Difference between revisions of "Comply with Policies and Regulations"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Fundamental remarks== | ==Fundamental remarks== | ||
| + | '''<u>Mini grids</u>''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Over the last few years, mini-grids have played a key role in implementing Nigeria’s energy access and sustainable energy goals. They are now widely acknowledged as an integral component of the country’s energy ecosystem, delivering sustainable and reliable electricity access to nearly 27 thousand households living in areas that, until now, were out of reach of or unreliably served by the main grid infrastructure<ref>REAN (2022) Future-proofing the expanding market: Recommendations for improving the bankability of the mini-grid regulatory framework in Nigeria. Multi-stakeholder position paper. Available at: <nowiki>https://rean.org.ng/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/221220-NG-mini-grid-position-paper-1.pdf</nowiki> </ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 2016, two significant developments took place in the Nigerian energy sector. First, the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) released the [https://rea.gov.ng/download/rural-electrification-strategy-implementation-plan-resip/ Rural Electrification Strategy and Implementation Plan (RESIP)], which acknowledged mini-grids’ role in closing the energy access gap and improving supply. In the same year, the Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC) approved comprehensive mini-grid regulation, [https://rea.gov.ng/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/NERC-Mini-Grid-Regulation.pdf NERC Regulation for Mini-grids 2016], covering a broad set of issues, from mini-grid licensing to quality standards and tariff design. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Table 1: Summary of Key Policies Governing Off-grid Sector<ref>USAID (2021) PA-NPSP Off-Grid Market Intelligence Report. The Nigeria Power Sector Reform Program. </ref> | Table 1: Summary of Key Policies Governing Off-grid Sector<ref>USAID (2021) PA-NPSP Off-Grid Market Intelligence Report. The Nigeria Power Sector Reform Program. </ref> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 48: | Line 55: | ||
|This regulation was approved by NERC in 2014 and aims to promote the deliberate utilization of local human workforce and material resources across the value chain of the Nigerian Electricity Supply Industry (NESI). | |This regulation was approved by NERC in 2014 and aims to promote the deliberate utilization of local human workforce and material resources across the value chain of the Nigerian Electricity Supply Industry (NESI). | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | In | + | The Energypedia article [[Policy and Regulatory Framework for Energy in Nigeria]] discusses the regulatory landscape in more detail. |
| + | ==Guiding Principles== | ||
| + | This subsection will touch on regulations and policies that directly govern the development of minigrids, manufacturing and distribution of SHS, including regulations for consumer payments, and customs and importation duties. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Consumer payments === | ||
| + | Nigeria is largely a cash-based economy. In recent years, while mobile payment transactions have become more widely adopted, penetration still remains low. To tackle this issue, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) introduced Payment Service Banks (PSBs) in 2018. These PSBs enable telecom companies to use their extensive networks to offer financial services in underserved areas of Nigeria. While PSBs are relatively new, they hold great promise for off-grid companies looking to simplify payments for their offerings, especially in financially underserved regions<ref name=":0" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Relevant CBN regulations for consumer payments include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Guidelines for the Regulation of Agent Banking and Relationships in Nigeria (2013) | ||
| + | *Regulatory Framework for Mobile Money Services in Nigeria | ||
| + | *Guidelines on Mobile Money Services in Nigeria (2015) | ||
| + | *Consumer Protection Regulations (2019) | ||
| + | * Guidelines for Licensing and Regulation of PSBs (Revised in 2020) | ||
| + | * CBN Regulatory and Supervisory Guidelines for Microfinance Banks in Nigeria (TBA) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Customs and importation=== | ||
| + | The relevant regulations governing the importation of off-grid components and products into Kenya are the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) Common External Tariff (CET) and SON Conformity Assessment Program (SONCAP). Table 2 summarizes the primary customs duties for off-grid components in Nigeria. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+Table 2: Summary of Custom Duties for Off-Grid Components<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| + | !Category | ||
| + | !Duty Assessed | ||
| + | !For Mini-grids | ||
| + | ! For SHS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PV Modules | ||
