Difference between revisions of "Parts of a Biogas Plant"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[Portal:Biogas|►Back to Biogas Portal]]<br/> | |
| − | + | = Overview = | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The feed material is mixed with water in the influent collecting tank The fermentation slurry flows through the inlet into the digester. The bacteria from the fermentation slurry are intended to produce biogas in the digester. For this purpose, they need time. Time to multiply and to spread throughout the slurry. The digester must be designed in a way that only fully digested slurry can leave it. The bacteria are distributed in the slurry by stirring (with a stick or stirring facilities). The fully digested slurry leaves the digester through the outlet into the slurry storage.The biogas is collected and stored until the time of consumption in the gasholder. The gas pipe carries the biogas to the place where it is consumed by gas appliances. Condensation collecting in the gas pipe is removed by a water trap. Depending on the available building material and type of plant under construction, different variants of the individual components are possible. The following (optional) components of a biogas plant can also play an important role and are described seperatly: Heating systems, pumps, weak ring.<br/> | |
| − | + | = Influent Collecting Tank<br/> = | |
| − | + | {| cellpadding="10" border="0" align="right" class="IMGright" style="width: 220px" | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {| cellpadding="10" border="0" align="right" style="width: 220px | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | [[File:Bgfixeddomeinst.jpg| | + | [[File:Bgfixeddomeinst.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Bgfixeddomeinst.jpg]]<br/><br/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | '''<u>Size and Homogenization</u>'''<br/>Fresh substrate is usually gathered in an influent collecting tank prior to being fed into the digester. Depending on the type of system, the tank should hold one to two days' substrate. An influent collecting tank can also be used to homogenize the various substrates and to set up the required consistency, e.g. by adding water to dilute the mixture of vegetable solids (straw, grass, etc.), or by adding more solids in order to increase the bio-mass. The fibrous material is raked off the surface, if necessary, and any stones or sand settling at the bottom are cleaned out after the slurry is admitted to the digester. The desired degree of homogenization and solids content can be achieved with the aid of an agitator, [[Pumps_for_Biogas_Plants|pump]] or chopper. A rock or wooden plug can be used to close off the inlet pipe during the mixing process.<br/> | |
| − | + | <br/>'''<u>Location</u>'''<br/> | |
| − | <br/> | + | A sunny location can help to warm the contents before they are fed into the digester in order to avoid thermal shock due to the cold mixing water. In the case of a biogas plant that is directly connected to the stable, it is advisable to install the mixing pit deep enough to allow installation of a floating gutter leading directly into the pit. Care must also be taken to ensure that the low position of the mixing pit does not result in premature digestion. For reasons of hygiene, toilets should have a direct connection to the inlet pipe.<br/> |
| − | + | <br/>'''<u>Inlet and Outlet</u>'''<br/> | |
| − | + | The inlet (feed) and outlet (discharge) pipes lead straight into the digester at a steep angle. For liquid substrate, the pipe diameter should be 10-15 cm, while fibrous substrate requires a diameter of 20-30 cm. The inlet and the outlet pipe mostly consist of plastic or concrete.<br/> | |
| − | <br/> | + | <br/>'''<u>Position</u>'''<br/>Both the inlet and the outlet pipe must be freely accessible and straight, so that a rod can be pushed through to eliminate obstructions and agitate the digester contents. The pipes should penetrate the digester wall at a point below the lowest slurry level (i.e. not through the gas storage). The points of penetration should be sealed and reinforced with mortar. The inlet pipe ends higher in the digester than the outlet pipe in order to promote more uniform flow of the substrate. In a [[Types_of_Biogas_Digesters_and_Plants#Fixed_Dome_Biogas_Plants|fixed-dome plant]], the inlet pipe defines the bottom line of the gas-holder, acting like a security valve to release over-pressure. In a [[Types_of_Biogas_Digesters_and_Plants#Floating_Drum_Plants|floating-drum plant]], the end of the outlet pipe determines the digester's (constant) slurry level. Inlet and outlet pipe must be placed in connection with brick-laying. It is not advisable to break holes into the spherical shell afterwards, this would weaken the masonry structure.<br/> |
| − | + | <br/>'''<u>Toilet Connection at the Inlet</u>'''<br/>► [[Connection_of_a_Toilet_to_a_Biogas_Digester|Household Toilets can be connected to a Biogas Digester.]]<br/> | |
