Difference between revisions of "The Economics of Renewable Energy"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
= Overview = | = Overview = | ||
| − | In order to assess how [[Portal:Financing and Funding|private investment]] in <span data- | + | In order to assess how [[Portal:Financing and Funding|private investment]] in <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="1">renewables</span> can be increased, it is necessary to understand the economics of renewable energy. |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | + | = Rationale for <span data-scayt_word="Renewables" data-scaytid="4">Renewables</span> = | |
| − | Worldwide more energy is required to enable economic development. Fossil fuels are a finite resource that contribute to climate change and cause other problems like smog, extended supply lines and vulnerable power grids. Utilizing <span data- | + | Worldwide more energy is required to enable economic development. Fossil fuels are a finite resource that contribute to climate change and cause other problems like smog, extended supply lines and vulnerable power grids. Utilizing <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="2">renewables</span> would help to avoid these problems, create new job opportunities and reduce the drain on hard currency for poorer countries. Because conventional fuels have received long-term subsidies in the past, it is vital that governments support the development of <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="3">renewables</span> in the form of financial incentives that can create a level playing field <ref name="United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI), 2004. CEO briefing - Renewable Energy, Geneva, Switzerland: United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI).">United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI), 2004. CEO briefing - Renewable Energy, Geneva, Switzerland: United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI).</ref>. |
[[File:Economics of RE 1.PNG|thumb|right|300px|Investments in Renewables in 2012. Source: Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance]] | [[File:Economics of RE 1.PNG|thumb|right|300px|Investments in Renewables in 2012. Source: Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance]] | ||
<div></div> | <div></div> | ||
| − | According to [http://www.ren21.net/REN21Activities/GlobalFuturesReport.aspx REN-21’s Renewables Global Futures Report 2013], the future of renewable energy is uncertain as finance remains a key challenge. The future of the <span data- | + | According to [http://www.ren21.net/REN21Activities/GlobalFuturesReport.aspx REN-21’s Renewables Global Futures Report 2013], the future of renewable energy is uncertain as finance remains a key challenge. The future of the <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="8">renewables</span> industry depends on finance, risk-return profiles, business models, investment lifetimes and a host of other economic, policy and social factors. Many new [[Portal:Financing and Funding|sources of finance]] are possible such as insurance funds, pension funds and sovereign wealth funds along with new mechanisms for financial risk mitigation. Many new business models are also possible for local energy services, utility services, transport, community and cooperative ownership, and rural energy services <ref name="Appleyard, D., March 2013. The Future of Renewables: Economic, Policy and Social Impications - Renewable Energy World International. Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/03/from-the-editor20">Appleyard, D., March 2013. The Future of Renewables: Economic, Policy and Social Impications - Renewable Energy World International. Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/03/from-the-editor20</ref>. |
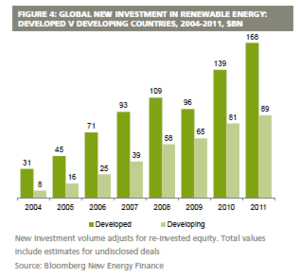
In 2011, the global investment in renewable power and fuels increased by 17% to a new record of $257 billion dollars. Significantly, developing economies made up 35% of this total investment <ref name="Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance, 2012. Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2012, Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance.">Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance, 2012. Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2012, Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance.</ref>. | In 2011, the global investment in renewable power and fuels increased by 17% to a new record of $257 billion dollars. Significantly, developing economies made up 35% of this total investment <ref name="Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance, 2012. Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2012, Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance.">Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance, 2012. Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2012, Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance.</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<div> | <div> | ||
| − | Despite these trends, renewable energy technologies (<span data- | + | <u>Despite these trends, '''renewable energy technologies (<span data-scayt_word="RETs" data-scaytid="12">RETs</span>) '''continue to face a number of '''[[Barriers and Risks to Renewable Energy Financing|barriers]] '''including:</u> |
*Financial and economic barriers such as higher upfront costs | *Financial and economic barriers such as higher upfront costs | ||
*Political and regulatory barriers due to policies generally not favoring renewable technologies | *Political and regulatory barriers due to policies generally not favoring renewable technologies | ||