| + | | 0% | ||
| + | |Yes | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PV Systems | ||
| + | |5% | ||
| + | |Yes | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PV Generator | ||
| + | |5% | ||
| + | |Yes | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Lithium Batteries | ||
| + | |20% | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Yes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Others (SHS) | ||
| + | |5-20% | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Yes | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Setting up an off-grid business=== | ||
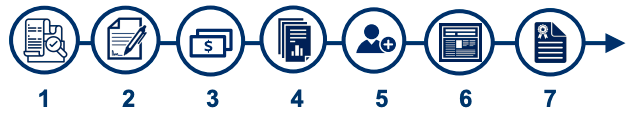
| + | According to the Doing Business Report by the World Bank, ease of doing business in Nigeria is low. It holds a score of 56.9, placing it at the 131st position among 190 countries<ref>World Bank. (2020). Ease of doing business in Nigeria. <nowiki>https://archive.doingbusiness.org/en/data/exploreeconomies/nigeria</nowiki></ref>. To tackle this challenge, key regulations pertaining to business establishment and registration in Nigeria are outlined in the Companies and Allied Matters Act of 2020. In August 2020, President Muhammadu Buhari of Nigeria signed into law the Companies and Allied Matters Act 2020 (CAMA 2020)<ref>Proshare. (2020). The Sea is History – the CAMA 2020 Aspires to Optimize Corporate Regulation. <nowiki>https://www.proshareng.com/news/DOING%20BUSINESS%20IN%20NIGERIA/The-Sea-is-History---the-CAMA-2020-Aspiresto-Optimize-Corporate-Regulation-in-Nigeria/52994</nowiki></ref>, replacing the previous 1990 Act. CAMA 2020 presents a comprehensive framework aimed at addressing burdensome legal, regulatory, and administrative hurdles that have made business operations particularly challenging, especially for MSMEs. Under this Act, the registration of businesses is handled by the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) – the government body responsible for providing business registration and regulatory services. Figure 8 illustrates the process for setting up a business in Nigeria. | ||
| + | Figure 1: Business registration process<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| − | + | [[File:Business Registration Process USAID.png]] | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |1 | ||
| + | |Check for availability of proposed company name. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2 | ||
| + | |Complete pre-registration form CAC 1.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |3 | ||
| + | |Pay filing and stamp duty fees. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |4 | ||
| + | |Prepare the signed scan copy of your pre-registration documents for uploads as follows: Form CAC 1.1 and the Memorandum and Article of Association (MEMART) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |5 | ||
| + | |Recognized form of identification for Director(s) Subscriber(s) and Secretary | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |6 | ||
| + | | Provide evidence of CAC and upload scanned documents for processing. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |7 | ||
| + | |Submit the original copies of the documents to the CAC office selected in exchange for your certificate and the Certified True copies of the documents. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | It is important to note the following for Foreign Nationals: | ||
| − | = | + | *Foreign nationals not resident in Nigeria do not require permits before establishing a business or investing in Nigeria. However, foreign national’s resident in Nigeria need a residence permit before forming a company. |
| + | *Companies intending to use the services of foreign workers need to obtain expatriate quota from the Nigerian Investment Promotion Council. | ||
| + | *Foreign companies intending to do business in Nigeria may apply for exemption from registration especially those undertaking special projects. <ref name=":0" /> | ||
| − | ====Provide training for your staff ==== | + | ====Provide training for your staff==== |
A cornerstone for the successful establishment and maintenance of an off-grid solar (OGS) project is its personnel. During the construction of the plant, care should be taken to train them beforehand. Before entering a solar plant, the employee needs a hazard briefing including health and safety regulations. The operation and maintenance (O&M) of the facility should be carried out by trained staff who meet the relevant qualifications to work safe, accountable and responsible. Especially in rural, emerging markets this can be challenging as qualified personnel is not always available. Therefore developers should consider offering their employee standard training which is provided by public training institutes and international organisations as well as further education opportunities for instance in the form of certifications/ diplomas. A selection of training institutions in the OGS sector can be found in Table 1. The industry is changing fast, and so is the technology. Therefore a developer should create a continuous internal and external training scheme, including opportunities for qualification and development<ref name=":1">Solar Power Europe (2021) Operation and Maintenance Best Practice Guidelines / Africa edition. Available at: <nowiki>https://api.solarpowereurope.org/uploads/Africa_edition_O_and_M_Best_Practice_Guidelines_fdea430b58.pdf</nowiki>.