Click here to register!
Wind Turbine Technology
Wind turbine control concepts
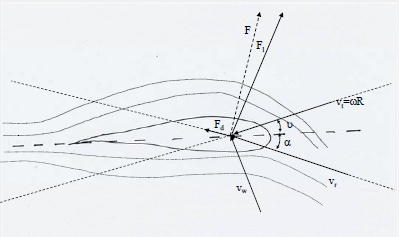
Aerodynamics
Stall
Stall Control:
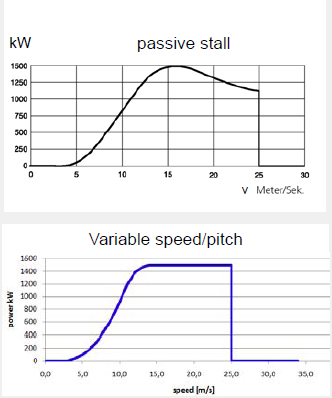
– Passive Stall:
Power of the wind turbine is limited by the aerodynamic characteristics
of the turbine.
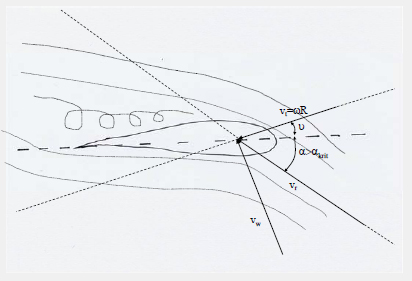
– Active stall:
Power of the wind turbine is limited additionally by decreasing the pitch
angle (increasing the inflow angle ).
Pitch
Pitch Control:
– Power of the wind turbine is limited by increasing the pitch angle
(decreasing the inflow angle )
Wind turbine operation
Operation of Fix Speed Wind Turbine (passive stall)
• Start up (with open breaker) if wind speed > cut-in wind speed
• Close breaker
• Operation at constant blade angle over the whole wind speed range
• In case of large wind speeds: Power limited by aerodynamic profile.
Operation of Variable Speed Wind-Turbines
Start up (with open breaker) if wind speed > cut-in wi
nd speed
• Close breaker
• Below rated wind-speed
– Maximum power coefficient (Max. Power Tracking)
– Evt: Speed Limitation
• Above rated wind-speed:
– P=Pr
ated (Limited by power electronics converter)
– Pitching
• Advantages of variable speed operation:
– Lower cut-in wind speeds
– Higher efficiency, especially at low wind speeds
– Lower power variations (compared to fixed speed turbines)
• Disadvantage: More expensive!
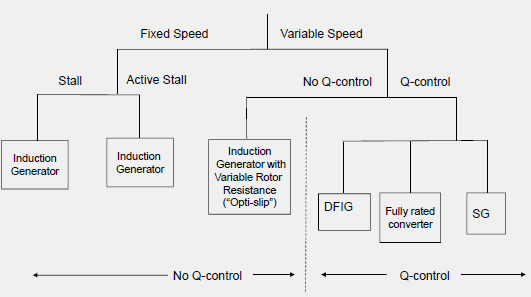
Generator concepts
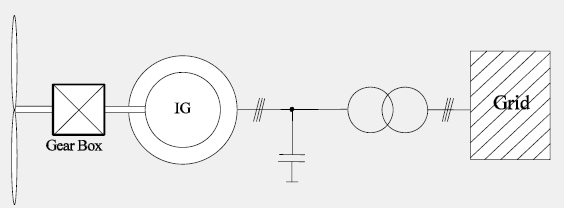
Fixed Speed Induction Generator
Only fix speed operation possible (stall control required)
• Reactive power compensation required
• No reactive power control capability. Additional devices required:
– TSCs (Thyristor switched capacitors)
– STATCOMs
• Risk of dynamic voltage collapse
GTZ Expert Workshop 2010: Grid and System Integration of Wind Energy, 22/23.11.2010, Berlin/Germany
y g p
– > Typically, wind generators based on induction generators are asked to
disconnect in case of voltage dips
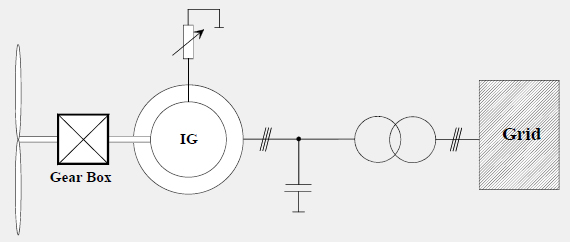
Induction Generator with Variable Rotor Resistance
Simple concept for variable speed operation.
• Reactive power compensation required.
• No reactive power control capability. Additional devices required:
– TSCs (Thyristor switched capacitors)
– STATCOMs
• Limited LVRT capability. Dynamic voltage collapse problems have to
GTZ Expert Workshop 2010: Grid and System Integration of Wind Energy, 22/23.11.2010, Berlin/Germany
be mitigated by:
– Fast increase of rotor resistance during faults
– Additional reactive power compensation devices (typically TSCs)
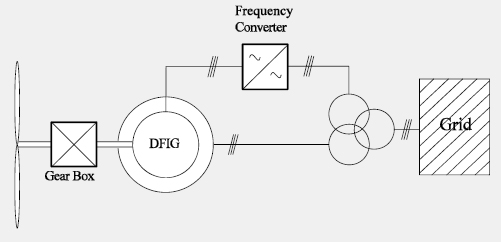
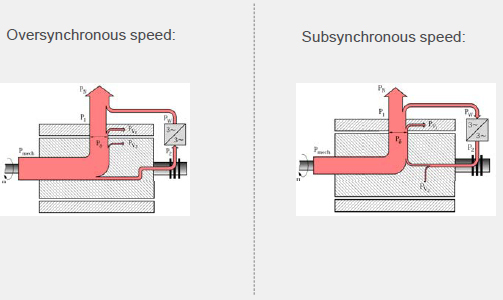
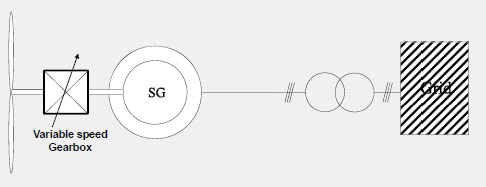
Doubly-Fed Induction Generator
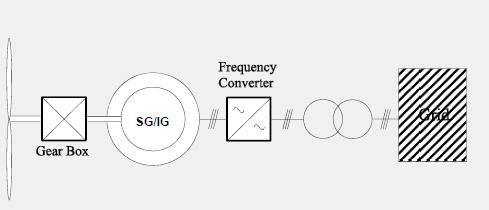
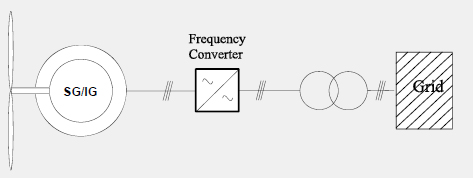
Generator with Fully Rated Converter
Generator with fully rated converter and direct drive