| − | = | + | = Digester = |
| − | + | In general terms, digesters consist of the digestion tank as such, which is thermally insulated, plus a heating system, mixer systems and discharge systems for sediments and the spent substrate.<br/><br/> | |
| − | <br/> | + | == Raw Material for Biogas Digesters<br/> == |
| − | + | ►[[Material_for_Biogas_Digesters|Read more here .....]]<br/><br/> | |
| − | + | == Types of Biogas Digesters == | |
| − | + | ►[[Types_of_Biogas_Digesters_and_Plants|Read more here .....]]<br/><br/> | |
| − | + | == Types of Gasholders for Biogas Plants == | |
| − | <br/> | + | ► [[Types_of_Gasholders_for_Biogas_Plants|Read more here .....]]<br/><br/> |
| − | = | + | = Gas Pipe, Valves and Accessories<br/> = |
| − | + | == Biogas Piping<br/> == | |
| − | + | {| cellpadding="10" border="0" align="right" class="IMGright" style="width: 348px" | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {| cellpadding="10" border="0" align="right" style="width: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Bgstirrer.jpg|thumb|right|248px]]<br/><br/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | At least 60% of all non-functional biogas units are attributable to defect gas piping. Utmost care has to be taken, therefore, for proper installation. For the sake of standardization, it is advisable to select a single size for all pipes, valves and accessories. The requirements for [[Piping_Systems_for_Biogas_Plants|biogas piping]], valves and accessories are essentially the same as for other gas installations. However, biogas is 100% saturated with water vapor and contains hydrogen-sulfide. Consequently, no piping, valves or accessories that contain any amounts of ferrous metals may be used for biogas piping, because they would be destroyed by corrosion within a short time. The gas lines may consist of standard galvanized steel pipes. Also suitable (and inexpensive) is plastic tubing made of rigid PVC or rigid PE. Flexible gas pipes laid in the open must be UV-resistant.<br/> | |
| − | < | + | <br/>[[Biogas_Gas_Pipe,_Valves_and_Accessories#Gas_Pipe|► Read More here...]]<br/><br/> |
| − | == | + | == Water Traps == |
| − | + | [[Biogas_Gas_Pipe,_Valves_and_Accessories#Water_Traps|► Read more here....]]<br/><br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | <br/> | ||
| − | == | + | == Valves == |
| − | + | [[Biogas_Gas_Pipe,_Valves_and_Accessories#Valves|► Read more here...]]<br/><br/> | |
| − | + | == Gas Analysis Equipment == | |
| − | + | [[Biogas_Gas_Pipe,_Valves_and_Accessories#Gas_Analysis_Equipment|►Read more here...]]<br/><br/> | |
| − | + | = Stirring Facilities<br/> = | |
| − | {| | + | {| cellpadding="10" border="0" align="right" class="IMGleft" style="width: 269px;" |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
| | | | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Bgstirring.gif|thumb|right|200px]]<br/><br/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | Optimum stirring substantially reduces the retention time. If [[Agitation_of_Digesters|agitation]] is excessive, the bacteria have "no time to eat". The ideal is gentle but intensive stirring about every four hours. Of similar importance is the breaking up of a scum layer which has lost contact with the main volume of substrate and is, therefore, not further digested. This top layer can form an impermeable barrier for biogas to move up from the digester to the gas holder.As a rule of thumb it can be stated that stirring facilities are more important in larger plants than in small scale farm plants.<br/><u>Types of Stirring Facilities</u>:<br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Optimum stirring substantially reduces the retention time. If [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | As a rule of thumb it can be stated that stirring facilities are more important in larger plants than in small scale farm plants. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
#The '''''impeller stirrer''''' has given good results especially in sewage treatment plants. | #The '''''impeller stirrer''''' has given good results especially in sewage treatment plants. | ||
#The '''''horizontal shaft''''' stirs the fermentation channel without mixing up the phases. Both schemes originate from large-scale plant practice. | #The '''''horizontal shaft''''' stirs the fermentation channel without mixing up the phases. Both schemes originate from large-scale plant practice. | ||
| − | #For simple household plants, '''''poking with a stick''''' is the simplest and safest stirring method. | + | #For simple household plants, '''''poking with a stick''''' is the simplest and safest stirring method. |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | + | = Heating Systems<br/> = | |
