Knowledge fuels change - Support energypedia!
For over 10 years, energypedia has been connecting energy experts around the world — helping them share knowledge, learn from each other, and accelerate the global energy transition.
Today, we ask for your support to keep this platform free and accessible to all.
Even a small contribution makes a big difference! If just 10–20% of our 60,000+ monthly visitors donated the equivalent of a cup of coffee — €5 — Energypedia would be fully funded for a whole year.
Is the knowledge you’ve gained through Energypedia this year worth €5 or more?
Your donation keeps the platform running, helps us create new knowledge products, and contributes directly to achieving SDG 7.
Thank you for your support, your donation, big or small, truly matters!
Difference between revisions of "Kyrgyzstan Energy Situation"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | GDP ( | + | GDP (current $US)<br> |
| | | | ||
| − | | + | 4.6 billion |
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | GDP Per capita | + | GDP Per capita (current $US) |
| | | | ||
| − | | + | 860 |
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | GNI per capita (current $US) | ||
| + | |||
| + | | | ||
| + | 840 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 103: | Line 110: | ||
= Geography and Climatic Conditions<ref name="GIZ">GIZ (2009): Regional Reports on Renewable Energies Energies - 30 Country Analysis on Potentials and markets</ref> = | = Geography and Climatic Conditions<ref name="GIZ">GIZ (2009): Regional Reports on Renewable Energies Energies - 30 Country Analysis on Potentials and markets</ref> = | ||
| − | | + | Kyrgyzstan, also known as the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country located in the heart of Central Asia. It is bordered by Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and China. |
| − | The Tien Shan mountain range cover roughly 95% of the country. | + | The Tien Shan mountain range cover roughly 95% of the country. Kyrgyzstan has a polar climate in the Tien Shan Mountains, a subtropical climate in the Southwest, and temperate climatic conditions in the Northern foothills. The average low temperature is 4.8°C while the average high temperature is 17.0°C.<ref name="UN Data">http://data.un.org/CountryProfile.aspx?crName=</ref> Shrub land, savannah, and grassland make up 56% of the land and cropland compromises 27%. The land area covered by forest is 4.5% but is decreasing. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 121: | Line 126: | ||
= National Energy Situation = | = National Energy Situation = | ||
| − | Kyrgyzstan has an abundant supply of hydro power. The bulk (90%) of Kyrgyzstan's generating capacity is hydro power and the country has for some time now considered the development of hydro power resources as the central foundation of its overall economic development. | + | In contrast to neighboring countries, Kyrgyzstan has small amounts of fossil fuels, but enjoys large amounts of water resources and an abundant supply of hydro power. The bulk (90%) of Kyrgyzstan's generating capacity is hydro power and the country has for some time now considered the development of hydro power resources as the central foundation of its overall economic development. |
Kyrgyzstan also has locally exploitable coal, oil, and natural gas.It was the first country in the Commonwealth of Independent States(CIS) to develop an independent regulatory agency for economic regulation of the energy sector. Primary energy shares in 2008 comprised of the following : Hydro 31.8%, coal 18.5%, gas 21.5%, oil 28.1%, renewable and waste 0.1%. <ref name="IEA">http://www.iea.org/stats</ref> Approximately 95% of the population is connected to the grid. Losses in the distribution system range from 40-50% and reliabality is poor. Electricity losses are greater in residential areas than non-residential areas and bout 30% of the distribution systems need to be replaced. | Kyrgyzstan also has locally exploitable coal, oil, and natural gas.It was the first country in the Commonwealth of Independent States(CIS) to develop an independent regulatory agency for economic regulation of the energy sector. Primary energy shares in 2008 comprised of the following : Hydro 31.8%, coal 18.5%, gas 21.5%, oil 28.1%, renewable and waste 0.1%. <ref name="IEA">http://www.iea.org/stats</ref> Approximately 95% of the population is connected to the grid. Losses in the distribution system range from 40-50% and reliabality is poor. Electricity losses are greater in residential areas than non-residential areas and bout 30% of the distribution systems need to be replaced. | ||
| Line 129: | Line 134: | ||
Low tariffs and abundant hydroelectric power resources have limited the development of renewable energy sources. Hydro-power is the only documented renewable energy source for electricity production on national level<ref name="IEA" /> | Low tariffs and abundant hydroelectric power resources have limited the development of renewable energy sources. Hydro-power is the only documented renewable energy source for electricity production on national level<ref name="IEA" /> | ||
| − | There are, however, some potentials for solar energy and large scale and micro-hydro power plants. There are about 2,600 hours of sunshine per year. | + | There are, however, some potentials for solar energy and large scale and micro-hydro power plants. There are about 2,600 hours of sunshine per year and radiation is 1,500-1,900 kW/m² per year. In addition, a law on renewable energy was adopted in 2008. It includes biomass small scale projects, small hydropower programs, solar small scale projects and wind energy in the national program. Finally, some biogas plants have been established, but only by private initiatives. |
| + | |||
| + | = Household Energy Situation = | ||
| − | = | + | === Share of Fuel Types === |
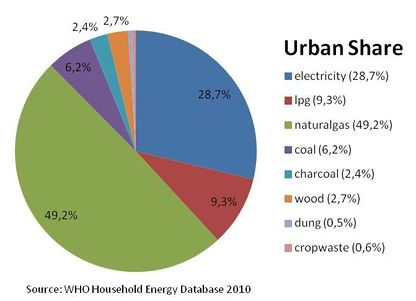
