|
|
| (146 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | + | <div class="grid"> <!-- Start grid --> |
| | + | <div class="width-1-1"> <!-- Content Column --> |
| | | | |
| − | {{SPIS Banner}}
| + | <div class="grid stretch-items"> <!-- Row1--> |
| − | | + | <div class="width-1-3"> |
| − | == '''<span style="color:#879637;">Background & Acknowledgement</span>''' ==
| + | {{Arabic Version|Toolbox on SPIS/ar}} |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |
| − | This manual was developed in an effort to contribute to the goal of the international initiative ‘Powering Agriculture – An Energy Grand Challenge for Development’. It supports the introduction of Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) as one technology option to sustain and increase agricultural production in developing countries. The development of the manual was commissioned by the program ‘Powering Agriculture – Sustainable Energy for Food’ of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ on behalf of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development).The manual was developed based on the “Stocktaking and Analysis Report on SPIS” prepared as a result of desk research and case studies in Chile, India, Morocco and Kenya. These were supplemented from exchanges and discussions with stakeholders from the public and private sector, and civil society organizations. The study was carried out in close co-operation with the GIZ sector program Poverty-oriented Basic Energy Services (HERA), which has more than three decades of experience in the field of energy access. The HERA-team provided a wealth of information and was instrumental in the organization and facilitation of the stakeholder workshop in March 2015 and a workshop at FAO in May 2015. The study benefitted from the contact management and facilitation of GIZ Country Offices in Chile, India, Kenya and Morocco. The study team could also largely benefit from support and fruitful discussions with key GIZ staff of the Program for Renewable Energies and Energy Efficiency in Chile, the Indo-German Energy Program in India, the Energizing Development Kenya Country Program in Kenya and the Program Promoting Renewable Energy Sources and Energy Efficiency for Sustainable Development in Morocco. During the case studies conducted in the four countries, the authors had the opportunity for exchanges and discussions with a large number of representatives of public services related to renewable energies and agriculture. Support to the research and information collection was largely extended by private sector suppliers and service providers in Germany and in the countries selected for case studies. Notably, the companies Lorentz GmbH and Grundfos have supported the study through their international networks.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Country-based assistance and information was also provided by iEnergia Group (Chile), Claro Energy Pvt. Ltd. (India), Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd., Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd. (India), Center for Alternative Technologies Ltd. (Kenya), Davies & Shirtliff Ltd. (Kenya), SunCulture Ltd. (Kenya) and AE Photonics Maroc S.a.r.l. (Morocco). The visits to solar-powered irrigation systems in these countries would not have been possible without the support and logistical assistance of these companies. The Delegations of the German Chamber of Commerce in Kenya and Morocco also provided valuable information and facilitated further contacts that were be followed up by the study team. Between May and July 2016, the manual and its tools have been tested in Ghana, Mali and India. We would like to thank the GIZ EnDeV (Ghana), PASSIP/SEWOH (Mali) and IGEN Access (India) programs for their support and initiative to pilot the manual. They enabled us to collect feedback on the manual and the tools and improve them. This second version of the manual and tools is the result of that. Our gratitude goes out to the participants of the workshops and field tests in Tamale, Bamako and Vaishali.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The authors of the study and the manual gratefully thank all stakeholders for their contributions, comments and support.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Hamburg & Niedernhausen, October 2016
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| − | == '''<span style="color:#879637;">Introduction</span>''' ==
| + | <div class="width-1-3"> |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | + | {{French Version|Toolbox on SPIS/fr}} |
| − | Most water pumps utilized for irrigation purposes worldwide are powered by engines run on fossil fuels (diesel, petrol, gas) or on electricity supplied from the grid. Fossil energy sources are limited and emissions from their utilization have negative climate impacts. At the same time, the electricity supply in many developing countries is often insufficient and unreliable or wholly absent in rural areas. Moreover, prices of solar panels have reduced while the quality has improved. Today, solar pumps for irrigation have become an economical, technical and environmentally viable alternative to conventional pumping systems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | However, major hindrance for the uptake of the technology is still a lack of information on solar pumps for irrigation and its relatively high investment costs. The knowledge on the potentials, limitations and risks of Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems (SPIS) is incomplete among policy makers, producers and other stakeholders. For example, SPIS are seldom designed in a way that producer needs and site specific conditions (environmental, agronomic and technical aspects) are comprehensively addressed. Consequently, the potential of the technology is not optimized, or worse, has negative ecological and economic impacts.
