Sandbox
Summary
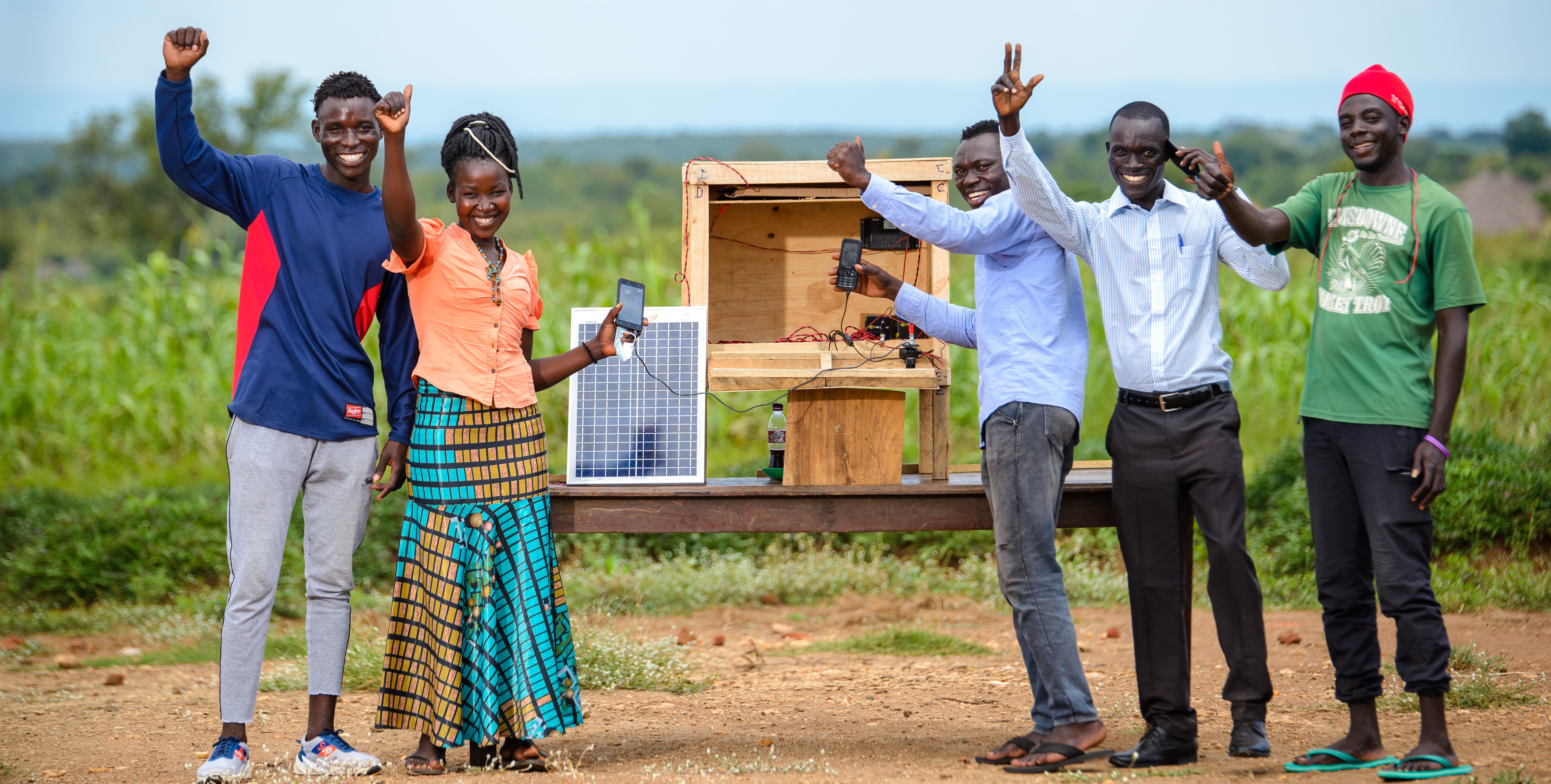
Source: © GIZ/Malaika Media and Nazil Muzungu. (L-R) Gibbson Lomude, Dinah Mbila, Justin Duku, Samuel Lemeri, and Clinton Kennedy, all of Idealise Charging Group, with the table for charging mobile phones that they made at the innovation centre at Ofua 3 Primary School, Uriama Sub-County in Terego District, on October 2, 2021. The table that the group hopes will prevent the destruction of phones from unsafe charging, was developed during the energy Creative Capacity Building workshop under the Design Lab pilot project.
