Click here to register!
Modern Solar Drying in Afghanistan
Overview
The project Modern Solar Drying in Afghanistan aimed at testing of small solar dryers to improve the quality of solar dried fruits in Afghanistan, the promotion of the technology amongst the population, the development of capacity building and the launch of a small solar food business. The project partner was Afghan Bedmoschk Solar Center e.V., a NGO specialised in environmental protection, education and development aid. The project was part of the ISES Solar Food Processing Project.
Technology and Processing
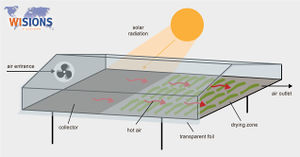
In Afghanistan, due to the dry climate, the drying of fruits and vegetables is a common way to preserve them. Traditionally, the edibles are cut in pieces and placed on flat ground such as rooftops. This method has some drawbacks as the food is not protected against dust, dirt and insects.
As an alternative, solar tunnel dryers of 2x1 m in size, small versions of the Hohenheim Solar Tunnel Dryer, have been tested under the afghan conditions. Their small size allows farmers to test and evaluate the technology in a useful and non-expensive way. The dryers were distributed as a package, which included training about set-up, use and maintenance, storing and marketing and a set of packaging materials. Training was offered in German and Persian. During the process of drying, the products were dried from 7kg to 0,4 to 1kg. The drying process took 3 to 5 days. The dried products were packed into 200gr packages and sold using newly-designed labels in Dari and English.