| |
| − | | |
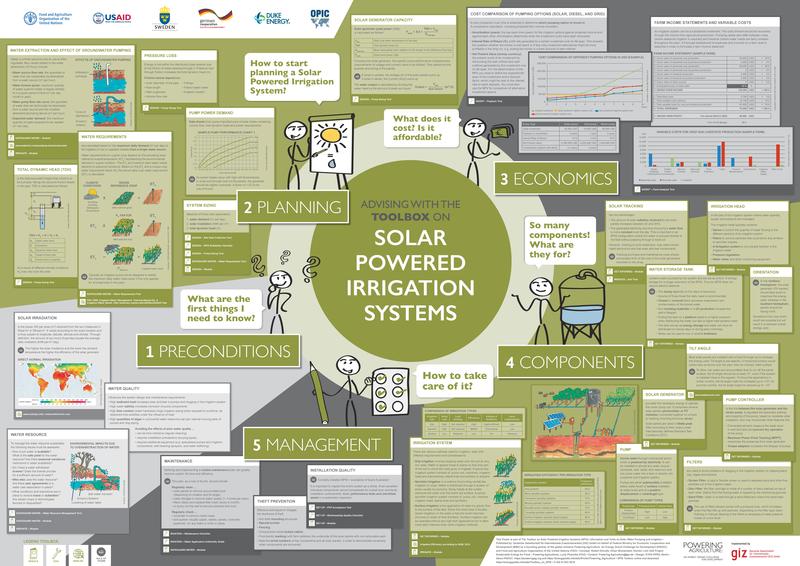
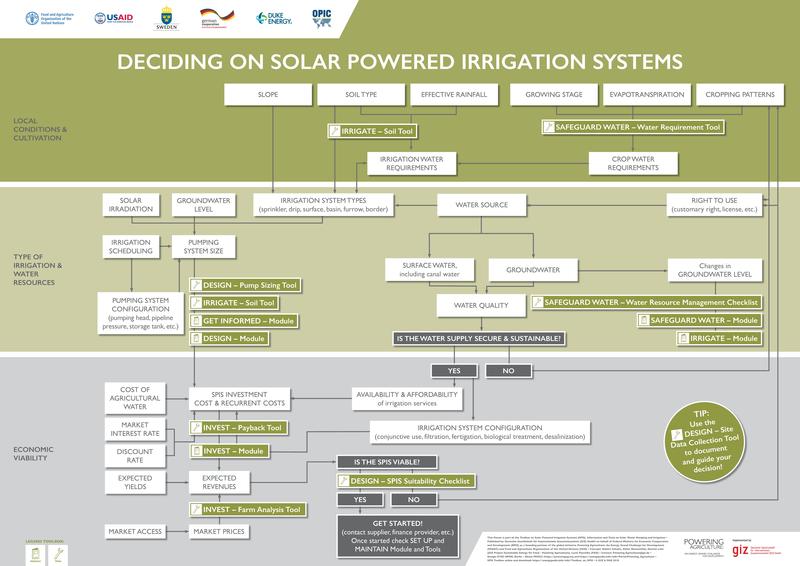
| − | This manual provides up-to-date information on the technology and methods of promotion, as well as how to finance SPIS. Furthermore it gives insight into how SPIS are designed, set up and maintained. It is accompanied by a set of tools, such as maintenance check lists, data collection guidelines and design calculations. It strives to help find the optimal design of a system, thereby avoiding risks related to system efficiency, financial viability and the unsustainable use of water resources. The manual and tools target stakeholders who advise or finance medium-sized agricultural enterprises. These are agricultural (irrigation) extension advisors and credit officers / risk managers in financing institutions. Furthermore the manual support the advisory function of SPIS suppliers, by providing them with a holistic set of knowledge through which they can guide their clients towards a financially and environmentally sound decision.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The manual follows the course of action involved when giving advice on SPIS for an agricultural enterprise. It consists of this introduction and seven further modules. The modular approach enables the user to pick out specific information relevant to his/her situation. Each module however relates to and supplements the other modules.
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''[[SPIS - Get Informed|GET INFORMED]]''' specifies the components and common configurations of a SPIS. Each component is described in detail.
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''[[SPIS - Promote + Initiate|PROMOTE & INITIATE]]''' provides important information and tips for someone who wants to promote the SPIS technology in a particular area. It focuses on the analysis of opportunities and risks, the stakeholders involved, as well as promotion strategies and activities.<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''[[SPIS Safeguard Water|SAFEGUARD WATER]]''' focuses on water governance issues and potential negative impacts of (ground-)water depletion through solar pumping.<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''[[SPIS Finance|FINANCE]]''' provides information to financial service providers financing or planning to finance SPIS. The module targets stakeholders at management level who decide on credit policies and loan officers who assess single loan applications for financing SPIS.
