Difference between revisions of "Malaysia Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
{{CES Country | {{CES Country | ||
|CES Country Name=Malaysia | |CES Country Name=Malaysia | ||
|CES Country Capital=Kuala Lumpur | |CES Country Capital=Kuala Lumpur | ||
| − | |CES Country Region=East Asia & Pacific | + | |CES Country Region East Asia and Pacific=East Asia & Pacific |
|CES Country Coordinates=3.1333° N, 101.7000° E | |CES Country Coordinates=3.1333° N, 101.7000° E | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Introduction = | ||
= Energy Sector = | = Energy Sector = | ||
| + | |||
Malaysia is an industrialized market economy. About 40% of the country's revenue is generated from oil and gas export. Therefore, it is not surprising to note that that fossil fuel is the primary source for electricity generation. According to the data from the national Energy Balance 2010, 53% of the electricity generation is met by natural gas, 40% is met by coal, 5% by hydro and 2% by coal.<ref name="ASEAN">http://aseanrenewables.info/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/MY-Malaysia_Rev03.pdf</ref> | Malaysia is an industrialized market economy. About 40% of the country's revenue is generated from oil and gas export. Therefore, it is not surprising to note that that fossil fuel is the primary source for electricity generation. According to the data from the national Energy Balance 2010, 53% of the electricity generation is met by natural gas, 40% is met by coal, 5% by hydro and 2% by coal.<ref name="ASEAN">http://aseanrenewables.info/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/MY-Malaysia_Rev03.pdf</ref> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
= Renewable energy sector = | = Renewable energy sector = | ||
| + | |||
In terms of installed capacity of the renewable energy in Malaysia, biomass is the highesht with about 48%. This high number comes from the fact that malaysia is the largest palm oil producers and has abundant biomass. Solar occupies the second position with about 19% of the total installed capacity, followed by hydro with 17% of the total installed capacity.<ref name="ASEAN">http://aseanrenewables.info/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/MY-Malaysia_Rev03.pdf</ref> | In terms of installed capacity of the renewable energy in Malaysia, biomass is the highesht with about 48%. This high number comes from the fact that malaysia is the largest palm oil producers and has abundant biomass. Solar occupies the second position with about 19% of the total installed capacity, followed by hydro with 17% of the total installed capacity.<ref name="ASEAN">http://aseanrenewables.info/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/MY-Malaysia_Rev03.pdf</ref> | ||
| − | The Malaysian Government is very keen on developing the renewable energy market of Malaysia and thus has introduced various schemes such as Feed-in tariff (FIT), tax exemptions and so on. The FIT scheme covers biomass,biogas ,small hydro and solar photovoltaics.<ref name="ASEAN">http://aseanrenewables.info/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/MY-Malaysia_Rev03.pdf</ref> | + | The Malaysian Government is very keen on developing the renewable energy market of Malaysia and thus has introduced various schemes such as Feed-in tariff (FIT), tax exemptions and so on. The FIT scheme covers biomass,biogas ,small hydro and solar photovoltaics.The FIT is explained in detail in the figure below<ref name="ASEAN">http://aseanrenewables.info/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/MY-Malaysia_Rev03.pdf</ref> [[File:Feed in Tariff in Malaysia 2013 and 2014.PNG|border|657px|Feed in Tariff in Malaysia (2013 and 2014)|alt=Feed in Tariff in Malaysia (2013 and 2014)]] |
| − | + | = Electricity Situation = | |
| + | Malaysia has in total 16 electricity tariffs, however the figure below provides an overview of the electricity tariff in three main sectors mainly residential , commercial and industrial.<ref name="ASEAN">http://aseanrenewables.info/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/MY-Malaysia_Rev03.pdf</ref> [[File:Electricity Tariff of Malaysia.PNG|border|707px|Electricity Tariff of Malaysia|alt=Electricity Tariff of Malaysia]] | ||
= References = | = References = | ||
| + | |||
<references /><br/> | <references /><br/> | ||
[[Category:East_Asia_and_Pacific]] | [[Category:East_Asia_and_Pacific]] | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Malaysia]] | [[Category:Malaysia]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:21, 3 September 2018
Capital:
Kuala Lumpur
Region:
Coordinates:
3.1333° N, 101.7000° E
Total Area (km²): It includes a country's total area, including areas under inland bodies of water and some coastal waterways.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.
