Difference between revisions of "Kazakhstan Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
Population- Rural | Population- Rural | ||
| − | | 41% (6.4 million | + | | |
| + | 41% (6.4 million | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Population- Urban | + | | |
| − | | 59% (9.1 million) | + | Population- Urban |
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | 59% (9.1 million) | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Population Density | Population Density | ||
| − | | 6 people/ km² (one of lowest in the world) | + | | |
| + | 6 people/ km² (one of lowest in the world) | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Avg. Household | + | Avg. Household Size |
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | 6 members | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 86: | Line 96: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | GDP | + | GDP per Capita <br> |
| | | | ||
| Line 92: | Line 102: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | GNI | + | | |
| − | | $ 7769.40 | + | GNI per Capita |
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | $ 7769.40 | ||
| + | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 103: | Line 117: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Time | + | Time Zone<br> |
| | | | ||
| Line 110: | Line 124: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | Calling | + | Calling Code<br> |
| | | | ||
| Line 158: | Line 172: | ||
==== Sources ==== | ==== Sources ==== | ||
| + | Biomass and hydropower <ref name="IEA">http://iea.org/stats/renewdata.asp?COUNTRY_CODE=KZ</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== Stability ==== | ==== Stability ==== | ||
| − | + | The losses of energy in the transmission and distribution process are 25–50%. | |
| − | |||
| − | The losses of energy in the transmission and distribution process are 25–50%. | ||
== Energy Consumption == | == Energy Consumption == | ||
| Line 180: | Line 190: | ||
==== Share of Fuel Types ==== | ==== Share of Fuel Types ==== | ||
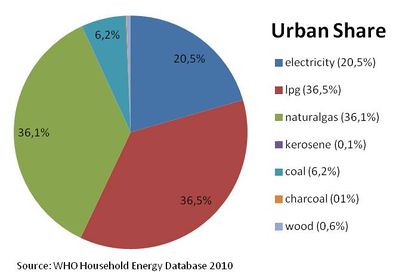
| − | + | Percentage of energy types used for cooking in urban areas <ref name="WHO 2010">fckLRWHO 2010: WHO Household Energy Database</ref> | |
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 188: | Line 198: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
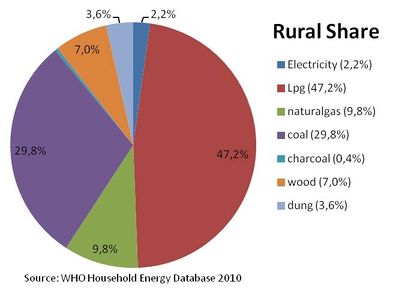
| − | + | Percentage of energy types used for cooking in rural areas<ref name="WHO 2010">WHO 2010: WHO Household Energy Database</ref> | |
| | ||
| Line 200: | Line 210: | ||
==== Share of Solid Fuels<ref name="WHO 2007">WHO 2007</ref> ==== | ==== Share of Solid Fuels<ref name="WHO 2007">WHO 2007</ref> ==== | ||
| − | Percentage of population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy: | + | Percentage of population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy: |
| − | National: 11.6%, Urban: 5.5%, Rural: 25.2% | + | National: 11.6%, Urban: 5.5%, Rural: 25.2% |
==== Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health<ref name="WHO" /> ==== | ==== Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health<ref name="WHO" /> ==== | ||
| Line 216: | Line 226: | ||
=== Electrification Rate === | === Electrification Rate === | ||
| − | + | 72,7% | |
| − | |||
| − | 72,7% | ||
== Renewable Energies == | == Renewable Energies == | ||
| − | === In Use === | + | === In Use === |
| − | wind and hydropower | + | wind and hydropower |
| − | === Potentials<ref name="INOGATE">http://www.inogate.org/index.php?option=com_inogate&view=countrysector&id=30&Itemid=63&lang=en</ref> === | + | === Potentials<ref name="INOGATE">http://www.inogate.org/index.php?option=com_inogate&amp;view=countrysector&amp;id=30&amp;Itemid=63&amp;lang=en</ref> === |
Wind energy: Kazakhstan has enormous wind resources but only a small part of the wind potential is used; 500kv out of a potential of 1.3 trillion kWh of electric energy per year at the Jungar Gates.<br> | Wind energy: Kazakhstan has enormous wind resources but only a small part of the wind potential is used; 500kv out of a potential of 1.3 trillion kWh of electric energy per year at the Jungar Gates.<br> | ||
| − | Despite the very favourable conditions for solar energy, there is little use of the resource. | + | Despite the very favourable conditions for solar energy, there is little use of the resource. |
==== Solar Energy ==== | ==== Solar Energy ==== | ||
| Line 276: | Line 284: | ||
=== Specific strategies (Biomass, renewable energies, rural electrification, energy access strategy etc.) === | === Specific strategies (Biomass, renewable energies, rural electrification, energy access strategy etc.) === | ||
