP Statistical Review of World Energy. Retrieved From: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy/downloads.html
- ↑ http://www.iisd.org/GSI/sites/default/files/ffs_egypt_update_august_2014.pdf
- ↑ http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/9da3cb08-007d-11e4-a3f2-00144feab7de.html#axzz3PwcopOCd
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). (2018). The World FactBook: Africa: Egypt. Retrieved From: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/eg.html
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 http://www.egelec.com/mysite1/pdf/report%20E.pdf
- ↑ https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 Abo Salem, A. (2017). Egyptian Renewable Energy Plan. Retrieved From: http://auptde.org/Article_Files/Egypt.pdf
- ↑ http://english.alarabiya.net/en/business/2014/07/04/Minister-Egypt-raises-electricity-prices-.html
- ↑ http://www.iea.org/statistics/statisticssearch/report/?year=2012&country=EGYPT&product=ElectricityandHeat
- ↑ https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1
- ↑ http://www.eia.gov/countries/cab.cfm?fips=eg
- ↑ http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/11/05/egypt-cement-coal-idUSL6N0SU2YB20141105
- ↑ http://www.rcreee.org/sites/default/files/egypt_ee_fact_sheet_print.pdf
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 Meier, P. Vagliasindi, M. Imran, M. Eberhard, A. & Siyambalapitiya, T. (2015). The Design and Sustainability of Renewable Energy Incentives: An Economic Analysis. Retrieved From: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1
- ↑ https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/20524/922240PUB0978100Box385358B00PUBLIC0.pdf?sequence=1
- ↑ http://egyptera.org/en/curr_egy.aspx
- ↑ http://www.powertek.com.my/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=60&Itemid=70
- ↑ http://www.auswaertiges-amt.de/EN/Aussenpolitik/Laender/Laenderinfos/01-Nodes/Aegypten_node.html