Licensing
| File from GIZ Source. | This file has been produced specifically for GIZ, but someone other than the author has uploaded the file. Therefore the copyright provisions of the original source apply to this file. In case that the original source and its copyright provisions are unclear, this file can be only used on energypedia within the context of the German Copyright Law. Please report copyright infringements to the energypedia staff so that it can delete the appropriate files. |
|---|
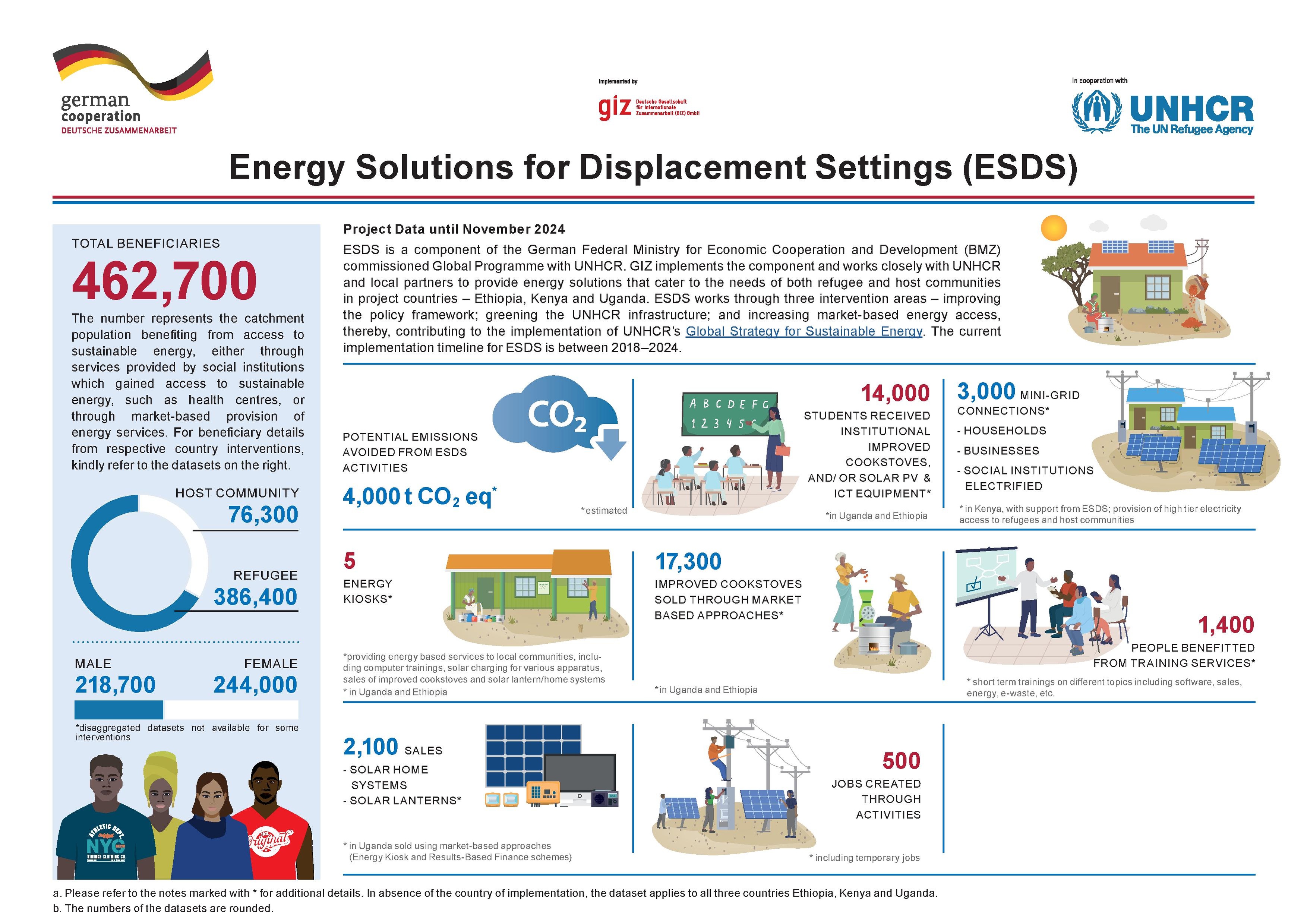
Background Information ESDS
The BMZ commisioned Global Programme "Support to UNHCR in the implementation of the Global Compact on Refugees in the Humanitarian-Development-Peace Nexus”(SUN), implemented by GIZ, seeks to support UNHCR in its role as facilitator of the implementation of the Global Compact on Refugees (GCR) and the Comprehensive Refugee Response Framework (CRRF) in selected refugee contexts and sectors. The Global Programme is part of the German Special Initiative Tackling the Root Causes of Displacement, (Re-)integrating Refugees The Global Programme also aims to operationalise the Humanitarian-Development-Peace (HDP) Nexus. The HDP Nexus envisions actors working in humanitarian, development and peace realms to work more cohesively together, capitalizing on their respective comparative advantages following the recommendations of the 2016 World Humanitarian Summit (WHS) and in line with the 2030 Agenda. Under the “New Way of Working” agreed at the WHS, the various actors are expected to work towards “collective outcomes” that reduce risk and vulnerability and serve as instalments towards the achievement of the SDGs. Read more
The Global Programme consists of 4 components that include implementing activities with UNHCR in 8 countries, accompanied by organisational capacity development. The aim is the consolidation, analysis and sharing of lessons learned from implementation experiences in order to better implement the HDP Nexus. This is key in generating knowledge on ‘what works under which conditions’ and contributes to public, organisational and mutual learning between the two partners GIZ and UNHCR. The cooperation can result in better informed and coordinated programming and implementation of the GCR, CRRF and HDP Nexus.