| − | + | RE-Law from 2009: 5% of Kazakhstan’s energy balance must by renewable by 2024. The law also uses feed-in tariffs and renewable energy certificates to encourage renewable energy investment. | |
| − | |||
| − | RE-Law from 2009: 5% of Kazakhstan’s energy balance must by renewable by 2024. The law also uses feed-in tariffs and renewable energy certificates to encourage renewable energy investment. | ||
== Institutional set up in the energy sector == | == Institutional set up in the energy sector == | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 1 November 2011
| Kazakhstan | |||
| |
| ||
|
Capital |
Astana (51°10′N 71°25′E) | ||
|
Official language(s) |
Kazakh (1st)/Russian (2nd) | ||
|
Government |
Presidential republic | ||
|
President |
Nursultan Nazarbayev | ||
|
Prime Minister |
Karim Massimov | ||
|
Total area |
2,724,900 km2 | ||
|
Population |
16,600,000 (2011 estimate) | ||
|
Population- Rural |
41% (6.4 million | ||
|
Population- Urban |
59% (9.1 million) | ||
|
Population Density |
6 people/ km² (one of lowest in the world) | ||
|
Avg. Household Size |
6 members | ||
|
Literacy Rate |
99.5% | ||
|
GDP (nominal) |
$180.147 billion | ||
|
GDP per Capita |
$10,951 | ||
|
GNI per Capita |
$ 7769.40 | ||
|
Currency |
Tenge (KZT) | ||
|
Time Zone |
(UTC+5/6) | ||
|
Calling Code |
+7-6xx, +7-7xx | ||
Environmental Sitution
Climate:
Continental, cold winters and hot summers, arid and semiarid[1]
Mean temperature (°C min/max)[2] : 3.8/14.6
Resources:
natural gas, coal, major deposits of petroleum[1]
Forest situation [3]:
Land Area Covered by Forest: 1.2%
Forest Annual Rate of Change: -0.17%
Socioeconomical Situation
Income Sources[1]
Agriculture: 28%, Industry: 18%, Services: 54%
Energy Situation
Type your text here
Energy Supply
Type your text here
Electricity
Sources
Biomass and hydropower [4]
Stability
The losses of energy in the transmission and distribution process are 25–50%.
Energy Consumption
Type your text here
National Level
Electricity
Household Level
Percentage of energy types used for cooking in urban areas [5]
Percentage of energy types used for cooking in rural areas[5]
Percentage of population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy:
National: 11.6%, Urban: 5.5%, Rural: 25.2%
Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health[7]
• Total annual deaths attributable to solid fuel use: < 100 persons
• Percentage of national burden of diseases attributable to solid fuel use: 0%
Type your text here
Access Rate
Electrification Rate
72,7%
Renewable Energies
In Use
wind and hydropower
Potentials[8]
Wind energy: Kazakhstan has enormous wind resources but only a small part of the wind potential is used; 500kv out of a potential of 1.3 trillion kWh of electric energy per year at the Jungar Gates.
Despite the very favourable conditions for solar energy, there is little use of the resource.
Solar Energy
Type your text here
Wind Energy
Type your text here
Biomass
Type your text here
Biogas
Type your text here
Hydro Power
Type your text here
Other renewable Sources
Type your text here
Key problems of the energy sector
Type your text here
Policy framework, laws and regulations
Type your text here
General Energy policy, Energy strategy
Type your text here
Important Laws and regulations
Type your text here
Specific strategies (Biomass, renewable energies, rural electrification, energy access strategy etc.)
RE-Law from 2009: 5% of Kazakhstan’s energy balance must by renewable by 2024. The law also uses feed-in tariffs and renewable energy certificates to encourage renewable energy investment.
Institutional set up in the energy sector
Type your text here
Governmental institutions Private sector (enterprises, NGOs)
Type your text here
Activities of other donors, activities of NGOs
Type your text here
Existing projects
Type your text here
Publications
Type your text here
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/kz.html
- ↑ http://data.un.org/CountryProfile.aspx?crName=Kazakhstan
- ↑ http://rainforests.mongabay.com/deforestation/
- ↑ http://iea.org/stats/renewdata.asp?COUNTRY_CODE=KZ
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 fckLRWHO 2010: WHO Household Energy Database Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "WHO 2010" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ WHO 2007
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedWHO - ↑ http://www.inogate.org/index.php?option=com_inogate&view=countrysector&id=30&Itemid=63&lang=en