| − | Normally, because of the rather high involved costs, small-scale biogas plants are built without [[ | + | Normally, because of the rather high involved costs, small-scale biogas plants are built without [[Digester_Heating|heating systems]]. But even for small scale plants, it is of advantage for the bio-methanation process to warm up the influent substrate to its proper process temperature before it is fed into the digester. If possible, cold zones in the digester should be avoided (see also [[Parameters_and_Process_Optimisation_for_Biogas#Substrate_temperature|substrate temperature]]). There are a number of different ways to get the required amount of thermal energy into the substrate are described. <u>In principle, one can differentiate between:</u> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*'''direct heating''' in the form of steam or hot water, and | *'''direct heating''' in the form of steam or hot water, and | ||
*'''indirect heating''' via heat exchanger, whereby the heating medium, usually hot water, imparts heat while not mixing with the substrate. | *'''indirect heating''' via heat exchanger, whereby the heating medium, usually hot water, imparts heat while not mixing with the substrate. | ||
| − | <br/> | + | <br/>[[Digester_Heating|►]][[Digester_Heating|More information here...]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = Pumps = | |
| − | + | Pumps become necessary parts of a biogas unit, when the amounts of substrate require fast movement and when gravity cannot be used for reasons of topography or substrate characteristics. Pumps transport the substrate from the point of delivery through all the stages of fermentation. Therefore, several pumps and types of pumps may be needed. Pumps are usually found in large scale biogas units. | |
| − | == | + | == Types of Pumps == |
| − | + | ► [[Pumps_for_Biogas_Plants|Read more here....]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | + | = Weak Ring<br/> = | |
| + | {| cellpadding="10" border="0" align="right" class="IMGleft" style="width: 304px" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="width: 276px" | [[File:Weakstrongring.jpg|thumb|right|280px]]<br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | The weak/strong ring improves the gas-tightness of [[Fixed-dome_Biogas_Plants|fixed-dome plants]] It was first introduced in Tanzania and showed promising results. The weak ring separates the lower part of the hemispherical digester, (filled with digesting substrate), from the upper part (where the gas is stored). Vertical cracks, moving upwards from the bottom of the digester, are diverted in this ring of lean mortar into horizontal cracks. These cracks remain in the slurry area where they are of no harm to the gas-tightness. The strong ring is a reinforcement of the bottom of the gas-holder, it could also be seen as a foundation of the gas-holder. It is an additional device to prevent cracks from entering the gas-holder. Weak and strong ring have been successfully combined in the CAMARTEC design<br/><u>Materials and Construction</u><br/>The weak ring consists of mortar of a mixture of sand, lime and cement (15:3:1). The top of the weak ring restores the horizontal level. It is interrupted only by the inlet pipe passing through. The strong ring rests on the weak ring and is the first layer of the upper part of the hemispherical shell. It consists of a row of header bricks with a concrete package at the outside. In case of soft or uncertain ground soil one may place a ring reinforcement bar in the concrete of the strong ring. The brick of the strong ring should be about three times wider than the brickwork of the upper wall. A detailed description of the weak/strong ring construction can be found in Sasse, Kellner, Kimaro (1991).<br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The weak ring consists of mortar of a mixture of sand, lime and cement (15:3:1). The top of the weak ring restores the horizontal level. It is interrupted only by the inlet pipe passing through. The strong ring rests on the weak ring and is the first layer of the upper part of the hemispherical shell. It consists of a row of header bricks with a concrete package at the outside. In case of soft or uncertain ground soil one may place a ring reinforcement bar in the concrete of the strong ring. The brick of the strong ring should be about three times wider than the brickwork of the upper wall. A detailed description of the weak/strong ring construction can be found in Sasse, Kellner, Kimaro (1991). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | = Pre-digestion Pit for Storage of Substrates = | |
| − | + | <u>Sizing depends on:</u> substrate arisings, digester capacity, length of time to be bridged between successive deliveries, land-use specifics and yield of co-substrates, supply contracts for substrates from off-site sources, possible disruptions in operation<br/><u>Special considerations:</u> | |
| − | + | *Avoid the possibility of storage plant freezing, for example by siting storage tanks indoors, heating storage containers or locating the plant for pits below grade level | |
| + | *Avoid biodegradation processes that reduce gas yield | ||
| + | *Do not permit intermingling of hygienically problematic and hygienically acceptable substrates | ||