| Line 24: | Line 26: | ||
*Technical barriers such as the intermittent nature of renewable technologies, issues related to the scale of the project and higher transaction costs. | *Technical barriers such as the intermittent nature of renewable technologies, issues related to the scale of the project and higher transaction costs. | ||
| − | When assessing decisions to support RET’s, policy-makers need answers to the following questions:<br/> | + | |
| − | #Are <span data- | + | |
| − | #Can <span data- | + | <u>When assessing decisions to support RET’s, policy-makers need answers to the following questions:</u><br/> |
| + | #Are <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="13">renewables</span> more expensive that fossil fuels?<br/> | ||
| + | #Can <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="15">renewables</span> be made available on a scale large enough to replace fossil fuels? | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | = <span style="font-size: 19px; line-height: 23px | + | = <span style="font-size: 19px; line-height: 23px">Costs of Renewable Energy</span> = |
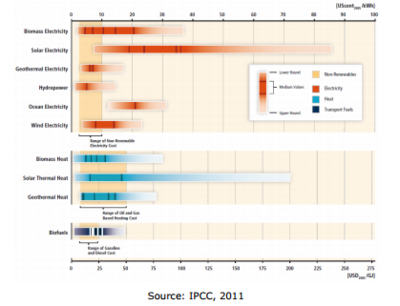
Generally the economics of renewable energy are not competitive, as production costs per unit of energy are usually higher than those for fossil fuels as depicted in the figure below, which shows the relative costs for renewable energy technologies compared with each other, and with non-renewable energy<ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. | Generally the economics of renewable energy are not competitive, as production costs per unit of energy are usually higher than those for fossil fuels as depicted in the figure below, which shows the relative costs for renewable energy technologies compared with each other, and with non-renewable energy<ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 40: | ||
[[File:Economics of RE 2.PNG|thumb|right|400px|Relative costs for renewable energy technologies compared with each other, and with non-renewable energy. Source: Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011.]] | [[File:Economics of RE 2.PNG|thumb|right|400px|Relative costs for renewable energy technologies compared with each other, and with non-renewable energy. Source: Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011.]] | ||
| − | As shown in the figure, while non-renewable costs are found in the range of US$0.3–US$0.10/<span data- | + | As shown in the figure, while non-renewable costs are found in the range of US$0.3–US$0.10/<span data-scayt_word="KwH" data-scaytid="18">KwH</span> (kilowatt hour), most <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="17">renewables</span> are '''more expensive''' and have a far '''greater cost range'''. This indicates the relative maturity of technologies and also the key significant '''cost difference of renewable energy production''' (which is dependent on factors such as wind speed and degrees of solar intensity.)<br/> |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | '''Scale '''is also an important issue. This is due to the fact that fossil-fuel technologies have been developed, improved and manufactured on an increasing scale for a century. This is not yet the case for <span data- | + | '''Scale '''is also an important issue. This is due to the fact that fossil-fuel technologies have been developed, improved and manufactured on an increasing scale for a century. This is not yet the case for <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="20">renewables</span><ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em">.</span> |
| − | These factors suggest that there is scope to reduce the varying production costs of <span data- | + | These factors suggest that there is scope to reduce the varying production costs of <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="22">renewables</span>.<span style="font-size: 0.85em; line-height: 1.5em"></span> |
*The most expensive form of renewable energy is [[Portal:Hydro|ocean/tidal electricity]], which, even at the bottom of the potential cost range, remains uncompetitive with fossil fuels. | *The most expensive form of renewable energy is [[Portal:Hydro|ocean/tidal electricity]], which, even at the bottom of the potential cost range, remains uncompetitive with fossil fuels. | ||
| − | **Onshore and offshore wind and large solar photovoltaic (PV) plants today require policy support in order to bridge the gap between generation costs and the market prices of electricity. This is expected to change in the near future as [http://iea-retd.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/20130710-RE-COST-FINAL-REPORT.pdf reported] by the [http://iea-retd.org/ International Energy Agency's Renewable Energy Technology Deployment Group] (<span data- | + | **Onshore and offshore wind and large solar photovoltaic (PV) plants today require policy support in order to bridge the gap between generation costs and the market prices of electricity. This is expected to change in the near future as [http://iea-retd.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/20130710-RE-COST-FINAL-REPORT.pdf reported] by the [http://iea-retd.org/ International Energy Agency's Renewable Energy Technology Deployment Group] (<span data-scayt_word="IEA" data-scaytid="24">IEA</span>). The report finds that technology and market dynamics are driving down the costs of renewable power generation while increasing the costs involved in non-renewable generation. Thus in the near future, onshore wind and large scale PV plants could be able to offer attractive business cases to investors in regions with a high proportion of thermal generation without resorting to incentives <ref name="Bayar, T., 2013. The Cost of New Renewable Power Generation: Approaching Parity? Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/07/costing-renewable-power-generation?cmpid=rss">Bayar, T., 2013. The Cost of New Renewable Power Generation: Approaching Parity? Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/07/costing-renewable-power-generation?cmpid=rss</ref>. |