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''[[SPIS Design|DESIGN]]''' helps to select the suitable system configuration for a specific situation. A substantial set of tools helps to assess site conditions, select and design the appropriate type of SPIS and conduct a simplified financial viability assessment and calculates the detailed financial viability of the producer. <br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''[[SPIS Set Up|SET UP]]''' provides information and tools to enable the installation of a SPIS. It focuses on the selection of installers, acceptance and system tests as well as documentation and hand over of the system.
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''[[SPIS Maintain|MAINTAIN]]''' elaborates on maintenance plans, the selection of service providers, regular routines and documentation and monitoring.
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| − | == '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Module Structure</span>''' ==
| + | <div class="width-1-3"> |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | + | {{Spanish Version|Toolbox on SPIS/es}} |
| − | The modules are all structured uniformly. It starts with the module aim and orientation and a brief description of the relevant process steps. These are processes that are recommended to be considered in a particular order. They are numbered and summarized in a flow diagram at the beginning of each module for easy reference
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| − | == '''<span style="color:#879637;">Structure of Each Process Step</span>''' ==
| + | </div> <!-- End Row1 --> |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |
| − | Each step in the process of each module is described on one or two pages. The process step is concluded with an overview of the most relevant aspects:
| |
| | | | |
| − | *Outcome / products
| + | {{SPIS Banner}} <!-- This banner contains Row 3 --> |
| − | *Data requirements;
| |
| − | *People and stakeholders involved;
| |
| − | *Important issues to be considered.
| |
| | | | |
| − | At the end of each module links for further readings and multimedia files are provided. This last page is also used to describe what tools supplement to the module. The tools are available online and users can adapt them to their specific needs.
| + | <div class="grid stretch-items"> <!-- Row 4 --> |
| − | </div> | + | <div class="width-1-1"> |
| − | == '''<span style="color:#879637;">Content of Modules</span>''' ==
| + | <center>{{#widget:YouTube|id=x-nTUgkiv7o|width=800|height=450}}</center> |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |
| − | {| border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width:100%;" | |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="3" style="background-colour: rgb(153,153,102)" | I WANT TO | |
| − | | colspan="2" style="background-colour: rgb(153,153,102)" | GIVE ADVISE ON HOW TO
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | GET INFORMED
| |
| − | | PROMOTE + INITIATE
| |
| − | | SAFEGUARD WATER
| |
| − | | FINANCE
| |
| − | | DESIGN
| |
| − | | SET UP
| |
| − | | MAINTAIN
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="6" style="text-align: center;" | PROCESS STEPS
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | | <br/>
| |
| − | |}
| |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | + | </div> <!-- End Row 4 --> |
| | | | |
| | + | <div class="grid stretch-items"> <!-- Row 5 --> |
| | + | {{SPIS Background}} |
| | + | </div> <!-- End Row 5 --> |
| | | | |
| − | == '''<span style="color:#879637;">Imprint</span>''' ==
| + | </div> <!-- End Content column --> |
| − | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | + | </div> <!-- End .grid --> |
| − | ===== '''Published by''' =====
| |
| − | | |
| − | Powering Agriculture – An Energy Grand Challenge for Development<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Internet: [https://poweringag.org https://poweringag.org]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== '''Production''' =====
| |
| − | | |
| − | Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Project Powering Agriculture – Sustainable Energy for Food Security<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Registered offices<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Bonn and Eschborn, Germany Friedrich-Ebert Allee 40<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | 53113 Bonn, Germany<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | T +49 228 4460-0<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | F +49 228 4460-1766<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Dag-Hammarskjöld-Weg 1-5<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | 65760 Eschborn, Germany<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | T +49 61 96 70-0<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | F +49 61 96 79-1115<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | [mailto:info@giz.de info@giz.de]<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | [http://www.giz.de/ www.giz.de]
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===== '''Editorial Team''' =====
| |
| − | | |
| − | Robert Schultz, GIZ Powering Agriculture<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Jan Sass, GFA Consulting Group GmbH (GFA)<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Christine Fröhlich, GFA<br/>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Andreas Hahn, ah Advice International<br/>
| |
| | | | |
| − | Lennart Woltering, GFA<br/>
| + | {{SPIS_Magic_Words}} |
| | | | |
| − | Katja Diembeck, GFA
| + | {{#Widget:Heatmap}} |
| | | | |
| − | <br/>
| + | [[Category:CSS VI]] |
| − | | |
| − | GIZ is responsible for the content of this publication. Eschborn, October 2016
| |
| − | | |
| − | <br/>
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − | === '''<span style="color: rgb(135, 150, 55);">Logos</span>''' ===
| |
| − | </div>
| |