Knowledge fuels change
For over a decade, Energypedia has shared free, reliable energy expertise with the world.
We’re now facing a serious funding gap.
Help keep this platform alive — your donation, big or small, truly matters!
Thank you for your support
Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) - Basics and Introduction
Introduction to and Basics of CSP
|
For a short introduction to Concentrating Solar Power, the idea behind and the general plant design as well as its benefits and obstacles, please feel free to watch the video provided by SolarReserve.
CSP Systems are replacing fossil fuels with CO2-emission free energy and therefore reduce the overall greenhouse gas emissions. According to Greenpeace the energy pay back time of an CSP plant can amount to just 5 months depending on its configuration and size.[1] CSP Plants can remain in operation for almost 40 years and thus demonstrate its durability and reliability.
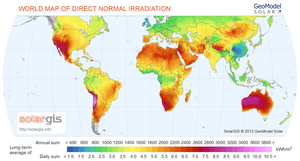
Solar Resource
The favourable regions to apply CSP Technology are open for discussion. However, a good indicator to identify CSP potentials is the direct normal irradiation (DNI). Maps can show the distribution of DNI all over the world and thus give a first clue as to where CSP power plants should be built. For further reference please also see the Project Database of CSP Power Plants and overlay the DNI map with it.
Mainly the MENA region, western USA, Southern Africa, Australia and parts of South America.
Generation Costs
Generation costs are currently at reasonable levels and still dropping. They range from 150 US-$/ MWh to 200 US-$/ MWh.[2] The diagram below is taken from the report of the NREL. Hours of TES meaning the thermal storage capacity of the power plant: the time measured in hours that the given power plant can run at rated power output with the storage as its only energy source. The Solar Multiple describes the relation of the installed solar power to the power of the motor block. An over-sized power plant (SM > 1) produces more energy at full solar power intake than the motor can transform. It therefore needs storage facilities to divert the power surplus; otherwise the energy gets spilled.
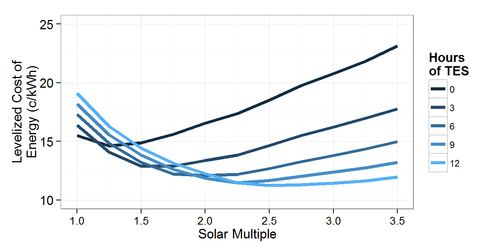
The SunShot Initiative Concentrating Solar Power Research and Development is trying to reach generation costs of 60 US-$/ MWh by addressing technical barriers for solar fields, receivers and power plants.[3] For more information on levelized cost of energy/ generation costs also see the Cost Analysis of the International Renewable Energy Agency.
Environmental Impacts
According to investigations done by the European Academies Science Advisory Board Concentrating Solar Power plants potentially impact the environment in the following ways.
- Atmospheric pollution from fuel combustion (in hybrid operation) and during production and construction of equipment (lifecycle emissions)
- Impacts on flora and fauna
- Water consumption
- Land use and visual impact
- Consumption of energy and materials
- Noise of cooling towers when applying air or evaporation cooling
- Smell and potential pollution of soil and water and fire hazard for systems using synthetic oil heat transfer fluid, which is considered a hazardous material.[4][5]
CSP Today
List of CSP projects
Click here to view, browse and add project information about CSP projects on Energypedia: CSP Projects.
See List of solar thermal power stations and List of concentrating solar thermal power companies (Wikipedia)
References
- ↑ Greenpeacce International - Concentrating Solar Power Global Outlook
- ↑ NREL - Estimating the Performance and Economic Value of Multiple Concentrating Solar Power Technologies in a Production Cost Model
- ↑ SunShot Concentrating Solar Power ResearchfckLRand Development - http://www1.eere.energy.gov/solar/pdfs/55467.pdf
- ↑ Trieb et al. - Concentrating Solar Power in a sustainable future electrictiy mix (https://energypedia.info/wiki/Concentrating_solar_power_in_a_sustainable_future_electricity_mix)
- ↑ European Academies Science Advisory Council - http://www.easac.eu/fileadmin/Reports/Easac_CSP_Web-Final.pdf