</ref>. | A cornerstone for the successful establishment and maintenance of an off-grid solar (OGS) project is its personnel. During the construction of the plant, care should be taken to train them beforehand. Before entering a solar plant, the employee needs a hazard briefing including health and safety regulations. The operation and maintenance (O&M) of the facility should be carried out by trained staff who meet the relevant qualifications to work safe, accountable and responsible. Especially in rural, emerging markets this can be challenging as qualified personnel is not always available. Therefore developers should consider offering their employee standard training which is provided by public training institutes and international organisations as well as further education opportunities for instance in the form of certifications/ diplomas. A selection of training institutions in the OGS sector can be found in Table 1. The industry is changing fast, and so is the technology. Therefore a developer should create a continuous internal and external training scheme, including opportunities for qualification and development<ref name=":1">Solar Power Europe (2021) Operation and Maintenance Best Practice Guidelines / Africa edition. Available at: <nowiki>https://api.solarpowereurope.org/uploads/Africa_edition_O_and_M_Best_Practice_Guidelines_fdea430b58.pdf</nowiki>.</ref>. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | |+Table 1: List of training institutions and materials (own extended illustration based on USAID, 2022<ref>USAID & Power Africa. (2022). PA NPSP Off-Grid Market Intelligence Report. <nowiki>https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PA00ZB5X.pdf</nowiki></ref>) | + | |+Table 1: List of training institutions and materials (own extended illustration based on USAID, 2022<ref name=":0">USAID & Power Africa. (2022). PA NPSP Off-Grid Market Intelligence Report. <nowiki>https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PA00ZB5X.pdf</nowiki></ref>) |
!Name | !Name | ||
!Area of action | !Area of action | ||
| Line 101: | Line 184: | ||
*Technical vocational education & training TVET) | *Technical vocational education & training TVET) | ||
*Energy management course | *Energy management course | ||
| − | *Solar system sizing & maintenance | + | * Solar system sizing & maintenance |
*Finance | *Finance | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[https://ecowatt.com.ng/ Ecowatt Nigeria] | |[https://ecowatt.com.ng/ Ecowatt Nigeria] | ||
| − | |Nigeria | + | | Nigeria |
| − | |Ecowatt is a solution provider for sustainable development with focus on affordable and clean energy development. The company offers hands-on training courses and workshops which can vary from standard to tailor-made courses. They also organize trainings and study tours to Germany/Europe. | + | | Ecowatt is a solution provider for sustainable development with focus on affordable and clean energy development. The company offers hands-on training courses and workshops which can vary from standard to tailor-made courses. They also organize trainings and study tours to Germany/Europe. |
*Due Diligence for Solar | *Due Diligence for Solar | ||
| Line 117: | Line 200: | ||
|GreCo Academy provides quality training that covers the entire solar energy value chain from finance, marketing, management policy-making and solar engineering. They also offer a variety of free courses. Excerpt of course offer: | |GreCo Academy provides quality training that covers the entire solar energy value chain from finance, marketing, management policy-making and solar engineering. They also offer a variety of free courses. Excerpt of course offer: | ||
| − | * Basics of how to start a solar business | + | *Basics of how to start a solar business |
*Business and Finance | *Business and Finance | ||
*Energy efficiency in buildings | *Energy efficiency in buildings | ||
| Line 137: | Line 220: | ||
Non technical courses: | Non technical courses: | ||
| − | * Leadership & Management | + | *Leadership & Management |
*Marketing & Customer Service | *Marketing & Customer Service | ||
*Electricity trading, regulation & pricing | *Electricity trading, regulation & pricing | ||
| Line 147: | Line 230: | ||
*Design and Installation | *Design and Installation | ||
| − | * Safety course | + | *Safety course |
*Maintenance | *Maintenance | ||
*Business and entrepreneurship | *Business and entrepreneurship | ||
| Line 154: | Line 237: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[https://www.rubitecsolar.com/academy/ Rubitec Academy] | |[https://www.rubitecsolar.com/academy/ Rubitec Academy] | ||
| − | | Nigeria | + | |Nigeria |