| − | *The next is [[Portal:Solar|solar power]], which at its cheapest is potentially competitive with fossil fuels. However, its midrange costs are well above fossil fuels. This wide range reflects the cost implications of different technologies. For example, large-scale '''Concentrated Solar Power (<span data- | + | *The next is [[Portal:Solar|solar power]], which at its cheapest is potentially competitive with fossil fuels. However, its midrange costs are well above fossil fuels. This wide range reflects the cost implications of different technologies. For example, large-scale '''Concentrated Solar Power (<span data-scayt_word="CSP" data-scaytid="25">CSP</span>)''' techniques employed in a desert environment could produce electricity at a far lower cost than small solar panels fitted to residential properties.<br/> |
*[[Portal:Wind|Wind power]] can be cheaper, but remains more expensive than fossil fuels in most instances. This range reflects differing scales of energy generation, but also the different cost structures of onshore and offshore wind.<br/> | *[[Portal:Wind|Wind power]] can be cheaper, but remains more expensive than fossil fuels in most instances. This range reflects differing scales of energy generation, but also the different cost structures of onshore and offshore wind.<br/> | ||
*[[Portal:Bioenergy|Biomass]], [[Geothermal Energy|geothermal]] and [[Portal:Hydro|hydropower]] in particular are already competitive with fossil fuels in some circumstances <ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. | *[[Portal:Bioenergy|Biomass]], [[Geothermal Energy|geothermal]] and [[Portal:Hydro|hydropower]] in particular are already competitive with fossil fuels in some circumstances <ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 57: | ||
= Costs of Fossil Fuels = | = Costs of Fossil Fuels = | ||
| − | Costs relative to fossil fuels are also important particularly because: | + | <u>Costs relative to fossil fuels are also important particularly because:</u> |
'''1. Fossil-fuel energy does not reflect its full social costs. '''<br/> | '''1. Fossil-fuel energy does not reflect its full social costs. '''<br/> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 79: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | The International Energy Agency's (<span data- | + | The '''International Energy Agency's (<span data-scayt_word="IEA" data-scaytid="26">IEA</span>)''' [http://iea-retd.org/ Renewable Energy Technology Deployment Group] reports that generation costs for renewable power are also falling and approaching the costs for gas and coal fired plants, especially when the hidden subsidies that thermal generation plants receive is taken out of the equation. |
| − | On the other hand, the cost of gas and coal fired plants is increasing because they are being used less, largely due to policy support for <span data- | + | On the other hand, the cost of gas and coal fired plants is increasing because they are being used less, largely due to policy support for <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="28">renewables</span> construction delays, higher financing rates, and the increasing cost of fuel in some European countries and in Japan. |
| − | Crucially, the higher capital costs involved in some new-build thermal plants due to emission reduction systems will be positively or negatively influenced by the shape and provisions of future policies for emission control<ref name="Bayar, T., 2013. The Cost of New Renewable Power Generation: Approaching Parity? Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/07/costing-renewable-power-generation?cmpid=rss">Bayar, T., 2013. The Cost of New Renewable Power Generation: Approaching Parity? Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/07/costing-renewable-power-generation?cmpid=rss</ref><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em | + | Crucially, the higher capital costs involved in some new-build thermal plants due to emission reduction systems will be positively or negatively influenced by the shape and provisions of future policies for emission control<ref name="Bayar, T., 2013. The Cost of New Renewable Power Generation: Approaching Parity? Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/07/costing-renewable-power-generation?cmpid=rss">Bayar, T., 2013. The Cost of New Renewable Power Generation: Approaching Parity? Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/07/costing-renewable-power-generation?cmpid=rss</ref><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em">.</span> |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 86: | Line 90: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
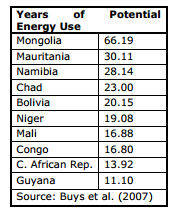