Population: It is based on the de facto definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship--except for refugees not permanently settled in the country of asylum, who are generally considered part of the population of their country of origin.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Rural Population (% of total population): It refers to people living in rural areas as defined by national statistical offices. It is calculated as the difference between total population and urban population.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
GDP (current US$): It is the sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes and minus any subsidies not included in the value of the products. It is calculated without making deductions for depreciation of fabricated assets or for depletion and degradation of natural resources.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.2 ()
GDP Per Capita (current US$): It is gross domestic product divided by midyear population
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6. ()
Access to Electricity (% of population): It is the percentage of population with access to electricity.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Energy Imports Net (% of energy use): It is estimated as energy use less production, both measured in oil equivalents. A negative value indicates that the country is a net exporter. Energy use refers to use of primary energy before transformation to other end-use fuels, which is equal to indigenous production plus imports and stock changes, minus exports and fuels supplied to ships and aircraft engaged in international transport.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Fossil Fuel Energy Consumption (% of total): It comprises coal, oil, petroleum, and natural gas products.
XML error: Mismatched tag at line 6.no data
Introduction
Energy Sector
Malaysia is an industrialized market economy. About 40% of the country's revenue is generated from oil and gas export. Therefore, it is not surprising to note that that fossil fuel is the primary source for electricity generation. According to the data from the national Energy Balance 2010, 53% of the electricity generation is met by natural gas, 40% is met by coal, 5% by hydro and 2% by coal.[1]
Renewable energy sector
In terms of installed capacity of the renewable energy in Malaysia, biomass is the highesht with about 48%. This high number comes from the fact that malaysia is the largest palm oil producers and has abundant biomass. Solar occupies the second position with about 19% of the total installed capacity, followed by hydro with 17% of the total installed capacity.[1]
The Malaysian Government is very keen on developing the renewable energy market of Malaysia and thus has introduced various schemes such as Feed-in tariff (FIT), tax exemptions and so on. The FIT scheme covers biomass,biogas ,small hydro and solar photovoltaics.The FIT is explained in detail in the figure below[1] 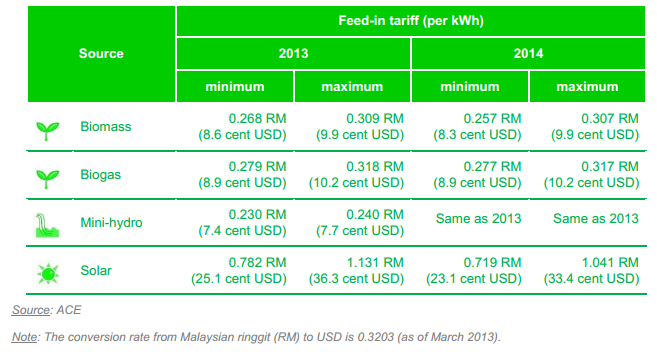
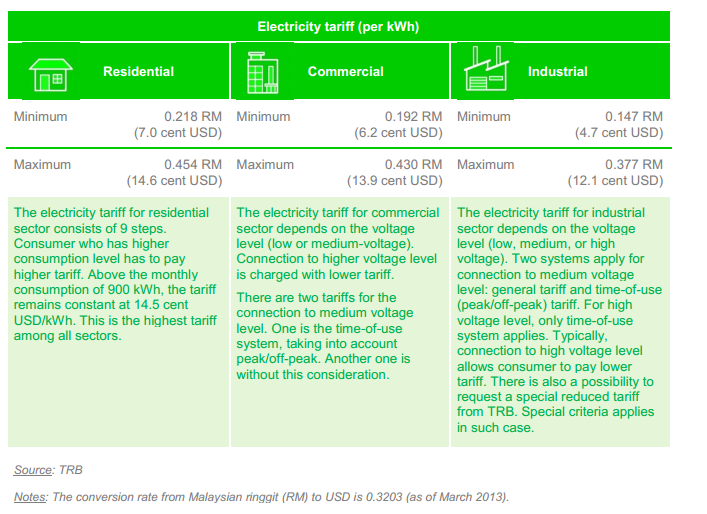
Electricity Situation
Malaysia has in total 16 electricity tariffs, however the figure below provides an overview of the electricity tariff in three main sectors mainly residential , commercial and industrial.[1]