|Rubitec Limited is a leading Nigerian renewable energy company. Rubitec Academy is an initiative to partner with academic and training institutions in Nigeria and abroad in developing future leaders in Renewable Energy and Environmental Science through a 1-year workplace training programme. Requirement is experience in the field. | |Rubitec Limited is a leading Nigerian renewable energy company. Rubitec Academy is an initiative to partner with academic and training institutions in Nigeria and abroad in developing future leaders in Renewable Energy and Environmental Science through a 1-year workplace training programme. Requirement is experience in the field. | ||
| Line 162: | Line 245: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==Existing Tools == | + | ==Existing Tools== |
* | * | ||
| Line 174: | Line 257: | ||
|[https://www.all-on.com/media/publications/simplified-guides-to-nigerias-energy-access-policies-and-regulations/_jcr_content/par/textimage.stream/1595008807872/c0fb235222b78a401a7d20fd05ed733af78e6b7d/mini-grid-regulations.pdf Regulations for Mini-Grids 2016, Simplified Summary] | |[https://www.all-on.com/media/publications/simplified-guides-to-nigerias-energy-access-policies-and-regulations/_jcr_content/par/textimage.stream/1595008807872/c0fb235222b78a401a7d20fd05ed733af78e6b7d/mini-grid-regulations.pdf Regulations for Mini-Grids 2016, Simplified Summary] | ||
|Yes | |Yes | ||
| − | | Yes | + | |Yes |
|This Guide provides a simplified summary of the regulation primarily for stakeholders in the off grid renewable energy sector. It further provides some context for the regulation – including the definition and types of mini-grids, process and requirements for permit and licenses, project development processes, tariffs and other charges, relationship between stakeholders, compliance and technical requirements, compensation, dispute resolution and current implementation status. | |This Guide provides a simplified summary of the regulation primarily for stakeholders in the off grid renewable energy sector. It further provides some context for the regulation – including the definition and types of mini-grids, process and requirements for permit and licenses, project development processes, tariffs and other charges, relationship between stakeholders, compliance and technical requirements, compensation, dispute resolution and current implementation status. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[https://rean.org.ng/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/221220-NG-mini-grid-position-paper-1.pdf Future-proofing the expanding market: Recommendations for improving the bankability of the mini-grid regulatory framework in Nigeria] | |[https://rean.org.ng/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/221220-NG-mini-grid-position-paper-1.pdf Future-proofing the expanding market: Recommendations for improving the bankability of the mini-grid regulatory framework in Nigeria] | ||
| − | | Yes | + | |Yes |
| − | | Yes | + | |Yes |
|This position paper aims to discuss further the identified gaps/lack of clarity – regulatory and policy – which are slowing down the scaling of the mini-grid sector in Nigeria and to propose ways for further improvement. It has been developed jointly by key stakeholders – developers, financiers, and industry associations – driving Nigeria's mini-grid sector's growth. | |This position paper aims to discuss further the identified gaps/lack of clarity – regulatory and policy – which are slowing down the scaling of the mini-grid sector in Nigeria and to propose ways for further improvement. It has been developed jointly by key stakeholders – developers, financiers, and industry associations – driving Nigeria's mini-grid sector's growth. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 193: | Line 276: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==Bibliography == | + | ==Bibliography== |
</div> <!-- End .Moz --> | </div> <!-- End .Moz --> | ||
Revision as of 10:05, 9 October 2023
Introduction
Nigerian developers working on decentralized renewable electricity solutions for off-grid areas should consider several key aspects of regulations and policies to ensure compliance and the successful implementation of their projects. This page will give an overview of the regulatory landscape and list tools and resources that are of use specifically for developers.
Fundamental remarks
Mini grids
Over the last few years, mini-grids have played a key role in implementing Nigeria’s energy access and sustainable energy goals. They are now widely acknowledged as an integral component of the country’s energy ecosystem, delivering sustainable and reliable electricity access to nearly 27 thousand households living in areas that, until now, were out of reach of or unreliably served by the main grid infrastructure[1].
In 2016, two significant developments took place in the Nigerian energy sector. First, the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) released the Rural Electrification Strategy and Implementation Plan (RESIP), which acknowledged mini-grids’ role in closing the energy access gap and improving supply. In the same year, the Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC) approved comprehensive mini-grid regulation, NERC Regulation for Mini-grids 2016, covering a broad set of issues, from mini-grid licensing to quality standards and tariff design.