The table below shows the top 10 countries globally in terms of renewable energy potential relative to energy use. They are all developing countries, which reflects their relatively low energy use at present, but also the relative abundance of solar, wind, hydro and geothermal energy <ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. It's clear that there is significant scope to increase the use of renewable energy in developing countries. | The table below shows the top 10 countries globally in terms of renewable energy potential relative to energy use. They are all developing countries, which reflects their relatively low energy use at present, but also the relative abundance of solar, wind, hydro and geothermal energy <ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. It's clear that there is significant scope to increase the use of renewable energy in developing countries. | ||
| − | <div><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em | + | <div><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em"></span><br/></div> |
[[File:Economics of RE 4.PNG|thumb|center|180px|Top ten countries globally in terms of renewable energy potential relative to energy use.]] | [[File:Economics of RE 4.PNG|thumb|center|180px|Top ten countries globally in terms of renewable energy potential relative to energy use.]] | ||
| Line 93: | Line 97: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | = <span style="font-size: 22px; line-height: 30px | + | = <span style="font-size: 22px; line-height: 30px">Increasing the Use of Renewable Energy</span> = |
| − | There is significant scope to increase the use of <span data- | + | There is significant scope to increase the use of <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="34">renewables</span> especially in developing countries. However, this potential is not limitless. Although it can be expected that the costs of <span data-scayt_word="renewables" data-scaytid="35">renewables</span> will continue to fall relative to fossil fuels, (especially in countries with high renewable energy potential), fossil fuels will probably retain a cost advantage<ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em">.</span> |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | The <span data- | + | The <span data-scayt_word="IEA" data-scaytid="38">IEA</span> in a recent [http://iea-retd.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/20130710-RE-COST-FINAL-REPORT.pdf report] concluded that there is no unique costs of renewable or non-renewable power generation. Cost ranges associated with any power generation are relatively large and highly dependent on the regulatory and market contexts. |
The report stressed the necessity of maintaining current incentives in order to provide business cases that can interest investors as generally the costs of both new renewable power plants and new-non-renewable generation are higher than the market price of electricity. | The report stressed the necessity of maintaining current incentives in order to provide business cases that can interest investors as generally the costs of both new renewable power plants and new-non-renewable generation are higher than the market price of electricity. | ||
| Line 107: | Line 111: | ||
'''Expansion of Renewable Energy Use:''' | '''Expansion of Renewable Energy Use:''' | ||
#The basic economics of renewable energy need to be artificially altered, either by increasing the cost of fossil fuel-based energy (e.g. through taxes or equivalent mechanisms), or by reducing the costs of renewable energy (e.g. subsidies), or by boosting the returns to renewable energies (e.g. through paying a premium for this form of energy) <ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. | #The basic economics of renewable energy need to be artificially altered, either by increasing the cost of fossil fuel-based energy (e.g. through taxes or equivalent mechanisms), or by reducing the costs of renewable energy (e.g. subsidies), or by boosting the returns to renewable energies (e.g. through paying a premium for this form of energy) <ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref>. | ||
| − | #Developing countries should not necessarily be required to meet these costs. This is particularly so where the development of renewable energy capacity may place countries at a competitive disadvantage and/or these countries bear no responsibility for climate change. The costs should be met by countries that do bear these responsibilities. This case is even stronger while developed countries are [[Subsidies|subsidizing fossil-fuel energy]]<ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em | + | #Developing countries should not necessarily be required to meet these costs. This is particularly so where the development of renewable energy capacity may place countries at a competitive disadvantage and/or these countries bear no responsibility for climate change. The costs should be met by countries that do bear these responsibilities. This case is even stronger while developed countries are [[Subsidies|subsidizing fossil-fuel energy]]<ref name="Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf">Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf</ref><span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em">.</span><br/> |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 127: | Line 131: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| + | [[Category:Biomass]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Wind]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Bioenergy]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Geothermal]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Hydro]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Solar]] | ||
[[Category:Financing_and_Funding]] | [[Category:Financing_and_Funding]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 11:28, 12 June 2014
► Back to Financing & Funding Portal
Overview
In order to assess how private investment in renewables can be increased, it is necessary to understand the economics of renewable energy.