| + | *Implement suitable structural measures to minimise odours | ||
| + | *Avoid material emissions to soil and to the surface and underground water system | ||
| − | <br/> | + | <br/><u>Designs</u> Containers for storing solid substrates in widespread use in agriculture, such as mobile silos, upright silos, plastic-tunnel silos and round-bale silos and open or roofed storage areas (e.g. solid-manure deposits) and pits/hoppers Containers for storing liquid substrates in widespread use in agriculture, such as tanks and predigester pits<br/><u>Costs</u> Storage facilities are generally in place; when new builds are needed the price has to be calculated on<br/>a case-to-case basis factoring in the multiplicity of influencing variables indicated above<br/> |
| − | = | + | = Measurement Instruments<br/> = |
| − | + | Flow-measuring devices (in the pipes) Ultrasonically (pre pits) Radar (pre-pits)<br/>Wheel loader scales | |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | = | + | = Further Information = |
| − | + | *[[Portal:Biogas|Biogas Portal on energypedia]] | |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | + | '''<u>Information on materials and devices used in the construction of biogas plants:</u>''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Checklist_for_the_Construction_of_a_Biogas_Plant|Checklist for the Construction of a Biogas Plant]] | |
| + | *[[Agitation_of_Digesters|Agitation of Digesters]] | ||
| + | *[[Digester_Heating|Digester Heating]] | ||
| + | *[[Piping_Systems_for_Biogas_Plants|Piping Systems for Biogas Plants]] | ||
| + | *[[Plasters_and_Coats_for_Biogas_Digesters_and_Gas-holder|Plasters and Coats for Biogas Digesters and Gas-holder]] | ||
| + | *[[Pumps_for_Biogas_Plants|Pumps for Biogas Plants]] | ||
| + | *[[Slurry-Use_Equipment|Slurry-Use Equipment]] | ||
| + | *[[Biogas_Implementation_-_Groundwater_Management|Biogas Implementation - Groundwater Management]] | ||
| − | + | <br/><u>'''Web based sources'''</u> | |
| − | + | *[http://biogas.ifas.ufl.edu/ad_development/documents/biogasplants.pdf biogas.ifas - biogasplants (pdf]) | |
| − | + | *[[Checklist_for_the_Construction_of_a_Biogas_Plant|Checklist for the Construction of a Biogas Plant]] | |
| − | + | *[http://www.haase-energietechnik.de/en/Products_and_Services/24-e_BiogasBrochure_Feb2011_1.pdf haase-energietechnik - BiogasBrochure (pdf)] | |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | = | + | = References<br/> = |
| − | + | <references /> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*'''Ringkamp, M.; Tentscher, W.; Schiller, H.''': Preliminary results on: statical optimization of family-sized fixed-dome digesters. Tilche, A.; Rozzi, A. (ed.): Poster Papers. Fifth International Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion, Bologna 1988, pp. 321-324 | *'''Ringkamp, M.; Tentscher, W.; Schiller, H.''': Preliminary results on: statical optimization of family-sized fixed-dome digesters. Tilche, A.; Rozzi, A. (ed.): Poster Papers. Fifth International Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion, Bologna 1988, pp. 321-324 | ||
*'''Sasse, L.; Kellner, Ch.; Kimaro, A.''': Improved Biogas Unit for Developing Countries. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft Braunschweig, 1991 | *'''Sasse, L.; Kellner, Ch.; Kimaro, A.''': Improved Biogas Unit for Developing Countries. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft Braunschweig, 1991 | ||
| + | *J.; Sasse, L. (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit): Production and utilization of biogas in rural areas of industrialized and developing countries. TZ-Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Roßdorf, 1986, 278 S.</span> | ||
| − | + | <br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Biogas]] | [[Category:Biogas]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:01, 8 April 2015
Overview
The feed material is mixed with water in the influent collecting tank The fermentation slurry flows through the inlet into the digester. The bacteria from the fermentation slurry are intended to produce biogas in the digester. For this purpose, they need time. Time to multiply and to spread throughout the slurry. The digester must be designed in a way that only fully digested slurry can leave it. The bacteria are distributed in the slurry by stirring (with a stick or stirring facilities). The fully digested slurry leaves the digester through the outlet into the slurry storage.The biogas is collected and stored until the time of consumption in the gasholder. The gas pipe carries the biogas to the place where it is consumed by gas appliances. Condensation collecting in the gas pipe is removed by a water trap. Depending on the available building material and type of plant under construction, different variants of the individual components are possible. The following (optional) components of a biogas plant can also play an important role and are described seperatly: Heating systems, pumps, weak ring.
