Difference between revisions of "Fuel Prices Brazil"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Fuel Price Factsheet | {{Fuel Price Factsheet | ||
|Fuel Price Country=Brazil | |Fuel Price Country=Brazil | ||
| − | |Fuel Pricing Policies= | + | |Fuel Pricing Policies="Pricing policy: Prices were deregulated by law in Jan 2002, but in practice the national oil company, Petrobras, has virtually frozen ex-refinery prices for years on end, with mounting losses. The national average producer price of pure gasoline were kept within a narrow band of R$1.51−1.55/liter between Sep 2005 and Jan 2013, that of diesel within R$1.33−1.37 between Aug 2009 and Jul 2012, and that of LPG sold in 13-kg cylinders has been kept within R$1.03−1.05 per kg since Nov 2003 (with higher prices earlier). Ex-refinery prices of gasoline and diesel were raised in Jan 2013. Government adjusts a tax on gasoline and diesel contributing to intervention in the economic domain, called CIDE (Contribuição e Intervenção no Domínio Econômico), to further stabilize retail prices. A negative CIDE tax was levied on LPG until Apr 2002. Monthly average retail prices of diesel (averaged across the country) and FOB benchmark prices relevant to Brazil since 2007 are shown below. The plot shows significant price smoothing. |
| + | |||
| + | Consequences of pricing policy: Petrobras’ refining, transportation, and marketing division lost US$8.5 billion in 2011 and US$17.5 billion in 2012. The recent decline in the company’s financial performance, including its first quarterly loss in 13 years posted in August 2012, has been blamed in large part on low domestic fuel prices. Cuts in CIDE in recent years have cost hundreds of millions of dollars. | ||
| − | + | Social protection: In Apr 2002, the LPG subsidy was eliminated and replaced with assistance to enable the poor to use LPG through LPG vouchers in Bolsa Familia, government’s social welfare program. | |
| − | + | Information: Agência Nacional do Petróleo, Gás Natural e Biocombustíveis (ANP, National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels) posts detailed historical and current information on prices on its Web site. Information posted includes weekly surveys of retail prices of gasoline, diesel, and LPG and marketing margins. In May 2004, the survey coverage was expanded to a total of 555 locations. ANP also issues annual reports on global and domestic prices." | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
(Source: Kojima, Masami. (2013, forthcoming). “Petroleum product pricing and complementary policies:Experience of 65 developing countries since 2009.” Washington DC: World Bank.) | (Source: Kojima, Masami. (2013, forthcoming). “Petroleum product pricing and complementary policies:Experience of 65 developing countries since 2009.” Washington DC: World Bank.) | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 12 March 2013
Part of: GIZ International Fuel Price database
Brazil Energy Situation
Fuel Pricing Policies
| Local Currency: | BRL |
| Exchange Rate: | 1.73
|
| Last Update: |
"Pricing policy: Prices were deregulated by law in Jan 2002, but in practice the national oil company, Petrobras, has virtually frozen ex-refinery prices for years on end, with mounting losses. The national average producer price of pure gasoline were kept within a narrow band of R$1.51−1.55/liter between Sep 2005 and Jan 2013, that of diesel within R$1.33−1.37 between Aug 2009 and Jul 2012, and that of LPG sold in 13-kg cylinders has been kept within R$1.03−1.05 per kg since Nov 2003 (with higher prices earlier). Ex-refinery prices of gasoline and diesel were raised in Jan 2013. Government adjusts a tax on gasoline and diesel contributing to intervention in the economic domain, called CIDE (Contribuição e Intervenção no Domínio Econômico), to further stabilize retail prices. A negative CIDE tax was levied on LPG until Apr 2002. Monthly average retail prices of diesel (averaged across the country) and FOB benchmark prices relevant to Brazil since 2007 are shown below. The plot shows significant price smoothing.
Consequences of pricing policy: Petrobras’ refining, transportation, and marketing division lost US$8.5 billion in 2011 and US$17.5 billion in 2012. The recent decline in the company’s financial performance, including its first quarterly loss in 13 years posted in August 2012, has been blamed in large part on low domestic fuel prices. Cuts in CIDE in recent years have cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
Social protection: In Apr 2002, the LPG subsidy was eliminated and replaced with assistance to enable the poor to use LPG through LPG vouchers in Bolsa Familia, government’s social welfare program.
Information: Agência Nacional do Petróleo, Gás Natural e Biocombustíveis (ANP, National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels) posts detailed historical and current information on prices on its Web site. Information posted includes weekly surveys of retail prices of gasoline, diesel, and LPG and marketing margins. In May 2004, the survey coverage was expanded to a total of 555 locations. ANP also issues annual reports on global and domestic prices."
(Source: Kojima, Masami. (2013, forthcoming). “Petroleum product pricing and complementary policies:Experience of 65 developing countries since 2009.” Washington DC: World Bank.)
Fuel Prices and Trends
| Gasoline 95 Octane | Diesel | |
|---|---|---|
| in USD* |
|
|
| in Local Currency |
|
|
* benchmark lines: green=US price; grey=price in Spain; red=price of Crude Oil
Fuel Price Composition
Price composition for one litre of Gasoline 95 Octane as of 2010/11/01.
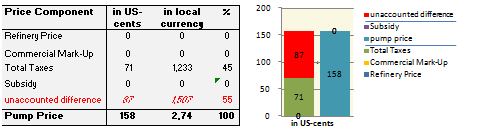
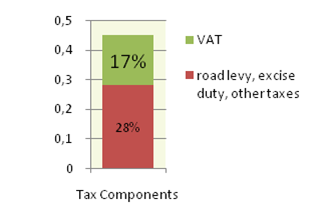
Source: http://www1.folha.uol.com.br/folha/dinheiro/ult91u438347.shtml
At a Glance
| Regulation-Price-Matrix |
| ||||
 |

|

|

| ||
Sources to the Public
| Type of Information | Web-Link / Source |
|---|---|
| Other Information | http://www.mme.gov.br (Ministry of Mines and Energy) |
| Other Information | http://www.petrobras.com.br (Petrobras) |
| Other Information | http://uneprisoe.org/Pricing/FuelPricingPolicies.pdf |
| Other Information | http://www.anp.gov.br (National Petroleum Agency of Brazil) |
| Pump prices and margins | http://www.anp.gov.br/preco/ |
| Pump prices and margins | http://www.precodoscombustiveis.com.br/ |
Contact
Please find more information on GIZ International Fuel Price Database and http://www.giz.de/fuelprices



