Implementation of the HDP Nexus in selected displacement settings (in Niger, Mexico, Mauritania)
Implementation of the HDP Nexus in the sector of sustainable energy (Energy Solutions for Displacement Settings in Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda)
Strengthening UNHCR's capacities to foster implementation of the GCR and cooperation within the HDP Nexus (UNHCR headquarters in Geneva, UNHCR national offices)
Strengthening capacities of governmental structures to implement the GCR at national and district levels (in Uganda, Rwanda)
ESDS is the German contribution to the Clean Energy Challenge issued by UNHCR in 2019 with the following objective:
To that end, ESDS offers global advisory services, implements technical measures and cooperates with relevant stakeholders to promote sustainable and affordable energy access via market-based solutions and to create enabling framework conditions. ESDS structures its activities along the following 3 intervention areas:
Highlights
Improving the policy framework
We work together with policy makers to create the necessary framework conditions to implement the GCR and ensure sustainable energy access for refugees and host communities at a national, regional and district level.
ESDS Factsheets
ESDS Webinars
- Collaborating for Change: Lessons from the SUN-ESDS Project
- Webinar Experiences on Operation and Maintenance in Displacement Settings
- Ewaste Value Chain in Humanitarian Settings
- Role of Energy Policies in Shaping Energy Access Dialogue in Displacement Contexts
- Access to Energy for Cooking in Displacement Settings
- Energy Efficiency in Humanitarian Organization Infrastructure
- Workshop on Participatory Design Processes for Energy Projects Planning and Implementation