Difference between revisions of "Control Equipment - Hydropower"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
</o:shapelayout></xml><![endif]--><!--StartFragment--> | </o:shapelayout></xml><![endif]--><!--StartFragment--> | ||
| − | <span | + | <span style="display: none" id="1274973221030S"></span> |
| − | = Overview = | + | = Overview<br/> = |
| − | + | Load- or Flow- controller ensure that the power output does not exceed the power demand (e.g. 230V, 50 Hz).<br/>If flow of water in a MHP-station is constant the energy output of a turbine/generator is constant as well. Power demand is usually fluctuating over the time (e.g. day/night). If supply is higher than demand, excess energy must be diverted, dumped. Alternatively the water flow can be reduced which results in less power output. In case of more power demand than supply the controller cuts of the of demand line. Load controller are placed between generator output and the consumer line.<br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | <u>Function Principles:</u><br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Mhp-scheme.jpg|thumb|center|521px|MHP Scheme|alt=Mhp-scheme.jpg]] | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
</o:shapelayout></xml><![endif]--><!--StartFragment--> | </o:shapelayout></xml><![endif]--><!--StartFragment--> | ||
| − | == | + | == Load Controller<br/> == |
| − | [[File:Controler.jpg|right|320px|Controler | + | [[File:Controler.jpg|thumb|right|320px|Controler|alt=Controler.jpg]]<br/> |
Electronic circuit, which keeps output power constant in Frequency- and Voltage- parameters. | Electronic circuit, which keeps output power constant in Frequency- and Voltage- parameters. | ||
Fluctuating energy demand requires a mechanism which either regulates the water input into the turbine (= flow control) or by diverting excess energy from the consumer connection (= ballast load). | Fluctuating energy demand requires a mechanism which either regulates the water input into the turbine (= flow control) or by diverting excess energy from the consumer connection (= ballast load). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ► [[Hydropower_-_Equipment#Load_Control_Governors|Hydropower Equipment - Load Control Governors]]<br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 46: | ||
== Ballast Load<br/> == | == Ballast Load<br/> == | ||
| − | usually electrical heaters in water or air. If energy demand is temporarily low the excess energy is converted into heat. | + | Ballast load are usually electrical heaters in water or air. If energy demand is temporarily low the excess energy is converted into heat.<br/> |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 52: | ||
== Flow Control<br/> == | == Flow Control<br/> == | ||
| − | regulates the amount of water into the turbine in order to match power output and power demand. | + | The flow control regulates the amount of water into the turbine in order to match power output and power demand.<br/> |
| − | Nowadays flow control is done mostly via electronics (which steer a valve) | + | Nowadays flow control is done mostly via electronics (which steer a valve). |
| − | [[File:Flow-control.jpg| | + | [[File:Flow-control.jpg|thumb|center|547px|The principle of flow control|alt=principle flow control]]<br/> |
| − | |||
| − | <br/> | ||
| − | = Further Information = | + | = Further Information<br/> = |
| − | *[[Portal:Hydro|Portal | + | *[[Portal:Hydro|Hydro Portal on energypedia]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Electrical-Mechanical Equipment|Electrical-Mechanical Equipment]]<br/> |
| + | *[[Hydropower - Equipment|Hydropower - Equipment]]<br/> | ||
| + | *General: [[Micro Hydro Power (MHP) Manuals|Micro Hydro Power Manuals]] | ||
| + | *[[:File:Good and bad of mini hydro power vol.1.pdf|Good and Bad of Mini Hydro Power]] | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 70: | ||
= References<br/> = | = References<br/> = | ||
| − | <references /> | + | <references /><br/> |
[[Category:Hydro]] | [[Category:Hydro]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:03, 4 November 2014
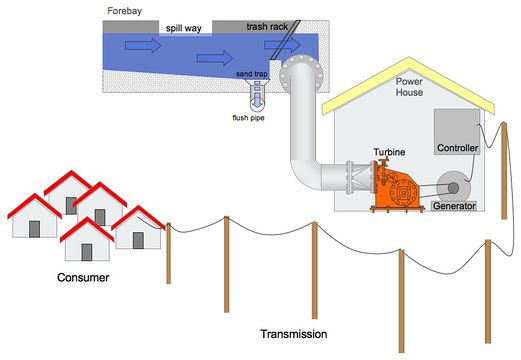
Overview
Load- or Flow- controller ensure that the power output does not exceed the power demand (e.g. 230V, 50 Hz).
If flow of water in a MHP-station is constant the energy output of a turbine/generator is constant as well. Power demand is usually fluctuating over the time (e.g. day/night). If supply is higher than demand, excess energy must be diverted, dumped. Alternatively the water flow can be reduced which results in less power output. In case of more power demand than supply the controller cuts of the of demand line. Load controller are placed between generator output and the consumer line.
Function Principles:
Controller Types
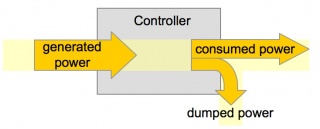
Load Controller
Electronic circuit, which keeps output power constant in Frequency- and Voltage- parameters.
Fluctuating energy demand requires a mechanism which either regulates the water input into the turbine (= flow control) or by diverting excess energy from the consumer connection (= ballast load).
► Hydropower Equipment - Load Control Governors
Ballast Load
Ballast load are usually electrical heaters in water or air. If energy demand is temporarily low the excess energy is converted into heat.
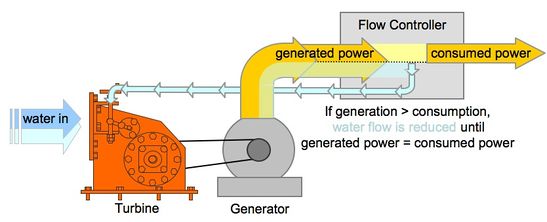
Flow Control
The flow control regulates the amount of water into the turbine in order to match power output and power demand.
Nowadays flow control is done mostly via electronics (which steer a valve).
Further Information
- Hydro Portal on energypedia
- Electrical-Mechanical Equipment
- Hydropower - Equipment
- General: Micro Hydro Power Manuals
- Good and Bad of Mini Hydro Power
References