Rationale for Renewables
Worldwide more energy is required to enable economic development. Fossil fuels are a finite resource that contribute to climate change and cause other problems like smog, extended supply lines and vulnerable power grids. Utilizing renewables would help to avoid these problems, create new job opportunities and reduce the drain on hard currency for poorer countries. Because conventional fuels have received long-term subsidies in the past, it is vital that governments support the development of renewables in the form of financial incentives that can create a level playing field [1].
According to REN-21’s Renewables Global Futures Report 2013, the future of renewable energy is uncertain as finance remains a key challenge. The future of the renewables industry depends on finance, risk-return profiles, business models, investment lifetimes and a host of other economic, policy and social factors. Many new sources of finance are possible such as insurance funds, pension funds and sovereign wealth funds along with new mechanisms for financial risk mitigation. Many new business models are also possible for local energy services, utility services, transport, community and cooperative ownership, and rural energy services [2].
In 2011, the global investment in renewable power and fuels increased by 17% to a new record of $257 billion dollars. Significantly, developing economies made up 35% of this total investment [3].
Despite these trends, renewable energy technologies (RETs) continue to face a number of barriers including:
- Financial and economic barriers such as higher upfront costs
- Political and regulatory barriers due to policies generally not favoring renewable technologies
- Environmental and social barriers like planning objections
- Technical barriers such as the intermittent nature of renewable technologies, issues related to the scale of the project and higher transaction costs.
When assessing decisions to support RET’s, policy-makers need answers to the following questions:
- Are renewables more expensive that fossil fuels?
- Can renewables be made available on a scale large enough to replace fossil fuels?
Costs of Renewable Energy
Generally the economics of renewable energy are not competitive, as production costs per unit of energy are usually higher than those for fossil fuels as depicted in the figure below, which shows the relative costs for renewable energy technologies compared with each other, and with non-renewable energy[4].
As shown in the figure, while non-renewable costs are found in the range of US$0.3–US$0.10/KwH (kilowatt hour), most renewables are more expensive and have a far greater cost range. This indicates the relative maturity of technologies and also the key significant cost difference of renewable energy production (which is dependent on factors such as wind speed and degrees of solar intensity.)
Scale is also an important issue. This is due to the fact that fossil-fuel technologies have been developed, improved and manufactured on an increasing scale for a century. This is not yet the case for renewables[4].
These factors suggest that there is scope to reduce the varying production costs of renewables.
- The most expensive form of renewable energy is ocean/tidal electricity, which, even at the bottom of the potential cost range, remains uncompetitive with fossil fuels.
- Onshore and offshore wind and large solar photovoltaic (PV) plants today require policy support in order to bridge the gap between generation costs and the market prices of electricity. This is expected to change in the near future as reported by the International Energy Agency's Renewable Energy Technology Deployment Group (IEA). The report finds that technology and market dynamics are driving down the costs of renewable power generation while increasing the costs involved in non-renewable generation. Thus in the near future, onshore wind and large scale PV plants could be able to offer attractive business cases to investors in regions with a high proportion of thermal generation without resorting to incentives [5].
- The next is solar power, which at its cheapest is potentially competitive with fossil fuels. However, its midrange costs are well above fossil fuels. This wide range reflects the cost implications of different technologies. For example, large-scale Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) techniques employed in a desert environment could produce electricity at a far lower cost than small solar panels fitted to residential properties.
- Wind power can be cheaper, but remains more expensive than fossil fuels in most instances. This range reflects differing scales of energy generation, but also the different cost structures of onshore and offshore wind.
- Biomass, geothermal and hydropower in particular are already competitive with fossil fuels in some circumstances [4].
Costs of Fossil Fuels
Costs relative to fossil fuels are also important particularly because:
1. Fossil-fuel energy does not reflect its full social costs.
- Climate change has been described as the "biggest market failure in history" (Stern Review, 2006) because the environmental costs associated with carbon emissions are not included in market prices.
- Furthermore, fossil fuels are subsidized for about US$300 billion per year. Removing theses subsidies and incorporating externalities into fossil fuel costs would dramatically change relative costs[4].
2. It is more expensive to deliver non-renewable energy in some places than others.
- For example, rural communities in developing countries are often not connected to the grid, resulting in "off-grid" energy production - particularly solar power - being more competitive[4].