Table 1: Summary of Key Policies Governing Off-grid Sector[2]
| Policy | Agency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| National Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Policy (NREEEP) | Federal Ministry of Power | This policy was approved by the Federal Executive Council in 2015 and details the Nigerian government’s blueprint for harnessing the country’s renewable energy resources to drive sustainable development. |
| National Renewable Energy Action Plans (NREAP) | Federal Ministry of Power | This action plan was approved by the National Council on Power (NACOP) in July 2016 and serves to implement the renewable energy component of the 2015 NREEEP. |
| National Energy Efficiency Action Plan (NEEAP) | Federal Ministry of Power | This action plan was approved by NACOP in July 2016 and serves to implement the energy efficiency component of the 2015 NREEEP. |
| Rural Electrification Strategy and Implementation Plan (RESIP) | Federal Ministry of Power/ REA | This strategy and implementation plan was approved in July 2016 and was prepared by the Federal Ministry of Power, Works and Housing (presently Federal Ministry of Power) to be executed by REA. The document was developed in line with FGN’s plan for rural electrification and provides the implementation framework and measures for driving rural electrification across the country using both on and off-grid energy solutions. |
| NERC Mini-Grid Regulations | NERC | These regulations were released by NERC in May 2017 and are the overarching document governing the development of mini-grid electricity generation (0-100 KW – 1 MW) in Nigeria. The regulation is designed to accelerate the electrification of unserved and underserved areas especially rural and peri-urban communities. It incentivizes and minimizes major risks associated with mini-grid investments and simplifies the process for private sector participation. |
| Sustainable Energy for All Action Agenda (SE4All-AA), | Federal Ministry of Power | Nigeria’s SE4All Action Agenda was approved by NACOP in July 2016. The key objectives of the SE4All initiatives globally are to ensure universal access to modern energy services, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency, and double the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix by 2030. |
| Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) | Federal Ministry of Environment | Nigeria’s NDCs are its global commitment to sustainable development measures that limit the rate of global warming and negative impacts of climate change. It includes the country’s climate targets and plans to achieve them |
| NERC Eligible Customer Regulations | NERC | The Eligible Customer Regulations were approved in 2017 by NERC and permit electricity companies and Independent Power Producers (IPPs) to by-pass the Bulk Trader (the Nigerian Bulk Electricity Trading Plc (NBET) and DISCOs in order to sell electricity directly to eligible customers. |
| Regulation on National Content Development for the Power Sector | NERC | This regulation was approved by NERC in 2014 and aims to promote the deliberate utilization of local human workforce and material resources across the value chain of the Nigerian Electricity Supply Industry (NESI). |
The Energypedia article Policy and Regulatory Framework for Energy in Nigeria discusses the regulatory landscape in more detail.
Guiding Principles
This subsection will touch on regulations and policies that directly govern the development of minigrids, manufacturing and distribution of SHS, including regulations for consumer payments, and customs and importation duties.
Consumer payments
Nigeria is largely a cash-based economy. In recent years, while mobile payment transactions have become more widely adopted, penetration still remains low. To tackle this issue, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) introduced Payment Service Banks (PSBs) in 2018. These PSBs enable telecom companies to use their extensive networks to offer financial services in underserved areas of Nigeria. While PSBs are relatively new, they hold great promise for off-grid companies looking to simplify payments for their offerings, especially in financially underserved regions[3].
Relevant CBN regulations for consumer payments include:
- Guidelines for the Regulation of Agent Banking and Relationships in Nigeria (2013)
- Regulatory Framework for Mobile Money Services in Nigeria
- Guidelines on Mobile Money Services in Nigeria (2015)
- Consumer Protection Regulations (2019)
- Guidelines for Licensing and Regulation of PSBs (Revised in 2020)
- CBN Regulatory and Supervisory Guidelines for Microfinance Banks in Nigeria (TBA)
Customs and importation
The relevant regulations governing the importation of off-grid components and products into Kenya are the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) Common External Tariff (CET) and SON Conformity Assessment Program (SONCAP). Table 2 summarizes the primary customs duties for off-grid components in Nigeria.
| Category | Duty Assessed | For Mini-grids | For SHS |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV Modules | 0% | Yes | |
| PV Systems | 5% | Yes | |
| PV Generator | 5% | Yes | |
| Lithium Batteries | 20% | Yes | |
| Others (SHS) | 5-20% | Yes |
Setting up an off-grid business
According to the Doing Business Report by the World Bank, ease of doing business in Nigeria is low. It holds a score of 56.9, placing it at the 131st position among 190 countries[4]. To tackle this challenge, key regulations pertaining to business establishment and registration in Nigeria are outlined in the Companies and Allied Matters Act of 2020. In August 2020, President Muhammadu Buhari of Nigeria signed into law the Companies and Allied Matters Act 2020 (CAMA 2020)[5], replacing the previous 1990 Act. CAMA 2020 presents a comprehensive framework aimed at addressing burdensome legal, regulatory, and administrative hurdles that have made business operations particularly challenging, especially for MSMEs. Under this Act, the registration of businesses is handled by the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) – the government body responsible for providing business registration and regulatory services. Figure 8 illustrates the process for setting up a business in Nigeria.