Influent Collecting Tank
|
|
Size and Homogenization
Fresh substrate is usually gathered in an influent collecting tank prior to being fed into the digester. Depending on the type of system, the tank should hold one to two days' substrate. An influent collecting tank can also be used to homogenize the various substrates and to set up the required consistency, e.g. by adding water to dilute the mixture of vegetable solids (straw, grass, etc.), or by adding more solids in order to increase the bio-mass. The fibrous material is raked off the surface, if necessary, and any stones or sand settling at the bottom are cleaned out after the slurry is admitted to the digester. The desired degree of homogenization and solids content can be achieved with the aid of an agitator, pump or chopper. A rock or wooden plug can be used to close off the inlet pipe during the mixing process.
Location
A sunny location can help to warm the contents before they are fed into the digester in order to avoid thermal shock due to the cold mixing water. In the case of a biogas plant that is directly connected to the stable, it is advisable to install the mixing pit deep enough to allow installation of a floating gutter leading directly into the pit. Care must also be taken to ensure that the low position of the mixing pit does not result in premature digestion. For reasons of hygiene, toilets should have a direct connection to the inlet pipe.
Inlet and Outlet
The inlet (feed) and outlet (discharge) pipes lead straight into the digester at a steep angle. For liquid substrate, the pipe diameter should be 10-15 cm, while fibrous substrate requires a diameter of 20-30 cm. The inlet and the outlet pipe mostly consist of plastic or concrete.
Position
Both the inlet and the outlet pipe must be freely accessible and straight, so that a rod can be pushed through to eliminate obstructions and agitate the digester contents. The pipes should penetrate the digester wall at a point below the lowest slurry level (i.e. not through the gas storage). The points of penetration should be sealed and reinforced with mortar. The inlet pipe ends higher in the digester than the outlet pipe in order to promote more uniform flow of the substrate. In a fixed-dome plant, the inlet pipe defines the bottom line of the gas-holder, acting like a security valve to release over-pressure. In a floating-drum plant, the end of the outlet pipe determines the digester's (constant) slurry level. Inlet and outlet pipe must be placed in connection with brick-laying. It is not advisable to break holes into the spherical shell afterwards, this would weaken the masonry structure.
Toilet Connection at the Inlet
► Household Toilets can be connected to a Biogas Digester.
Digester
In general terms, digesters consist of the digestion tank as such, which is thermally insulated, plus a heating system, mixer systems and discharge systems for sediments and the spent substrate.
Raw Material for Biogas Digesters
Types of Biogas Digesters
Types of Gasholders for Biogas Plants
Gas Pipe, Valves and Accessories
Biogas Piping
|
|
At least 60% of all non-functional biogas units are attributable to defect gas piping. Utmost care has to be taken, therefore, for proper installation. For the sake of standardization, it is advisable to select a single size for all pipes, valves and accessories. The requirements for biogas piping, valves and accessories are essentially the same as for other gas installations. However, biogas is 100% saturated with water vapor and contains hydrogen-sulfide. Consequently, no piping, valves or accessories that contain any amounts of ferrous metals may be used for biogas piping, because they would be destroyed by corrosion within a short time. The gas lines may consist of standard galvanized steel pipes. Also suitable (and inexpensive) is plastic tubing made of rigid PVC or rigid PE. Flexible gas pipes laid in the open must be UV-resistant.
Water Traps
Valves
Gas Analysis Equipment
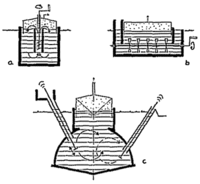
Stirring Facilities
|
|
Optimum stirring substantially reduces the retention time. If agitation is excessive, the bacteria have "no time to eat". The ideal is gentle but intensive stirring about every four hours. Of similar importance is the breaking up of a scum layer which has lost contact with the main volume of substrate and is, therefore, not further digested. This top layer can form an impermeable barrier for biogas to move up from the digester to the gas holder.As a rule of thumb it can be stated that stirring facilities are more important in larger plants than in small scale farm plants.
Types of Stirring Facilities:
- The impeller stirrer has given good results especially in sewage treatment plants.
- The horizontal shaft stirs the fermentation channel without mixing up the phases. Both schemes originate from large-scale plant practice.
- For simple household plants, poking with a stick is the simplest and safest stirring method.