| − | + | Percentage of energy types used for cooking in urban areas | |
[[Image:Kyrgz urban.JPG|416x301px|Kyrgz urban.JPG]] | [[Image:Kyrgz urban.JPG|416x301px|Kyrgz urban.JPG]] | ||
| Line 147: | Line 154: | ||
[[Image:Kyrgz rural.JPG|426x309px|Kyrgz rural.JPG]] | [[Image:Kyrgz rural.JPG|426x309px|Kyrgz rural.JPG]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | (Solid biomass will become even more popular with the current outages | ||
| − | + | of power, eventual tariff increase, and world pricing trends.)<br> | |
| − | |||
| − | of power, eventual tariff increase and world pricing trends.<br> | ||
| − | === Share of Solid Fuels === | + | === Share of Solid Fuels === |
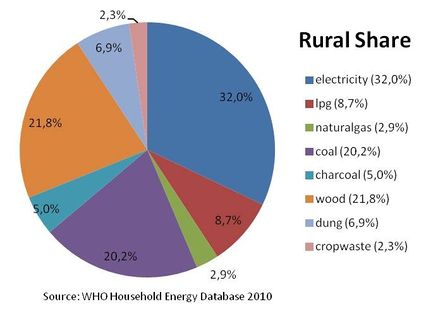
The percentage of the population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy: | The percentage of the population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy: | ||
| − | National: 37.4% urban: 12.4% rural: 56.4% | + | National: 37.4% urban: 12.4% rural: 56.4% |
| − | === Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health === | + | === Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health === |
• Total annual deaths attributable to solid fuel use: 1600 persons<br>• Percentage of national burden of diseases attributable to solid fuel use: 3.3%<br> | • Total annual deaths attributable to solid fuel use: 1600 persons<br>• Percentage of national burden of diseases attributable to solid fuel use: 3.3%<br> | ||
Revision as of 13:00, 9 March 2012
| Kyrgyzstan | |||
| |
| ||
|
Capital |
Astana | ||
|
Official language(s) |
Kazak, Russian | ||
|
Government |
| ||
|
President |
| ||
|
Prime Minister |
| ||
|
Total area |
2,725,000 km sq | ||
|
Population |
5.57 million | ||
|
Population density (per sq. km) |
27 | ||
|
GDP (current $US) |
4.6 billion | ||
|
GDP Per capita (current $US) |
860 | ||
|
GNI per capita (current $US) |
840 | ||
|
Currency |
| ||
|
Time zone |
| ||
|
Calling code |
| ||
Geography and Climatic Conditions[1]
Kyrgyzstan, also known as the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country located in the heart of Central Asia. It is bordered by Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and China.
The Tien Shan mountain range cover roughly 95% of the country. Kyrgyzstan has a polar climate in the Tien Shan Mountains, a subtropical climate in the Southwest, and temperate climatic conditions in the Northern foothills. The average low temperature is 4.8°C while the average high temperature is 17.0°C.[2] Shrub land, savannah, and grassland make up 56% of the land and cropland compromises 27%. The land area covered by forest is 4.5% but is decreasing.
Socio-economic Development[3]
Kyrgyzstan's population is 5.57 million and the population density is 27 people per square kilometer. Urban population compromises 35% while the rural population makes up 65%. The literacy rate (age 15+) is 98.7%
The GDP in 2010 was 4.6 billion US$ and the GDP per capital was US$ 860. GDP grew more than 6% in 2007-08, but declined after that. National income sources share consist of 48% agriculture, 12.5% industry, and 39.5% services.
National Energy Situation
In contrast to neighboring countries, Kyrgyzstan has small amounts of fossil fuels, but enjoys large amounts of water resources and an abundant supply of hydro power. The bulk (90%) of Kyrgyzstan's generating capacity is hydro power and the country has for some time now considered the development of hydro power resources as the central foundation of its overall economic development.
Kyrgyzstan also has locally exploitable coal, oil, and natural gas.It was the first country in the Commonwealth of Independent States(CIS) to develop an independent regulatory agency for economic regulation of the energy sector. Primary energy shares in 2008 comprised of the following : Hydro 31.8%, coal 18.5%, gas 21.5%, oil 28.1%, renewable and waste 0.1%. [4] Approximately 95% of the population is connected to the grid. Losses in the distribution system range from 40-50% and reliabality is poor. Electricity losses are greater in residential areas than non-residential areas and bout 30% of the distribution systems need to be replaced.
Potential for Renewable Energies
Low tariffs and abundant hydroelectric power resources have limited the development of renewable energy sources. Hydro-power is the only documented renewable energy source for electricity production on national level[4]
There are, however, some potentials for solar energy and large scale and micro-hydro power plants. There are about 2,600 hours of sunshine per year and radiation is 1,500-1,900 kW/m² per year. In addition, a law on renewable energy was adopted in 2008. It includes biomass small scale projects, small hydropower programs, solar small scale projects and wind energy in the national program. Finally, some biogas plants have been established, but only by private initiatives.
Household Energy Situation
Percentage of energy types used for cooking in urban areas
Percentage of energy types used for cooking in rural areas
(Solid biomass will become even more popular with the current outages
of power, eventual tariff increase, and world pricing trends.)
The percentage of the population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy:
National: 37.4% urban: 12.4% rural: 56.4%
Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health
• Total annual deaths attributable to solid fuel use: 1600 persons
• Percentage of national burden of diseases attributable to solid fuel use: 3.3%
Policy framework
Market Risks
Relevant Institutions and organisations
Existing projects
External links
References
- ↑ GIZ (2009): Regional Reports on Renewable Energies Energies - 30 Country Analysis on Potentials and markets
- ↑ http://data.un.org/CountryProfile.aspx?crName=
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/kg.html
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 http://www.iea.org/stats