Figure 1: Business registration process[3]
| 1 | Check for availability of proposed company name. |
| 2 | Complete pre-registration form CAC 1.1 |
| 3 | Pay filing and stamp duty fees. |
| 4 | Prepare the signed scan copy of your pre-registration documents for uploads as follows: Form CAC 1.1 and the Memorandum and Article of Association (MEMART) |
| 5 | Recognized form of identification for Director(s) Subscriber(s) and Secretary |
| 6 | Provide evidence of CAC and upload scanned documents for processing. |
| 7 | Submit the original copies of the documents to the CAC office selected in exchange for your certificate and the Certified True copies of the documents. |
It is important to note the following for Foreign Nationals:
- Foreign nationals not resident in Nigeria do not require permits before establishing a business or investing in Nigeria. However, foreign national’s resident in Nigeria need a residence permit before forming a company.
- Companies intending to use the services of foreign workers need to obtain expatriate quota from the Nigerian Investment Promotion Council.
- Foreign companies intending to do business in Nigeria may apply for exemption from registration especially those undertaking special projects. [3]
Provide training for your staff
A cornerstone for the successful establishment and maintenance of an off-grid solar (OGS) project is its personnel. During the construction of the plant, care should be taken to train them beforehand. Before entering a solar plant, the employee needs a hazard briefing including health and safety regulations. The operation and maintenance (O&M) of the facility should be carried out by trained staff who meet the relevant qualifications to work safe, accountable and responsible. Especially in rural, emerging markets this can be challenging as qualified personnel is not always available. Therefore developers should consider offering their employee standard training which is provided by public training institutes and international organisations as well as further education opportunities for instance in the form of certifications/ diplomas. A selection of training institutions in the OGS sector can be found in Table 1. The industry is changing fast, and so is the technology. Therefore a developer should create a continuous internal and external training scheme, including opportunities for qualification and development[6].
| Name | Area of action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Renewables Academy (RENAC) | Worldwide, online | RENAC is a provider for training and capacity building on renewable energy and energy efficiency based in Germany. Additionally to solar energy, they also offer courses on other renewable energy sources as well as on business development. The offer includes a variety of ready-made trainings for individuals, tailor-made trainings for industry and organisations and academic programmes. The formats take place online or on-site at the RENAC training center in Berlin. In addition to the regular training programmes, RENAC also offers projects in partnership with other organisations in developing countries. These are usually free through financial support by third parties. |
| Energy Delivery Modes (EDM) Training by UNITAR | Online | The United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) offers a wide range of courses and training activities for a diverse audience. The free EDM training aims to build staff capacity to support the integration of energy access and sustainable delivery models of modern energy services into humanitarian and development programming. It is based on the EDM Toolkit developed by IIED and CAFOD. The course consists of three modules:
|
| Cornerstone of rural electrification (CORE) | Online | The CORE initiative was jointly launched by ARE, ICA, IRENA, SforAll, UNEO and UNIDO to address the immense capacity building and technical assistance needs to support the development of DRE systems. It offers technical assistance to Practitioners on aspects related to improving safety, efficiency and reliability of decentralised electrification projects; Communities (especially women) on productive use of electricity; and to Governments on enhancing the policy and regulatory framework in support of decentralised electrification. |
| Asteven Renewable Energy Academy | Nigeria, UK | Asteven Energy is the first Innovation Enterprise Institution(IEI) approved by the Federal Ministry of Education (FME) and accredited by Nigeria’s National Board for Technical Education (NBTE) to offer a National Innovation Diploma (NID) in Solar Energy Technology. It is accredited by the ECOWAS Center for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency (ECREEE) as a recognized institution for training and certification in Solar Photovoltaic (Off Grid) Installation in Nigeria. Offers:
|
| Ashdam Solar Academy | Nigeria, online | Ashdam Solar specialized in design, installation and O&M of off-grid solar systems in Nigeria. They offer a variety of online courses, including basic information of renewable energy generation over system configuration and installment to customer service. Furthermore they have several onsite and blended (online and onsite) courses. One example is the “Solar Queen Program” which explicitly addresses women. |
| Blue Camel Energy Academy | Nigeria, online | The academy provides a range of online and onsite (tailored) training services for the renewable energy industry. Excerpt from the course list:
|
| Ecowatt Nigeria | Nigeria | Ecowatt is a solution provider for sustainable development with focus on affordable and clean energy development. The company offers hands-on training courses and workshops which can vary from standard to tailor-made courses. They also organize trainings and study tours to Germany/Europe.