Heating Systems
Normally, because of the rather high involved costs, small-scale biogas plants are built without heating systems. But even for small scale plants, it is of advantage for the bio-methanation process to warm up the influent substrate to its proper process temperature before it is fed into the digester. If possible, cold zones in the digester should be avoided (see also substrate temperature). There are a number of different ways to get the required amount of thermal energy into the substrate are described. In principle, one can differentiate between:
- direct heating in the form of steam or hot water, and
- indirect heating via heat exchanger, whereby the heating medium, usually hot water, imparts heat while not mixing with the substrate.
Pumps
Pumps become necessary parts of a biogas unit, when the amounts of substrate require fast movement and when gravity cannot be used for reasons of topography or substrate characteristics. Pumps transport the substrate from the point of delivery through all the stages of fermentation. Therefore, several pumps and types of pumps may be needed. Pumps are usually found in large scale biogas units.
Types of Pumps
Weak Ring
|
The weak/strong ring improves the gas-tightness of fixed-dome plants It was first introduced in Tanzania and showed promising results. The weak ring separates the lower part of the hemispherical digester, (filled with digesting substrate), from the upper part (where the gas is stored). Vertical cracks, moving upwards from the bottom of the digester, are diverted in this ring of lean mortar into horizontal cracks. These cracks remain in the slurry area where they are of no harm to the gas-tightness. The strong ring is a reinforcement of the bottom of the gas-holder, it could also be seen as a foundation of the gas-holder. It is an additional device to prevent cracks from entering the gas-holder. Weak and strong ring have been successfully combined in the CAMARTEC design
Materials and Construction
The weak ring consists of mortar of a mixture of sand, lime and cement (15:3:1). The top of the weak ring restores the horizontal level. It is interrupted only by the inlet pipe passing through. The strong ring rests on the weak ring and is the first layer of the upper part of the hemispherical shell. It consists of a row of header bricks with a concrete package at the outside. In case of soft or uncertain ground soil one may place a ring reinforcement bar in the concrete of the strong ring. The brick of the strong ring should be about three times wider than the brickwork of the upper wall. A detailed description of the weak/strong ring construction can be found in Sasse, Kellner, Kimaro (1991).
Pre-digestion Pit for Storage of Substrates
Sizing depends on: substrate arisings, digester capacity, length of time to be bridged between successive deliveries, land-use specifics and yield of co-substrates, supply contracts for substrates from off-site sources, possible disruptions in operation
Special considerations:
- Avoid the possibility of storage plant freezing, for example by siting storage tanks indoors, heating storage containers or locating the plant for pits below grade level
- Avoid biodegradation processes that reduce gas yield
- Do not permit intermingling of hygienically problematic and hygienically acceptable substrates
- Implement suitable structural measures to minimise odours
- Avoid material emissions to soil and to the surface and underground water system
Designs Containers for storing solid substrates in widespread use in agriculture, such as mobile silos, upright silos, plastic-tunnel silos and round-bale silos and open or roofed storage areas (e.g. solid-manure deposits) and pits/hoppers Containers for storing liquid substrates in widespread use in agriculture, such as tanks and predigester pits
Costs Storage facilities are generally in place; when new builds are needed the price has to be calculated on
a case-to-case basis factoring in the multiplicity of influencing variables indicated above
Measurement Instruments
Flow-measuring devices (in the pipes) Ultrasonically (pre pits) Radar (pre-pits)
Wheel loader scales
Further Information
Information on materials and devices used in the construction of biogas plants:
- Checklist for the Construction of a Biogas Plant
- Agitation of Digesters
- Digester Heating
- Piping Systems for Biogas Plants
- Plasters and Coats for Biogas Digesters and Gas-holder
- Pumps for Biogas Plants
- Slurry-Use Equipment
- Biogas Implementation - Groundwater Management
Web based sources
- biogas.ifas - biogasplants (pdf)
- Checklist for the Construction of a Biogas Plant
- haase-energietechnik - BiogasBrochure (pdf)
References
- Ringkamp, M.; Tentscher, W.; Schiller, H.: Preliminary results on: statical optimization of family-sized fixed-dome digesters. Tilche, A.; Rozzi, A. (ed.): Poster Papers. Fifth International Symposium on Anaerobic Digestion, Bologna 1988, pp. 321-324
- Sasse, L.; Kellner, Ch.; Kimaro, A.: Improved Biogas Unit for Developing Countries. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft Braunschweig, 1991
- J.; Sasse, L. (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit): Production and utilization of biogas in rural areas of industrialized and developing countries. TZ-Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Roßdorf, 1986, 278 S.</span>