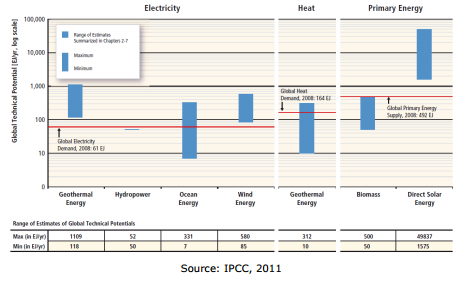
3. Fossil Fuels are fast depleting and more scarce than RE (See figure below).
- In terms of primary energy, it is already technically possible to generate many multiples of global energy supply using solar energy. There is also an abundant supply of wind or geothermal power to meet all of today’s global electricity demand[4].
The International Energy Agency's (IEA) Renewable Energy Technology Deployment Group reports that generation costs for renewable power are also falling and approaching the costs for gas and coal fired plants, especially when the hidden subsidies that thermal generation plants receive is taken out of the equation.
On the other hand, the cost of gas and coal fired plants is increasing because they are being used less, largely due to policy support for renewables construction delays, higher financing rates, and the increasing cost of fuel in some European countries and in Japan.
Crucially, the higher capital costs involved in some new-build thermal plants due to emission reduction systems will be positively or negatively influenced by the shape and provisions of future policies for emission control[5].
Significantly, much of the global solar power potential is concentrated in developing countries, although other areas also have a high potential.
The table below shows the top 10 countries globally in terms of renewable energy potential relative to energy use. They are all developing countries, which reflects their relatively low energy use at present, but also the relative abundance of solar, wind, hydro and geothermal energy [4]. It's clear that there is significant scope to increase the use of renewable energy in developing countries.
Currently most solar power installed globally is available in Europe, which accounts for more than 70% of the world's new PV installations[6].
Increasing the Use of Renewable Energy
There is significant scope to increase the use of renewables especially in developing countries. However, this potential is not limitless. Although it can be expected that the costs of renewables will continue to fall relative to fossil fuels, (especially in countries with high renewable energy potential), fossil fuels will probably retain a cost advantage[4].
The IEA in a recent report concluded that there is no unique costs of renewable or non-renewable power generation. Cost ranges associated with any power generation are relatively large and highly dependent on the regulatory and market contexts.
The report stressed the necessity of maintaining current incentives in order to provide business cases that can interest investors as generally the costs of both new renewable power plants and new-non-renewable generation are higher than the market price of electricity.
Expansion of Renewable Energy Use:
- The basic economics of renewable energy need to be artificially altered, either by increasing the cost of fossil fuel-based energy (e.g. through taxes or equivalent mechanisms), or by reducing the costs of renewable energy (e.g. subsidies), or by boosting the returns to renewable energies (e.g. through paying a premium for this form of energy) [4].
- Developing countries should not necessarily be required to meet these costs. This is particularly so where the development of renewable energy capacity may place countries at a competitive disadvantage and/or these countries bear no responsibility for climate change. The costs should be met by countries that do bear these responsibilities. This case is even stronger while developed countries are subsidizing fossil-fuel energy[4].
Further Information
- Assessing the Economic Viability of Business Ideas for Productive Use
- Economic and Financial Impacts of Grid Interconnections
- Economic Viability of a Biogas Plant
- Economic Analyses of Wind Energy Projects
- Macro-economic evaluation of Biogas Plants
- Socio-economic and Environmental Impacts of MHP
- Subsidies
References
- ↑ United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI), 2004. CEO briefing - Renewable Energy, Geneva, Switzerland: United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI).
- ↑ Appleyard, D., March 2013. The Future of Renewables: Economic, Policy and Social Impications - Renewable Energy World International. Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/03/from-the-editor20
- ↑ Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance, 2012. Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2012, Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Frankfurt School UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 Griffith-Jones, S., Ocampo, J. A. & Spratt, S., 2011. Financing Renewable Energy in Developing Countries: Mechanisms and Responsibilities. Available at: http://erd-report.eu/erd/report_2011/documents/dev-11-001-11researchpapers_griffith-jones-ocampo-spratt.pdf
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Bayar, T., 2013. The Cost of New Renewable Power Generation: Approaching Parity? Available at: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2013/07/costing-renewable-power-generation?cmpid=rss
- ↑ EPIA. Global Market Outlook for Photovoltaics 2013-2017. http://www.epia.org/news/publications/global-market-outlook-for-photovoltaics-2013-2017/