|
| GreCo Academy | Online | GreCo Academy provides quality training that covers the entire solar energy value chain from finance, marketing, management policy-making and solar engineering. They also offer a variety of free courses. Excerpt of course offer:
|
| National Power Training Institute of Nigeria (NAPTIN) | Nigeria | NAPTIN is a parastatal training institute under the supervision of the Federal Ministry of Power. In this context it offers training and certification among others for generation companies (GenCos) & distribution companies (DisCos), the Transmission Company of Nigeria (TCN) and the Rural Electrification Agency (REA). Excerpt of course offer:
Technical courses:
Non technical courses:
|
| Renewable Energy Technology Training Institute (RETTI) | Online | The training institute provides tailored education within and across the value chain of renewable energy and energy efficiency.
|
| Rubitec Academy | Nigeria | Rubitec Limited is a leading Nigerian renewable energy company. Rubitec Academy is an initiative to partner with academic and training institutions in Nigeria and abroad in developing future leaders in Renewable Energy and Environmental Science through a 1-year workplace training programme. Requirement is experience in the field.
|
Existing Tools
| Name | Nigeria specific | Open source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regulations for Mini-Grids 2016, Simplified Summary | Yes | Yes | This Guide provides a simplified summary of the regulation primarily for stakeholders in the off grid renewable energy sector. It further provides some context for the regulation – including the definition and types of mini-grids, process and requirements for permit and licenses, project development processes, tariffs and other charges, relationship between stakeholders, compliance and technical requirements, compensation, dispute resolution and current implementation status. |
| Future-proofing the expanding market: Recommendations for improving the bankability of the mini-grid regulatory framework in Nigeria | Yes | Yes | This position paper aims to discuss further the identified gaps/lack of clarity – regulatory and policy – which are slowing down the scaling of the mini-grid sector in Nigeria and to propose ways for further improvement. It has been developed jointly by key stakeholders – developers, financiers, and industry associations – driving Nigeria's mini-grid sector's growth. |
| Solar Power Europe - Operation & Maintenance: Best practice Guidelines Africa Edition | No | Yes | The document assists the reader in developing a general understanding of the topic. The guideline addresses O&M contractors as well as installers, owners, investors, financiers, monitoring tool providers, technical consultants and interested stakeholders in Sub-Saharan Africa. |
Bibliography
- ↑ REAN (2022) Future-proofing the expanding market: Recommendations for improving the bankability of the mini-grid regulatory framework in Nigeria. Multi-stakeholder position paper. Available at: https://rean.org.ng/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/221220-NG-mini-grid-position-paper-1.pdf
- ↑ USAID (2021) PA-NPSP Off-Grid Market Intelligence Report. The Nigeria Power Sector Reform Program.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 USAID & Power Africa. (2022). PA NPSP Off-Grid Market Intelligence Report. https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PA00ZB5X.pdf
- ↑ World Bank. (2020). Ease of doing business in Nigeria. https://archive.doingbusiness.org/en/data/exploreeconomies/nigeria
- ↑ Proshare. (2020). The Sea is History – the CAMA 2020 Aspires to Optimize Corporate Regulation. https://www.proshareng.com/news/DOING%20BUSINESS%20IN%20NIGERIA/The-Sea-is-History---the-CAMA-2020-Aspiresto-Optimize-Corporate-Regulation-in-Nigeria/52994
- ↑ Solar Power Europe (2021) Operation and Maintenance Best Practice Guidelines / Africa edition. Available at: https://api.solarpowereurope.org/uploads/Africa_edition_O_and_M_Best_Practice_Guidelines_fdea430b58.pdf.